Before incorporating a new product into your skincare or beauty regimen, it's essential to conduct a patch test at home to avoid any adverse reactions. While most products recommend spot testing, you might be unsure how to proceed. This guide outlines an easy method for assessing your skin's response to new products in the comfort of your own home, distinct from allergy testing performed by healthcare professionals.
Steps:
Apply the new product to a small area of your skin.

Select a discreet area, such as the inner bend of your elbow, to apply the product. Alternatively, choose a location like the underside of your arm or behind your ear, ensuring the product remains undisturbed. Clean and dry the chosen area before applying the product in a quarter-sized patch.
- The underside of the jaw is another suitable area for testing, but take care not to wash it off inadvertently during your skincare routine.
Allow the product to remain on your skin.

If the product is not intended for prolonged use, rinse it off after 5 minutes. For products meant to be left on, such as moisturizers, simply apply them to the test area and refrain from washing it off. However, if the product is typically washed off, wait for 5 minutes before rinsing it away.
- For example, if testing a new facial cleanser, apply a coin-sized amount and rinse it off after 5 minutes.
- If testing a face mask or similar product, adhere to the manufacturer's recommended duration for leaving it on.
Apply the product twice daily.

Consistent application helps identify allergic contact dermatitis. While a single patch test can reveal immediate reactions, consistent exposure helps determine delayed reactions. Immediate reactions indicate irritant contact dermatitis, while delayed reactions suggest allergic contact dermatitis.
- Certain ingredients like retinol and glycolic acid can cause irritation with regular use.
- It takes a minimum of 4 days to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis, emphasizing the importance of repeated applications.
Monitor for signs of a reaction.

Monitor the area for any signs of irritation. These signs may manifest immediately or take some time to appear. If no issues arise within 10 days, it's likely safe to continue using the new product. However, refrain from using the product if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Redness
- Itching
- Swelling
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Burning or tenderness
Remove the product if you experience a reaction.

An immediate reaction indicates a strong allergy to the product. Symptoms such as burning, intense itching, redness, or inflammation warrant immediate removal of the product. Wash the affected area thoroughly with warm water and gentle, fragrance-free soap. Cease further testing.
- Apply a cold compress and fragrance-free moisturizer to soothe the skin.
- If itching persists, apply a thin layer of hydrocortisone cream and take an over-the-counter antihistamine.
- Review the product's ingredient list to identify potential irritants, comparing it with other products that have caused similar reactions.
Avoid known skin irritants.

Check product labels to steer clear of potential allergens. Ingredients like fragrances, preservatives, sulfates such as sodium laurel sulfate, and irritants like retinol can trigger skin reactions. For instance, if certain acne skincare products cause rashes, it's possible you're allergic to salicylic acid. Opt for acne products without salicylic acid to prevent future reactions.
- If fragrance is a trigger, switch to fragrance-free alternatives to minimize the risk of irritation.
Consult a dermatologist for patch testing.
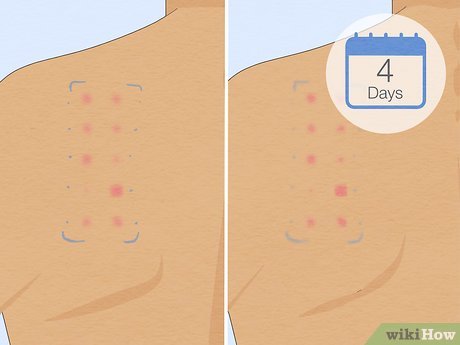
Seek professional testing if unsure of the cause of irritation. During a dermatologist-conducted patch test, various common allergens are applied to your back under patches for assessment. After 2 days, your skin is examined for reactions, with a follow-up after 2 more days to check for delayed reactions.
- If suspecting a specific product, bring it along for examination.
- The dermatologist will review the patch test results, identifying substances like specific cosmetic ingredients to avoid in the future.
Tips:
- If you have eczema, your skin is more sensitive, increasing susceptibility to product-induced irritation.
- Introduce one new product at a time to pinpoint causes of irritation. Always verify before incorporating new cosmetics, skincare items, deodorants, shampoos, or conditioners into your routine.
- Dermatologists can rule out other skin conditions. For instance, if suspecting psoriasis, they can provide a diagnosis.
Warnings:
- If you develop a rash that forms blisters and becomes infected, seek immediate medical attention. If accompanied by fever or the blisters start oozing pus, seek urgent treatment.
