Excel, the most powerful and widely used calculation tool today, is a constant companion for accounting professionals. Especially for accountants who frequently work with Excel spreadsheets, mastering smart Excel tricks enhances efficiency. This article provides detailed guidance on various Excel tricks and tips tailored for accountants.
1. Select and Add/Delete Entire Rows Using Keyboard Shortcuts
To add or delete rows or columns, select the adjacent row or column and use the following keyboard shortcut:
- Add row (column): Press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + “+”
- To delete a row (column): Press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + “-“
2. Swiftly Copy and Move Data
To quickly copy and move data, simply select the data range you want to move -> hover the mouse over the edge of the selected data range until the cursor turns into a 4-directional arrow -> hold down the mouse button and move it to the new area.
For quick copying, hold down the Ctrl key while moving.
3. Eliminate Empty Cells Within a Data Range
If your data file has numerous non-contiguous empty rows, manually selecting and deleting each empty row is time-consuming. To delete all empty rows within a data range, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Select the entire data range where you want to delete empty rows -> click Data Filter -> click the dropdown arrow in any cell -> uncheck Select All -> check the Blank option -> press OK:
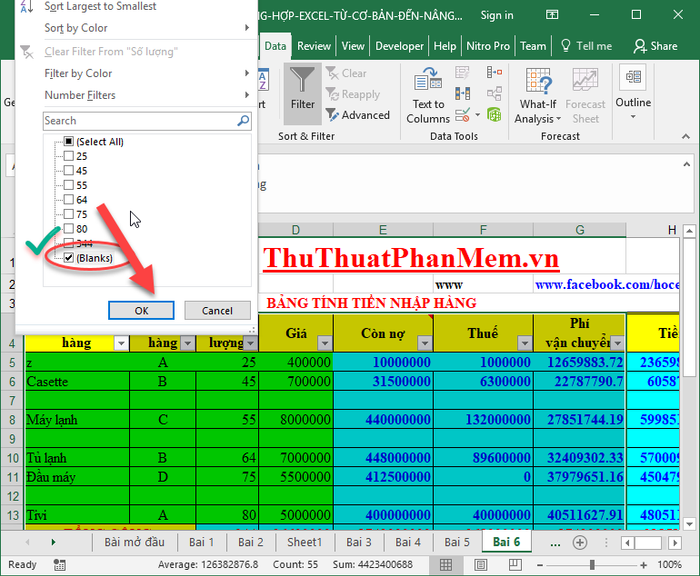
In step 2, after selecting Blank for all consecutive empty rows, simply choose those empty rows -> right-click and select Delete Rows:
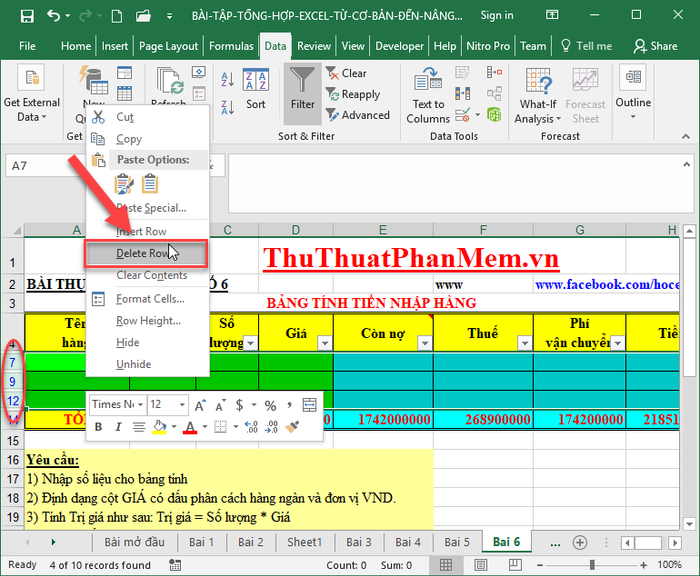
4. Utilizing Data Filtering in Excel
When dealing with a large amount of data and you want to view the results for a specific individual or filter a list of students in a class or a school attending competitions, quickly apply the filtering feature in Excel to save time.
Highlight the header row -> go to the Data tab -> click Filter:
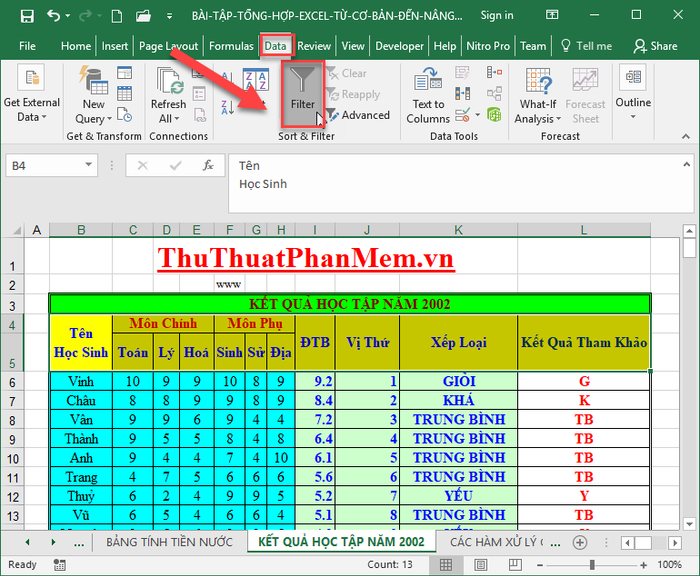
On the header row, click the dropdown arrow, choose the arrow, and filter the data according to your preference:
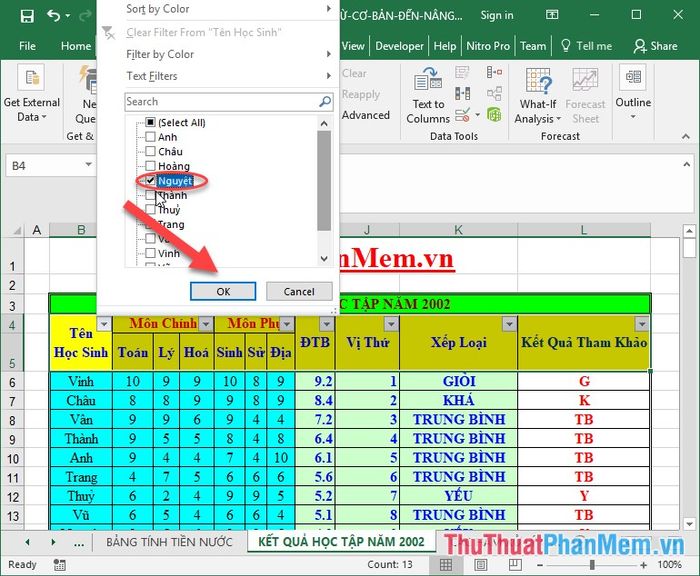
5. Restricting Input Values in Excel Spreadsheets.
For instance, to prevent someone from altering your data to a higher value, limit the value for the data cell.
Step 1: Select the data range to limit -> go to the Data tab -> Data Validation:
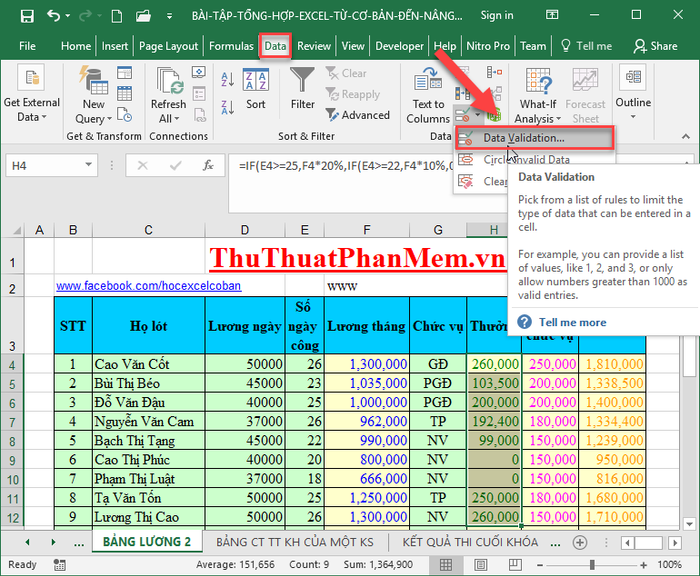
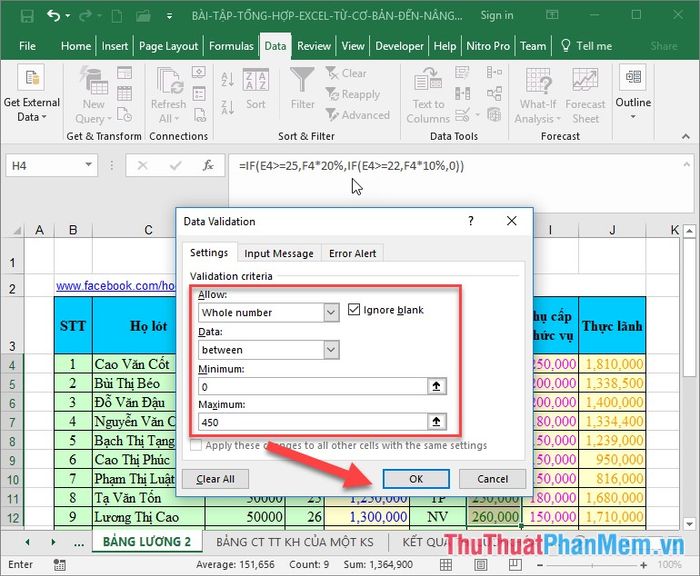
Step 2: A dialog box appears in the Allow section, choose Whole number -> in the Data section, select Between -> enter the corresponding value limits for Minimum and Maximum.
Now, if you enter a bonus value of 600k -> the system will display an error exceeding the limit:

6. Managing Fixed Product Categories with Validation
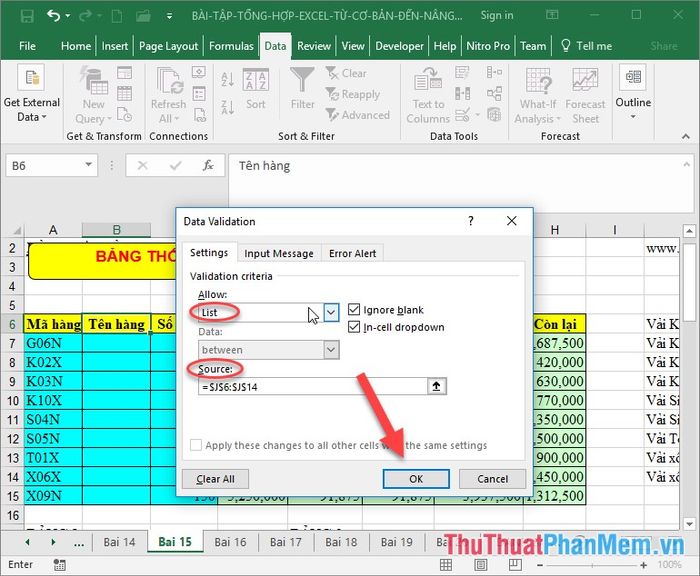
You want to manage the product categories to avoid entering items without names in the list. Simply, with a few steps, you can tightly control your inventory. For example, create a list of item names in the name column to limit users from entering incorrect items and items without names in the category.
Create a list of items -> click on the item name cell -> go to the Data tab and choose Data Validation -> in the dialog that appears, in the Allow section, select List -> in the Source section, choose the data range containing item names -> click OK:
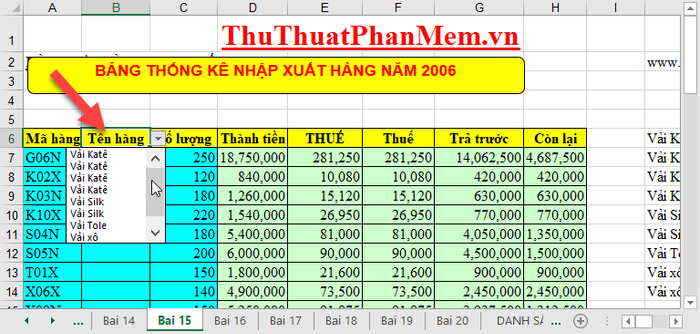
And here is the result:
7. Using Format Painter Multiple Times
Format Painter applies the previously used format to subsequent objects. If you want to use it for multiple objects, instead of left-clicking and selecting each object multiple times, simply double-click the paintbrush and select the objects you want to apply it to.
Transforming data from columns to rows and vice versa
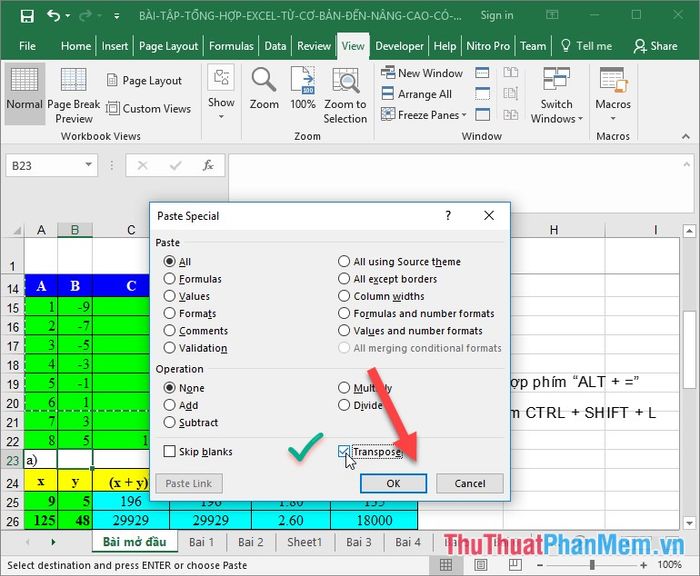
Concealing various data types
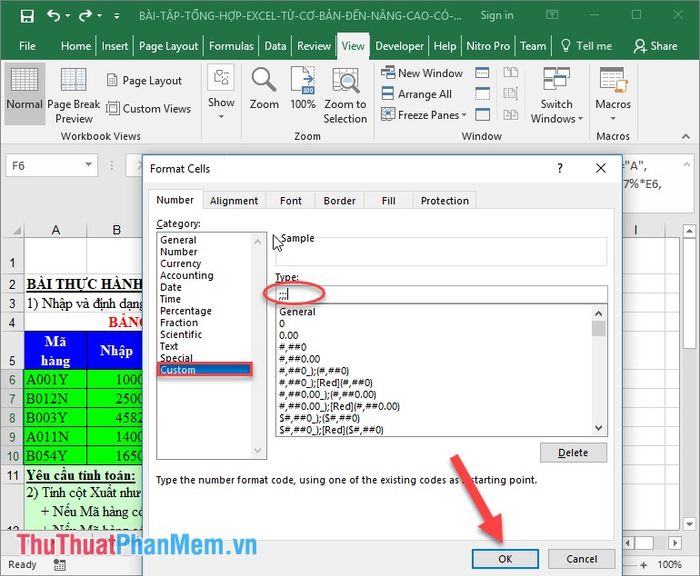
Entering numerical data starting with zero
Usually, Excel may not allow entering numbers starting with zero. There are two ways to address this issue:
1. Use single quotes ‘ before entering the desired value.
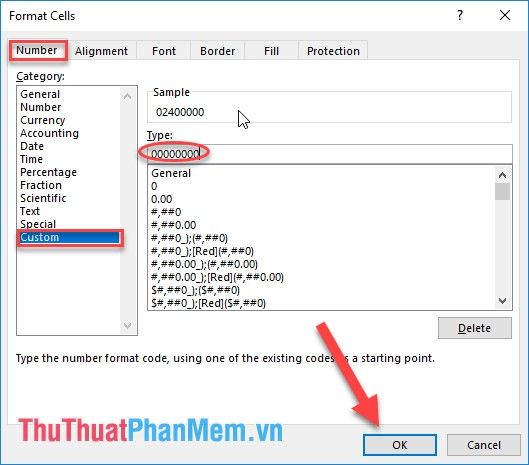
2. Format the data cell, under the Type section, enter 8 zeros:
3. Creating a drop-down list in Excel is as simple as performing similar actions in the 6. Managing fixed commodity categories with Validation section.
4. Follow the same procedure in the 6. Managing fixed commodity categories with Validation section for easy setup.
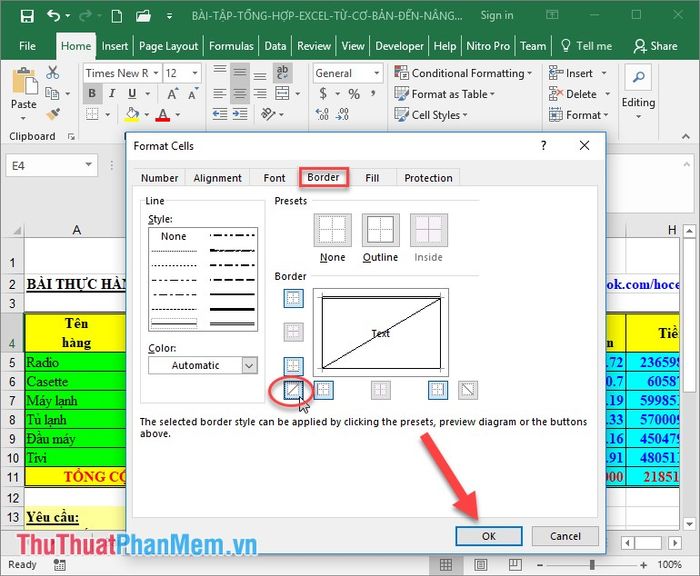
1. Add a diagonal line in a cell easily.
2. Select the data cell for the diagonal line -> right-click and choose Format Cell, then select the cell containing the diagonal line in your preferred direction.
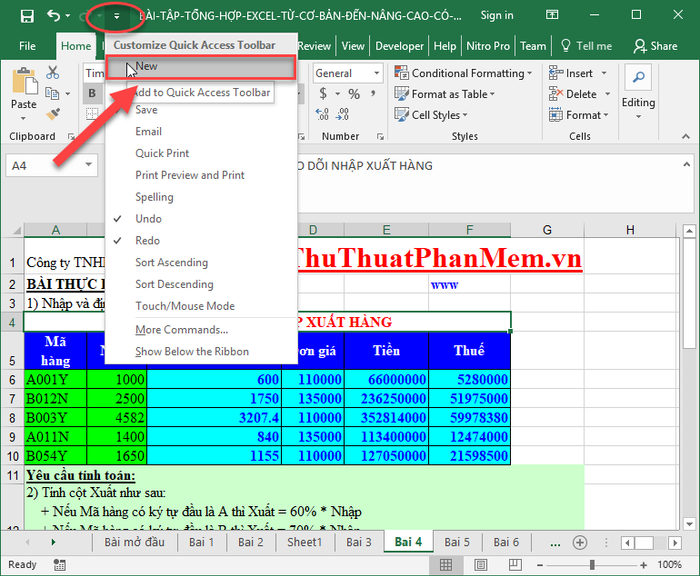
3. Set up quick access keys on Quick Access for efficient navigation.
4. Utilize Quick Access to swiftly access commonly used features in Excel. Add more features by selecting the arrow -> check the desired feature on Quick Access.
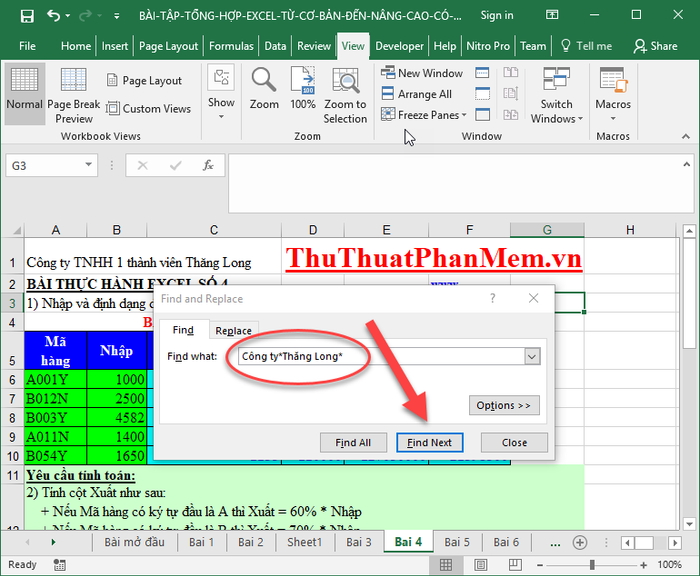
1. Harness the power of intelligent search in spreadsheets.
2. When unsure of the search term, use the smart search feature by incorporating the * character for enhanced results.
3. Easily create titles for multiple sheets simultaneously.
4. If your Excel file contains numerous sheets and you wish to set identical titles for all sheets when printing, follow these steps:
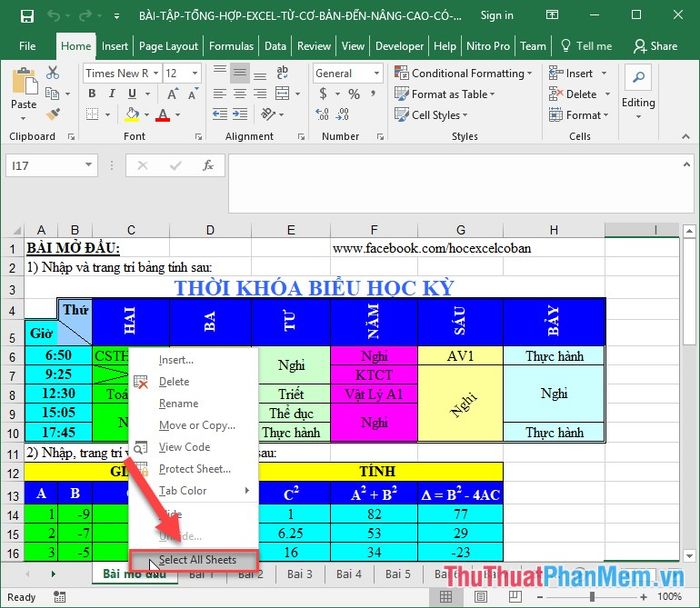
1. Right-click on any sheet -> choose Select All Sheets:
2. Input the common title you want to create for the sheets.
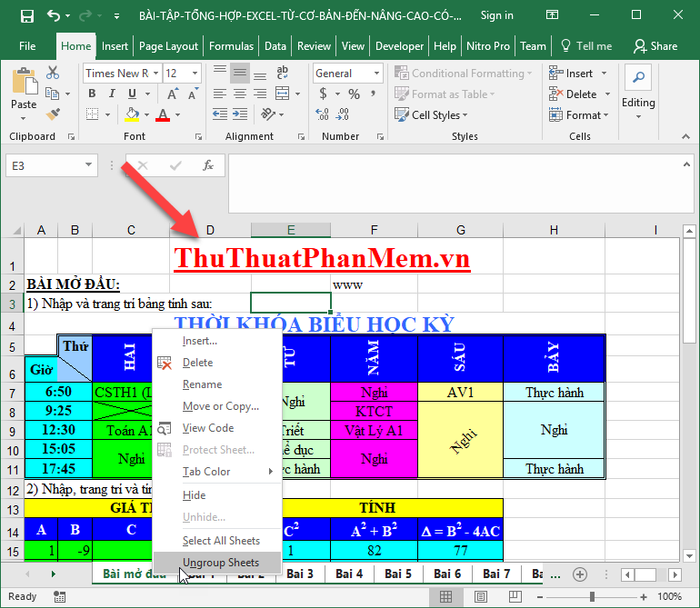
3. Right-click on any sheet, select Ungroup Sheets:
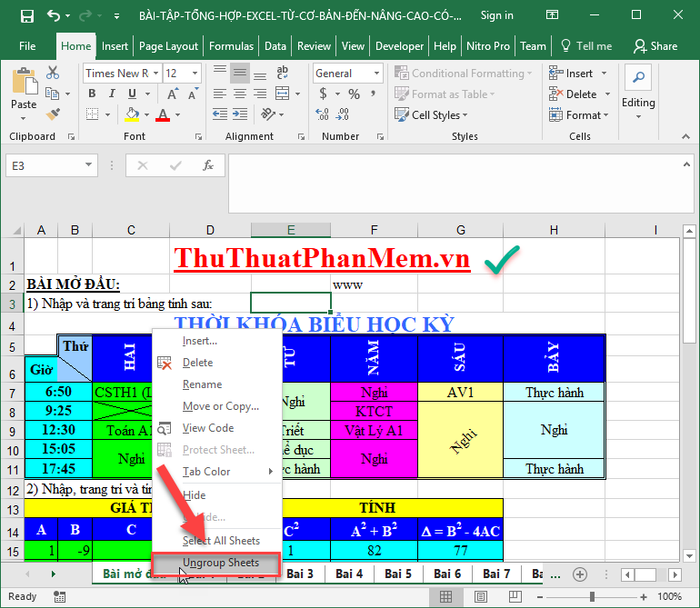
4. The result: all sheets in the Excel file will now have the same title.
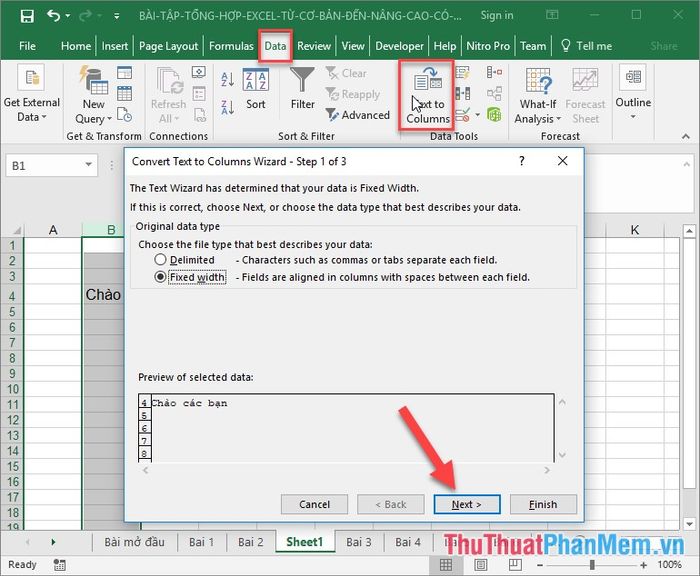
16. Importing Text Data into Excel
If your data in Word is formatted in tabs and you want to transfer it to Excel with each tab's data corresponding to a column, follow these steps: Copy the text content from Word to Excel -> go to the Data tab -> Data Validation -> in the dialog that appears, click Next until you complete Finish.
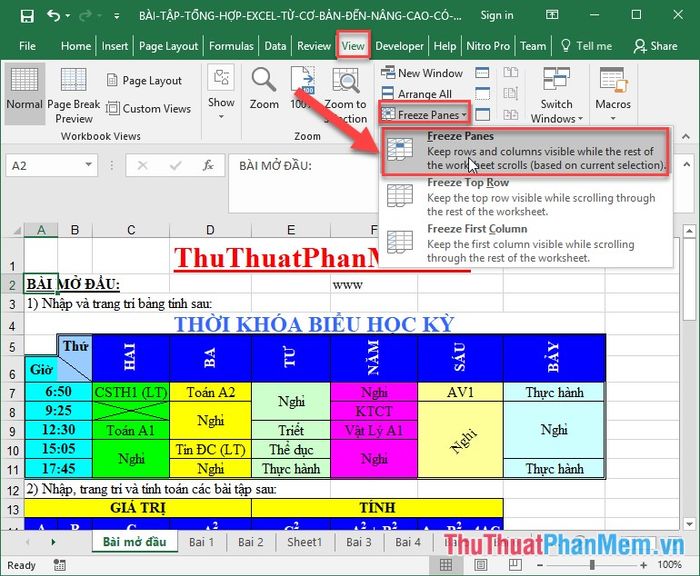
17. Freezing Header Rows
When dealing with large datasets and you want to keep the header row visible while scrolling, place the mouse cursor below the header row you want to freeze -> go to the View tab -> Freeze Panes.
18. Linking Data between Excel and Word
When your data exists in both Word and Excel files, and you want changes in one file to automatically update the other, follow these steps:
After copying data from the Word file, choose Paste Special -> in the appearing dialog, check Paste Link and select Microsoft Word Document…
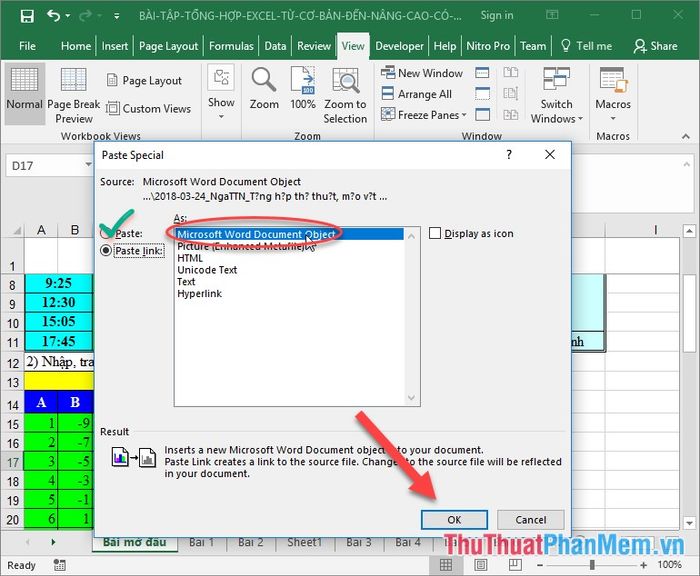
This way, the two data files are linked to each other.
Additionally, grasp some useful shortcuts in Excel:
1. Quickly sum without using a function with the shortcut “ALT + =”
2. Enable quick data filtering with the shortcut CTRL + SHIFT + L
3. Display formulas with the shortcut CTRL + ~
4. Swiftly navigate between sheets using the shortcut CTRL + PAGE UP, CTRL + PAGE DOWN
5. Switch between workbooks with CTRL + SHIFT TAB
Here's a detailed introduction to handy tips and tricks in Excel for accountants. Wishing you all success!
