When using a network, computers often default to dynamic IP address assignment. However, setting static IP addresses for each computer within the same internal network can prevent address conflicts. Additionally, changing DNS settings can improve web browsing speed and access restricted websites like Facebook...
Below, I'll guide you through setting up static IP addresses and changing DNS settings for your computer.
Step 1: Click on the network icon in the Taskbar, then select Open Network and Sharing Center.
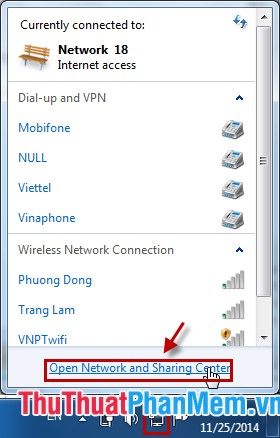
Step 2: Select the network under Connections.
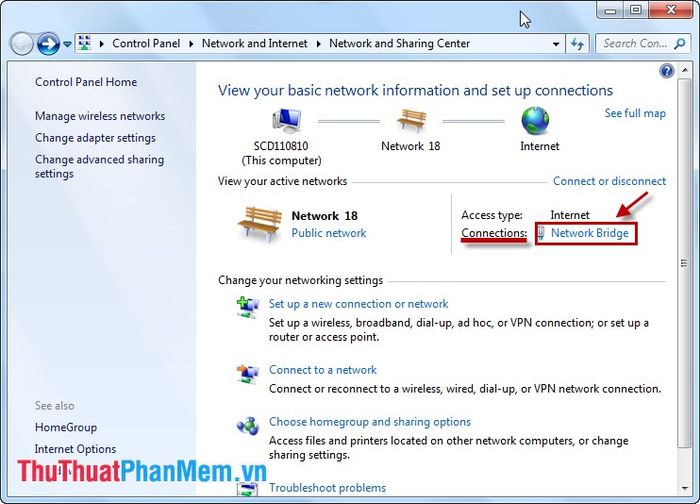
Step 3: Next, choose Properties.
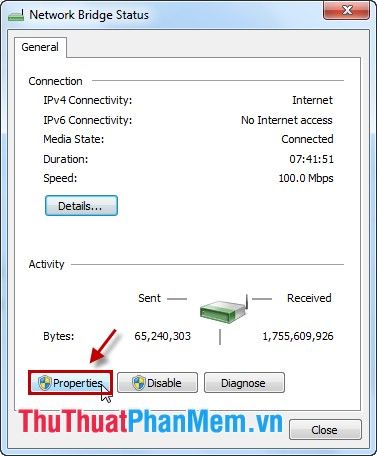
Step 4: In the This connection uses the following items section, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
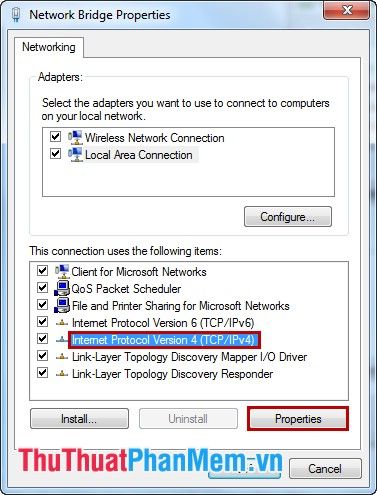
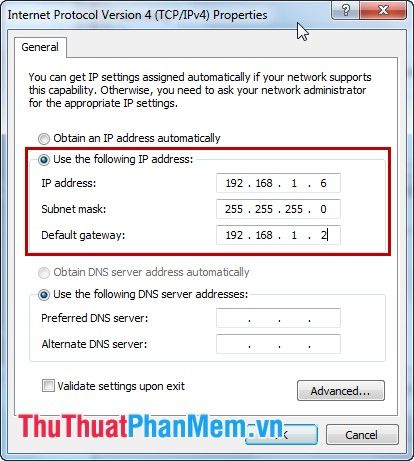
Step 5: Set a static IP address for your computer.
Choose Use the following IP address. Here, you need to enter:
IP address: The first three IP fields must match the network class within your internal network (similar to your modem's IP) to access the Internet. The fourth field represents the IP address of your device; ensure it doesn't conflict with other devices on your internal network.
Subnet mask: Leave this field blank for automatic assignment by the device.
Default gateway: This is the gateway for external connections; make sure to enter the correct IP address of your modem.
Step 6: Configure DNS settings.
Select Use the following DNS server addresses, then enter:
Preferred DNS server
Alternate DNS server
You can typically use Google or Open DNS servers as follows:
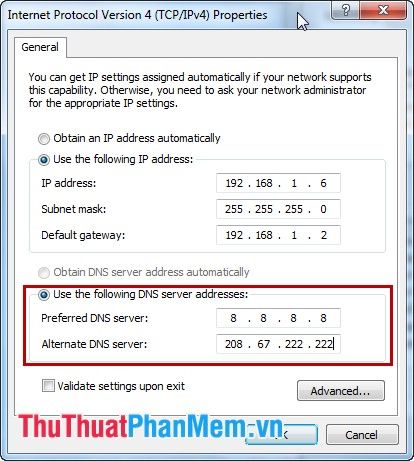
After making the changes, press OK to save the settings.
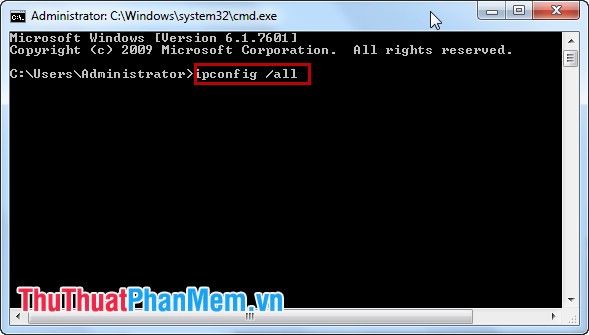
Step 7: Verify the IP and DNS after making the adjustments.
Go to Start, select cmd.exe. In the cmd window, type ipconfig[space]/all and press Enter.
Here, you'll find the IP address and DNS settings you've just configured.
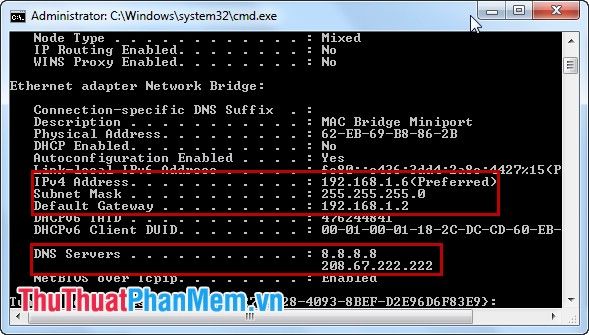
Congratulations! You've successfully set up a static IP address and changed DNS settings for your computer!
