Comprehensive walkthrough to identifying and updating your PC’s BIOS
How to Perform a BIOS Update
- Utilize the System Information tool to ascertain your precise model name and current BIOS or UEFI version prior to downloading any updates.
- Exclusively obtain BIOS updates directly from the manufacturer's official sources.
- Ensure your desktop or laptop PC is connected to a stable power source before commencing the update process. Power loss during the update can result in BIOS damage.
Procedural Steps
Obtaining the BIOS Update File

- You can alternatively use the ⊞ Win key to open the Start menu.
Accessing System Information. Input msinfo into the Start menu search bar, then select System Information from the search results.
Select System Summary. Within the System Information application, click on the System Summary option located in the left-hand panel.

Determine your computer's model name. Adjacent to the 'System Model' title, you'll find a combination of letters and numbers representing your computer's model name. This information will be necessary when searching for the appropriate BIOS update file.
- If you own a custom-built computer, skip this step.
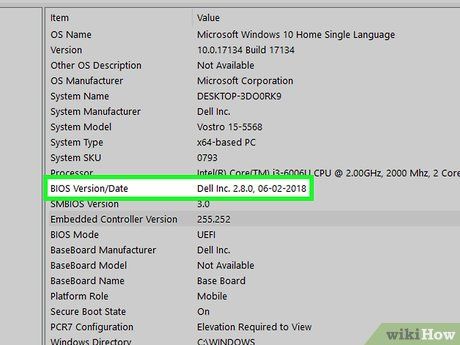
Locate your BIOS version. Scroll through the menu until you find the 'BIOS Version/Date' section. Here, you'll find the manufacturer's name, your computer's model, and a number after a dot. This number represents your BIOS version.
- For instance, if your computer model is 'Q553UB' and your BIOS version is 202, it will appear as 'Q553UB.202'.
- If you're using a custom-built PC, you'll need to identify your motherboard's model instead of relying on the computer's model number.
- You can also use the command prompt to find the BIOS version by typing wmic bios get biosversion.
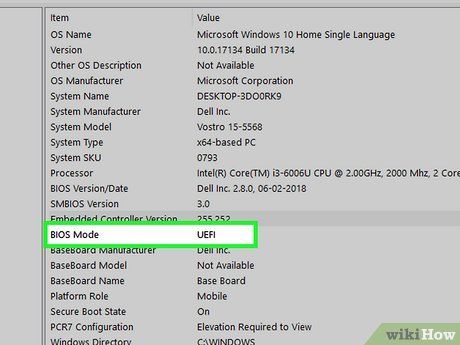
Verify the BIOS Mode line to determine whether you have BIOS or UEFI. A few lines below the BIOS Version/Date section, you'll find the BIOS Mode line. This will indicate whether your system operates on BIOS or UEFI.
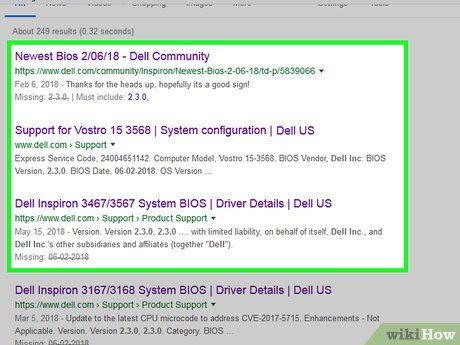
Access your BIOS manufacturer's support site. Typically, the simplest method is to enter your computer manufacturer's name, your computer model, and either 'drivers' or 'BIOS' into a search engine like Google. Follow the appropriate link. The process may vary depending on your computer's manufacturer, so you might need to navigate through several links to find the right one.
- If you're using a custom-built PC, you'll need to search for your motherboard's name along with 'BIOS' or 'UEFI' and 'update', then visit the manufacturer's website.
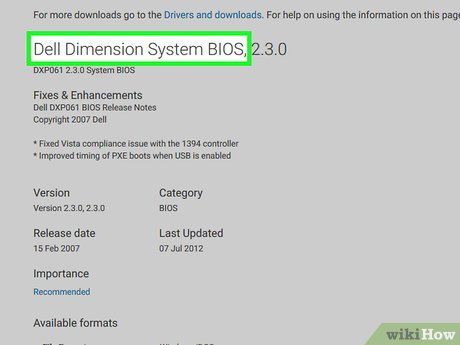
Locate the BIOS update file. You might need to navigate to the 'Updates', 'Support', or 'Downloads' section of the website, or click on a 'BIOS' link. Once you've found the BIOS file, you can proceed with the update.
- This process may require some trial and error.
EXPERT ADVICE

Mobile Kangaroo
Specialists in Computer & Phone Repair
Specialists in Computer & Phone Repair
Is it safe to update BIOS in Windows? Joseph Alexander, a computer repair technician, states: 'Updating your BIOS is generally safe if you obtain the update directly from the device manufacturer. It's crucial to carefully follow their provided instructions.'
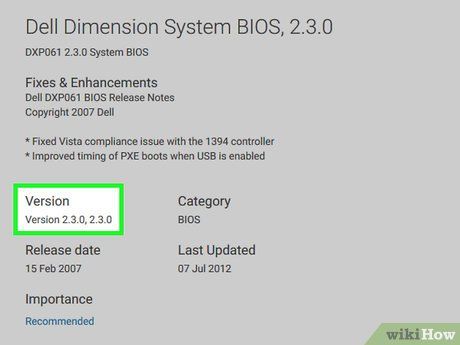
Confirm the update file is newer than your current BIOS version. Look for a version number in the file's name. If it's higher than your BIOS version number, your BIOS is outdated and eligible for an update.
- If the version number matches your BIOS version, it means your BIOS is already up-to-date.
- Even if your BIOS version is a whole number (e.g., 301) and the file on the site has a higher decimal (e.g., 301.1), the site's file is still a higher version.
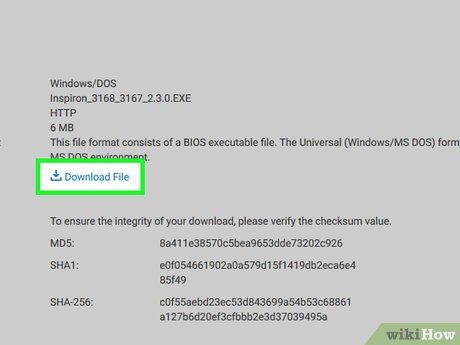
Retrieve the update file. Click on the Download link, button, or icon to initiate the download process. After the BIOS update file completes its download, proceed with updating your BIOS.
- In some instances, clicking the file's name might trigger the download.
- Most BIOS update files will download as ZIP folders.
BIOS Update Process

Ensure your computer is connected to a stable power source. It's crucial to avoid any interruptions during the BIOS update process, as it can permanently damage your BIOS. For laptop users, ensure both the battery is fully charged and the laptop is plugged in.
- If you're using a laptop, your computer's battery should be fully charged in addition to the laptop being plugged in.
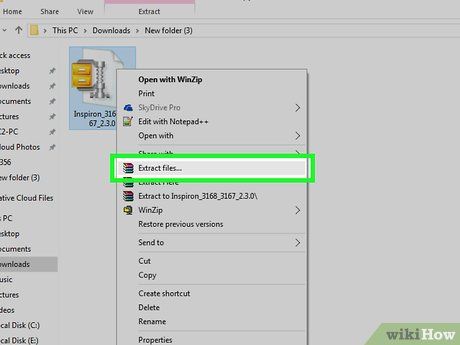
Extract the BIOS file. Typically, you'll need to extract (or 'unzip') the BIOS update file from its folder:
- Double-click the downloaded ZIP file to open it.
- Click the Extract tab at the top of the window.
- Choose Extract all.
- Click Extract when prompted.
- Wait for the extracted folder to appear.
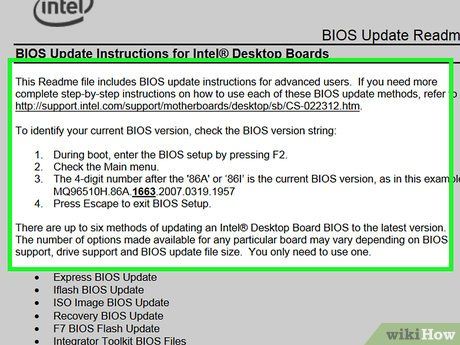
Review the README document for your BIOS file if available. If there's a text document named 'README' or similar, open it and read it thoroughly before proceeding.
- If the README instructions differ from those in this article, prioritize the README's instructions.
- Some older or custom-built computers may require BIOS installation via a USB flash drive instead of the hard drive. However, this isn't usually necessary for modern PCs. Refer to the README for clarification.
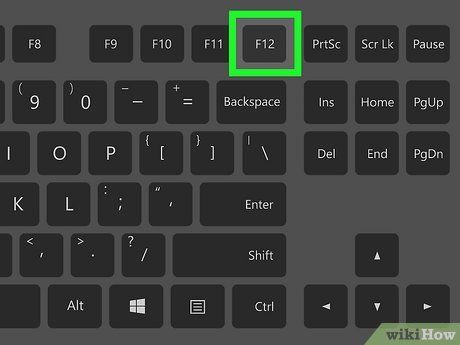 Enter the BIOS Setup.Startup
Enter the BIOS Setup.Startup Power On
Power On Reboot
Reboot- For most computers, the BIOS key is typically one of the function keys (e.g., F12), although some may use the Del or Esc key.
- If you're unsure of your computer's BIOS key, you can search for it by entering your computer's manufacturer name, model name, and 'BIOS key' into a search engine.
- In Windows 10 or 11, you can also access BIOS settings through the Settings menu. Navigate to Update & Security > Recovery > Restart Now (under Advanced startup). In the window that appears, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > UEFI Firmware Settings > Restart.
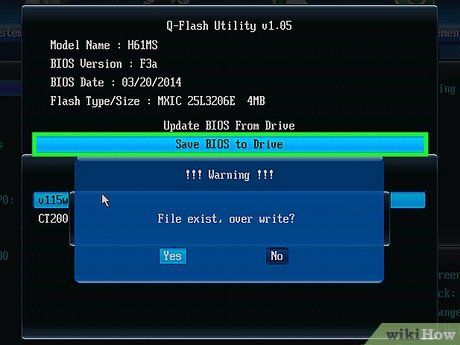
If possible, create a backup of your BIOS. Look for a 'Backup' or 'Save' option on the main BIOS screen, or check for a Backup tab at the top of the screen. Follow any on-screen instructions provided to ensure you can restore your BIOS settings if needed later on.
- You might also be prompted to back up your BIOS during the backup process.
- Keep in mind that not all BIOS pages offer the option to back up settings.
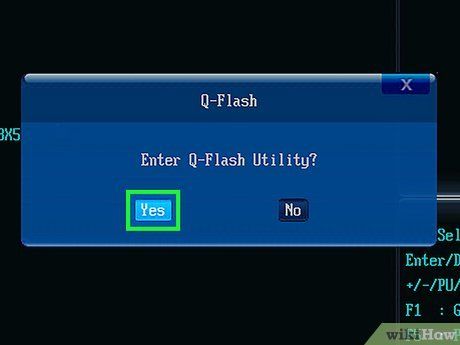
Activate and utilize your BIOS update utility. Each BIOS has its own method for accessing the update tool, so consult your BIOS manufacturer's support site for specific instructions.
- In most cases, you'll navigate to the Boot tab, verify that your USB flash drive is recognized, enable any backup or 'Flash' options in the menu, and then select Start Flash from the Advanced tab.
- Some computers, like Dell models, offer a unique menu when you press the BIOS key with a USB drive inserted. This menu allows you to select an Update option and follow on-screen instructions.
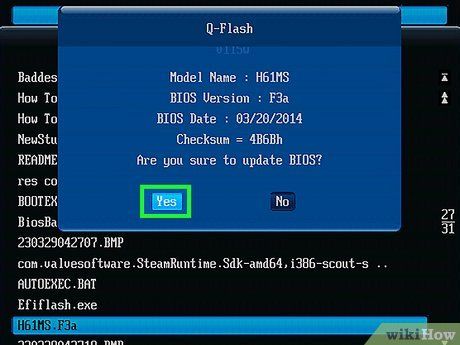
Allow your computer's BIOS to complete the update process. This may take anywhere from a few minutes to an hour, depending on your computer and the complexity of the BIOS update. Once the update is finished, your computer should restart automatically, though you might need to confirm this action.
- Do not power off your computer during the BIOS update. Interrupting the process can corrupt the BIOS, rendering your computer unable to boot or complete the installation.
Useful Tips
-
Prioritize whether a BIOS update is truly necessary. Updating BIOS or UEFI carries risks, so proceed only if you have a valid reason. Consider updating if:
- Your system repeatedly crashes due to motherboard issues.
- Your current BIOS or UEFI isn't compatible with new hardware, like a graphics card or additional memory.
- Your existing BIOS or UEFI is vulnerable to security threats.
-
For Windows 10 or 11 users, manufacturers may prompt BIOS updates through Windows Update. If so, there's no need for separate downloads—simply check for updates or enable automatic updates.
-
BIOS updates may address existing bugs, introduce support for new hardware or standards, or add new features. If available, review release notes or documentation to assess whether the update benefits your PC.
Important Notes
- Exercise caution when updating the BIOS. Failure to adhere to manufacturer instructions and precautions could result in BIOS corruption.
- Only obtain BIOS updates from the manufacturer's official website to avoid potential malware risks.
