Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) serves as a vital support for numerous individuals, whether navigating menopausal challenges or undergoing gender transition. However, there comes a time when discontinuing HRT becomes a consideration for various reasons. If you’re contemplating halting HRT, initiating a conversation with your healthcare provider is essential to determine the most suitable approach. Typically, your doctor will gradually taper your dosage over a period of 4-6 months. This gradual reduction is crucial as an abrupt cessation of HRT could precipitate sudden or exacerbated menopause symptoms. Therefore, allowing your body time to acclimate to its altered hormone levels is imperative. It's important to note that you may experience some side effects during this transition period, but these symptoms can often be managed with alternative treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
Guidelines
Consulting Your Physician

- The duration for which you should continue HRT may vary based on your individual circumstances and your physician's recommendations. Although hormone therapy can technically be continued indefinitely, many healthcare providers may opt to discontinue treatment after 2-5 years.
- While individual cases may differ, it's generally advised that transgender individuals remain on HRT until the age of 50 to mitigate the risk of osteoporosis.

- If you used HRT to alleviate menopausal symptoms, you may experience their return, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, anxiety, mood swings, muscle aches, or a decrease in libido.
- If you previously experienced vasomotor symptoms (like hot flashes or heart palpitations) before starting HRT, inquire with your doctor about strategies for managing these symptoms once you discontinue hormone therapy.
- While HRT can help prevent osteoporosis, discontinuing treatment may reintroduce this risk.

- Gradually discontinuing HRT can help mitigate the risk and severity of side effects.


Clinical Psychologist
Expert Advice: If you're currently undergoing hormone replacement therapy, you have the flexibility to discontinue it at any point and for any reason. Perhaps you seek only partial hormonal effects, or maybe you wish to temporarily halt treatment to explore fertility restoration or address unintended side effects. Nonetheless, it's prudent to consult your doctor before discontinuing therapy. Additionally, bear in mind that ceasing hormone use may result in reversal or partial reversal of certain effects, while others may be more enduring.
Cessation of Hormones




Addressing Side Effects

- For menopausal individuals, exercise may alleviate hot flashes.
- Individuals who have recently discontinued testosterone or estrogen therapy may face an increased risk of weight gain. Exercise can aid in weight maintenance or loss.
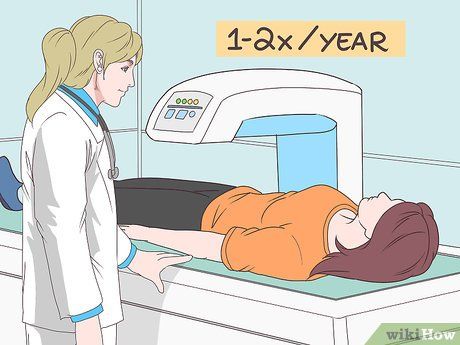
- Typically, your doctor will utilize a DEXA machine to assess bone density and fracture risk.
- Maintaining physical activity levels and supplementing with calcium and vitamin D can aid in preserving bone health.


- Tibolone may help alleviate hot flashes and enhance libido but shares similar side effects with HRT, such as abdominal and pelvic pain, breast tenderness, and an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Clonidine has a milder impact on menopausal symptoms without affecting hormone levels. Side effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, depression, and constipation.
- Antidepressants may offer relief from hot flashes but come with potential side effects such as dizziness, anxiety, agitation, and reduced libido.
- Gabapentin can assist in managing hot flashes and insomnia during menopause, albeit with side effects like headaches, dizziness, and drowsiness.