The human body is truly miraculous. Each cell in the body serves its purpose to ensure all organs function normally, preserving our lives and well-being.
Despite its strengths, the human body is delicate and prone to illnesses and disorders, some of which are extremely rare and mysterious. One such rare condition is anonychia, where individuals have no fingernails or toenails either completely or partially. Those affected may look like they are wearing invisible gloves.
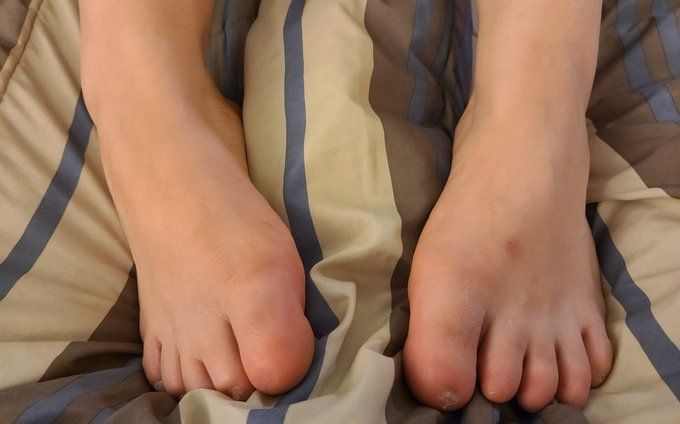
The absence of fingernails and toenails either completely or partially is referred to as anonychia. This rare condition can result from congenital dermal defects, but it can also be caused by disorders and conditions such as psoriasis, self-inflicted trauma, severe infections, or severe allergic contact dermatitis.
Anonychia congenita, the congenital absence of fingernails and toenails involving multiple digits, is extremely rare. This condition manifests at birth, and individuals with this condition often lack most (if not all) toenails and fingernails.
Even in the absence of nails, the surrounding tissues and structures that typically support nail growth remain seemingly normal. Individuals with anonychia congenita typically do not experience any symptoms or other health issues related to this condition.
Congenital anonychia arises from mutations in the RSPO4 gene, responsible for guiding the creation of a specific protein called R-spondin-4. This protein plays a crucial role in the Wnt signaling pathway, influencing various cellular activities and determining the development of tissues and cells. Wnt signals are vital for cell functions such as cell division, movement, cell adhesion, and many other activities.
In the early developmental stages, Wnt signals play a pivotal role in the growth and development of fingernails. R-spondin-4, active in the bone matrix, contributes to the formation of digits, especially the tips of toes and fingers where nails emerge. Mutations in the RSPO4 gene lead to the production of a less active or inactive protein, preventing R-spondin-4 from participating in the Wnt signaling pathway. This results in improper or nonexistent nail growth.
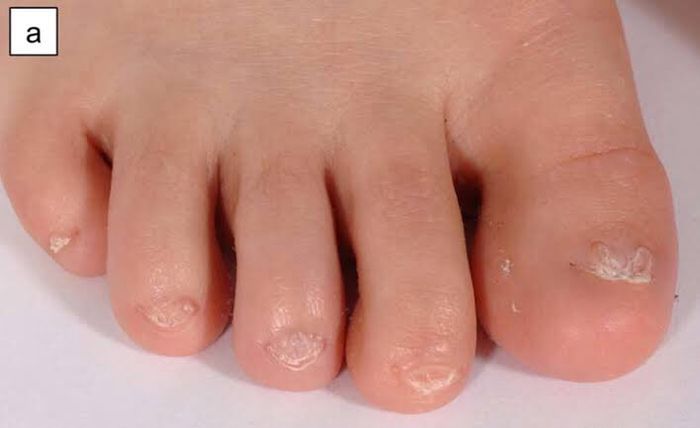
Congenital anonychia, resulting from RSPO4 gene mutations, is often inherited through a specific pattern known as 'autosomal recessive inheritance.' Autosomal recessive inheritance occurs when both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. Each parent of an individual with autosomal recessive inheritance carries one copy of the mutated gene. However, parents typically do not exhibit any symptoms or signs of this condition.
As autosomal recessive conditions tend to be relatively rare, the likelihood of both partners carrying the same recessive gene is usually low. Moreover, even if both spouses are carriers, there is only a 25% chance of passing the disease to their child.
Explore other rare conditions and unusual disorders you may not have heard of!
1. Aquagenic Urticaria is a rare condition causing extreme water allergy.
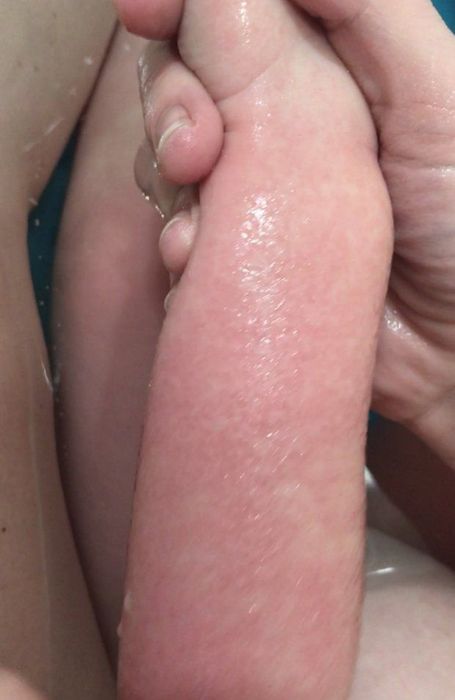
Aquagenic Urticaria refers to a rare condition where hives (a type of rash) rapidly develop when the skin comes into contact with water. Even snow, rain, tears, and sweat can trigger this allergic reaction. This physical rash causes a sensation of warmth and itching. Although research on this condition is limited, scientists know it's a water allergy primarily affecting women. The exact cause of aquagenic urticaria is still unknown.
2. Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva, also known as 'Stone Man's Disease,' is an extremely rare disorder turning connective tissue into bone
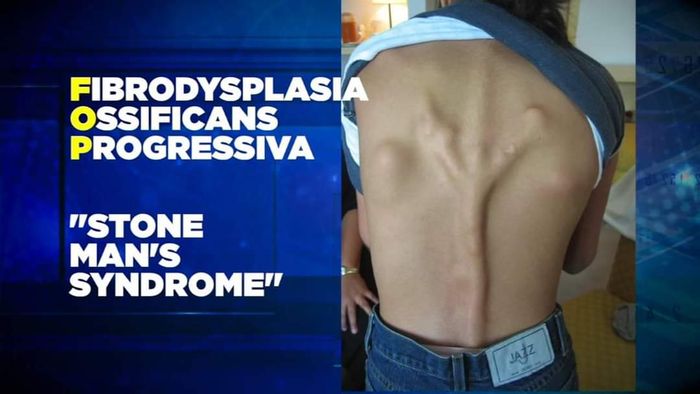
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva, an exceptionally rare connective tissue disorder, transforms muscles and connective tissues like tendons and ligaments into rigid structures (turning them into bone). This disorder causes bones to form outside the skeletal framework, resulting in restricted movement.
This disorder typically manifests symptoms from childhood, and those affected by it experience progressive loss of mobility. Over time, they may face difficulties in breathing, malnutrition, and a range of other health issues.
Individuals affected by this disorder cannot undergo any invasive medical procedures to remove bone growth, as it would worsen the condition and lead to more extensive bone development.
3. Alice in Wonderland Syndrome, also known as 'Todd's Syndrome,' causes perceptual distortions
Alice in Wonderland Syndrome is a rare psychological neurological disorder, causing episodes of distorted perception along with a loss of orientation. Those with this condition may feel smaller or larger than reality. They may also perceive their surroundings or furniture shifting or feel closer or farther than reality.
These distortions are not a result of hallucinations or visual problems. They are caused because the brain of the affected individual cannot accurately perceive the environment they are in or how their body appears.
4. 'Porphyria' refers to a group of disorders causing severe sensitivity to sunlight
'Porphyria' is used to describe a group of liver disorders that lead to the accumulation of a substance called 'porphyrin' in the body, negatively affecting the nervous system or skin. There are two types of porphyrin metabolism disorders – acute porphyrin metabolism disorder and cutaneous porphyrin metabolism disorder. Acute porphyrin metabolism disorder primarily affects the nervous system, while cutaneous porphyrin metabolism disorder affects the skin.
Individuals with acute porphyria may experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, urinary problems, high blood pressure, muscle pain, anxiety, hallucinations, or delusions. Common symptoms of cutaneous porphyria include extreme sensitivity to sunlight, blistering on exposed skin, itching, thin and red skin causing pain.
5. Auto-Brewery Syndrome, also known as 'Gut Fermentation Syndrome'
Auto-Brewery Syndrome, sometimes known as the 'drunkenness disease,' is characterized by the fermentation of carbohydrates in the digestive system. This rare medical condition makes people feel 'intoxicated' even without consuming a sip of alcohol. It transforms starch-rich and sugary foods into alcohol using fungi or bacteria.
Diagnosing this condition is challenging, often leading to confusion with various other disorders. Only a few cases of Auto-Brewery Syndrome have been reported in the past few decades.
