The following article introduces you to the BINOM.DIST function – one of the widely used statistical functions in Excel.

Description: Returns the binomial distribution probability of individual terms. Supported from Excel 2010.
Syntax: BINOM.DIST(number_s,trials,probability_s,cumulative)
Where:
- number_s: Number of successes in the trial, a required parameter.
- trials: Number of independent trials, a required parameter.
- probability_s: Probability of success for each trial, a required parameter.
- cumulative: Determines the form of the function if it is True -> returns the cumulative distribution function, if False returns the probability mass function.
Note:
- If number_s and trials are not integers, they are rounded to integers.
- If number_s and trials are not numbers -> the function returns the error value #VALUE!
If number_s is less than 0 or number_s is greater than trials, the function returns an error value #NUM!
If probability_s is less than 0 or probability_s is greater than 1, the function returns an error value #NUM!
The probability mass function for the binomial distribution is:
b(x,n,p)=(nx)pN(1−p)n−N
Where:
B(x,n,p)=N∑y=0b(y,n,p)
The cumulative binomial distribution function is:
B(x,n,p)=N∑y=0b(y,n,p)
Example:
Calculate the probability of trials with the data in the table below:

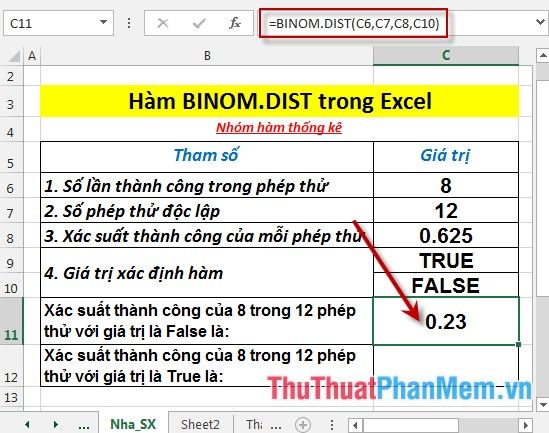
- Calculate the probability of 8 successes out of 12 trials with the value False. Enter the formula: =BINOM.DIST(C6,C7,C8,C10) into the cell to calculate.
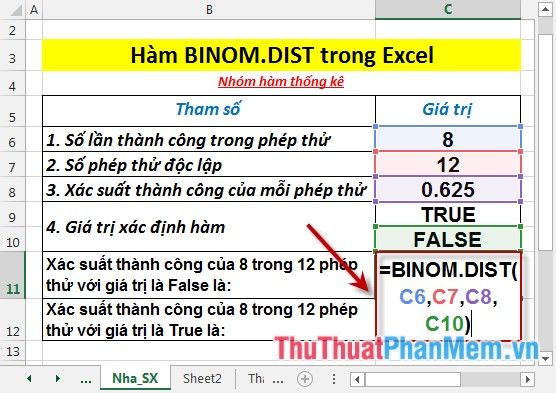
- Press Enter -> the probability of success is:
- Calculate the probability of 8 successes out of 12 trials with the value True. Enter the formula: =BINOM.DIST(C6,C7,C8,C9) into the cell to calculate.

- Press Enter -> the probability of success is:
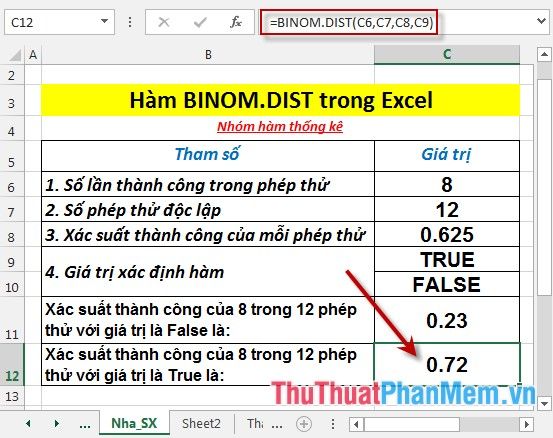
Thus, with different function parameters -> the function returns different results.
Above is the specific guidance and example of using the BINOM.DIST function in Excel.
Wishing you all success!
