Vietnamese is a unique language with various tones and word types, where adverbs play a crucial role. In this article, Mytour will provide you with a deeper understanding of what adverbs are in Grade 7 Literature. Examples, meanings, and types of adverbs, as well as what kind of word adverbs are.
What are Adverbs? Examples of Adverbs
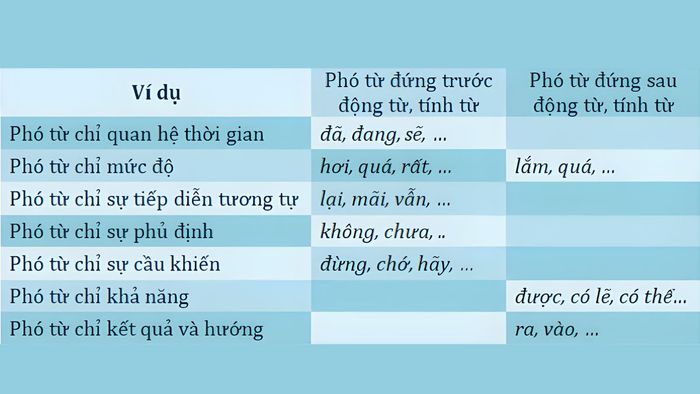
Adverbs are a group of words used to complement the meaning of verbs and adjectives in a sentence. They express the frequency of time, manner, degree, or the meaning of other verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in the sentence. These words help clarify how an action takes place or provide additional information about the frequency and intensity of an adjective or adverb.
 What are Adverbs? Examples of Adverbs
What are Adverbs? Examples of AdverbsCommon examples of adverbs include very, extremely, slowly, sometimes, often, and quickly. Each of these words plays a vital role in making the context of the sentence clearer and more detailed.
Characteristics of Adverbs
The characteristics of Grade 7 adverbs have been briefly mentioned. Here are some distinctive features of this type of word.
- Defined by Suffixes: Adverbs are often formed by adding suffixes to verbs, adjectives, or adverbs. These suffixes are commonly used to specify the frequency of time, manner, degree, state, or the meaning of the word.
- Positioned Before or After Modified Words: Adverbs usually stand before or after the word they modify, depending on the type of adverb and the intended meaning. For example, the adverb 'very' often precedes an adjective or adverb, while the adverbial phrase 'that' often follows a verb.
- Maintaining Form: Adverbs often remain unchanged in form when appearing in a sentence. For instance, an adverb like 'usually' stays the same regardless of the tense or whether it appears in an affirmative or negative sentence.
- Diverse Types: Adverbs come in various types such as adverbs indicating frequency, time, manner, degree, state, or meaning. Each type has distinct suffixes and usage.
- Plays a Vital Role in Expressing Sentence Meaning: Adverbs play a crucial role in expressing the precise and detailed meaning of a sentence, helping readers or listeners better understand how an action takes place or the intensity of an adjective or adverb.
Types of Adverbs
In the Vietnamese language, adverbs are highly diverse, including various types of adverbs:
- Various frequency adverbs like usually, always, sometimes, rarely, and never.
- The group of time adverbs includes now, when, night, late, morning, noon, afternoon, evening, yesterday, today, tomorrow, and the day before.
 There are many types of adverbs
There are many types of adverbs- Various manner adverbs such as slowly, quickly, skillfully, meticulously, attentively, dedicatedly, seriously, and carefully.
- Adverbs expressing degree like very, extremely, much, relatively, slightly, and quite.
- The group of adverbs related to state includes ongoing, already, still, all, still, new, about to, and will.
- A set of adverbs conveying meaning such as really, probably, surely, and also.
All these adverbs are used to modify the meaning of a sentence, providing additional information about the frequency of time, manner, degree, state, or adding meaning to words.
Order of Adverbs in a Sentence
The content about the order of adverbs in Grade 7 Literature has been briefly mentioned. Now let's delve deeper into the order and what type of word comes after adverbs. The sequence of adverbs in Vietnamese sentences is usually determined as follows:
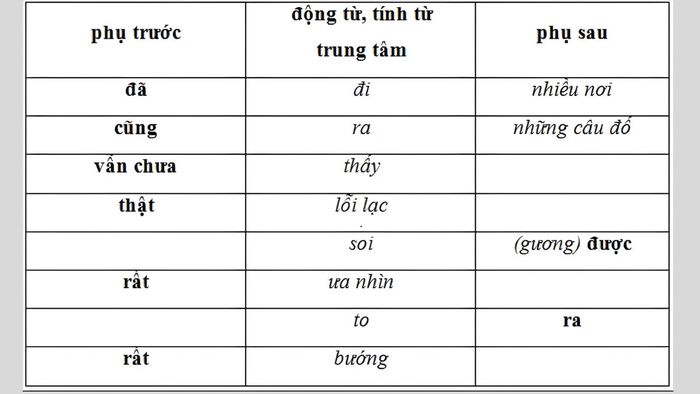
- Frequency adverbs often come after verbs. For example, in the sentence 'I frequently read books in the evening.'
- Time adverbs usually appear before verbs and after the subject. For instance, 'Today I arrived at school late.'
 Content about the order of adverbs in Grade 7 Literature
Content about the order of adverbs in Grade 7 Literature- Manner adverbs typically come after verbs. Illustrated in the sentence 'The teacher teaches very well.'
- Degree adverbs often precede adjectives or adverbs to provide clarification. For example, 'That boy is very cute.'
- State adverbs usually stand after verbs. For instance, 'I am listening to music.'
- Adverbs conveying meaning can appear in various positions within a sentence, often before verbs or after the subject.
Nevertheless, in Vietnamese, the order of words in a sentence can be flexible to create variations in meaning and expression.
Meaning of Adverbs
When appearing with verbs and adjectives, the meaning of adverbs is to supplement the sentence with various aspects:
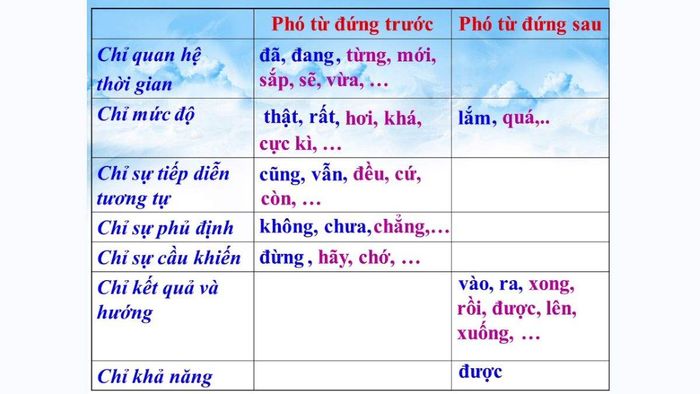
- In terms of time: By utilizing adverbs like currently, will, soon, recently, presently... The speaker or writer can make the time in the sentence clearer.
- For progression: Adverbs such as still, just, yet, also... help emphasize the continuous nature of an action or state.
- In terms of degree: By adding adverbs like very, much, somewhat, too, the speaker or writer can convey the degree accurately and fluently.
 Adverbs help supplement meaning in various aspects
Adverbs help supplement meaning in various aspects- Regarding negation: The subject can use adverbs like barely, never, not... to increase the negativity of the sentence.
- For causation: Adverbs like don't, let's, stop, please... can be added to the sentence to express requests or invitations politely and friendly.
- In terms of possibility: Adverbs like maybe, perhaps, impossible, hard... help highlight the possibility in the context of the sentence.
- For result: Adverbs like lost, gained, went, out are often used to describe the result or conclusion of an action.
- Indicating frequency: Using adverbs like often, usually, always can make the sentence more lively by creating clarity about the frequency of an action.
- Expressing mood: Adverbs like suddenly, unexpectedly, all of a sudden are often used to create an atmosphere of surprise or sudden change in mood or state.
How to differentiate types of adverbs
Here's how to classify different types of adverbs through their key characteristics:
- Adverbs indicating frequency often appear due to the addition of suffixes such as always, usually, sometimes, rarely, at times, almost, rarely, ever, and once. They are used to specify the frequency or intensity of an action or event.
- Adverbs indicating time often appear with suffixes such as today, yesterday, this morning, this afternoon, tonight, soon, still, and forever. They are used to specify the time or period when an action or event occurs.
- Adverbs indicating manner are often formed by suffixes. Like gently, quickly, slowly, easily, not easily, carefully, accidentally, and unintentionally. They are used to describe the manner, method, or way of performing an action or event.
- Adverbs indicating degree often appear due to the addition of suffixes such as very, too, extremely, immensely, entirely, only, not, mostly, and mostly. They are used to indicate the magnitude of an action or event.
- Adverbs indicating state are often created by adding suffixes such as healthy, happy, normal, sad, painful, lonely, confused, and hesitant. They are used to describe the emotional or mental state of the speaker or the person referred to.
- Adverbs indicating meaning are often formed by suffixes such as that, this, is, true, really, absolutely, of course. They are used to express affirmative or negative meanings in a sentence.
Distinguishing adverbs and auxiliaries
Based on grammatical structure:
- With adverbs, the position is usually placed before or after the main word or the center of the sentence.
- In contrast, with auxiliaries, they can appear at the beginning, middle, or end of the sentence without affecting the main word. Therefore, auxiliaries can be removed and still maintain the grammatical structure of the sentence.
 The difference between adverbs and auxiliaries
The difference between adverbs and auxiliariesBased on meaning:
- Adverbs play a supplementary role, elucidating the central word's meaning. They focus on aspects such as degree, time, frequency...
- Conversely, auxiliaries bring richness and new colors to the sentence, enabling effective expression of thoughts and emotions. They enhance expressive capabilities in writing.
Reference Exercises
Here are 5 short multiple-choice exercises about adverbs.
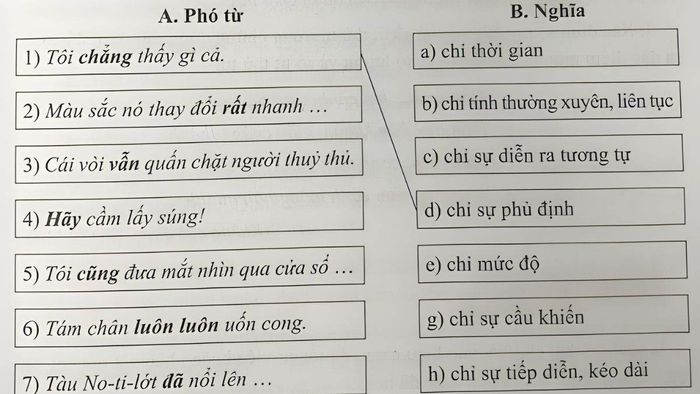
Question 1: What is an adverb?
- a) Words that accompany verbs and adjectives to supplement their meaning
- b) Words that follow nouns, providing additional meaning to nouns
- c) Words that function as the central element of a noun phrase
- d) Indeterminate
Question 2: 'We will start the class at 8 in the morning.' In this sentence, what type of adverb is 'at'?
- a) Adverb indicating frequency
- b) Adverb indicating time
- c) Adverb indicating manner
- d) Adverb indicating degree
 Question 3: 'He solved the problem very quickly.' In this sentence, what type of adverb is 'very'?
Question 3: 'He solved the problem very quickly.' In this sentence, what type of adverb is 'very'?- a) Adverb indicating time
- b) Adverb indicating frequency
- c) Adverb indicating manner
- d) Adverb indicating degree
Question 4: 'She speaks English quite well.' In this sentence, what type of adverb is 'quite'?
- a) Adverb indicating time
- b) Adverb indicating frequency
- c) Adverb indicating manner
- d) Adverb indicating degree
Question 5: 'However, he still continues to strive.' In this sentence, what type of adverb is 'However'?
- a) Adverb indicating time
- b) Adverb indicating frequency
- c) Adverb indicating manner
- d) Adverb indicating meaning
Answer:
- a) Are words that accompany verbs, adjectives to supplement the meaning of verbs, adjectives
- b) Adverb indicating time
- c) Adverb indicating manner
- d) Adverb indicating degree
- d) Adverb indicating meaning
Conclusion
In this article, Mytour has provided you with a clearer understanding of what adverbs are in Grade 7 Literature. Examples and types of adverbs, the meaning of adverbs as well as what comes after adverbs are types of words. Hopefully, the content that Mytour shares will help you understand more about this part of speech.
To meet the needs of studying and working, the computer is a very important device. You can explore quality laptop models at affordable prices, which are currently loved by many people.
- Explore more articles in the category: Technology Terms, Industry Terms
