Text files, known as .txt files, typically lack the formatting seen in MS Word documents but offer much smaller file sizes. They are perfect for emailing or web posting. Programming files are commonly in plain text format and often used for storing notes, CSS, and HTML files.
Steps
Access your Word document.
Double-click your Word document to open it in Word. Alternatively, use any application that supports Word documents such as Corel WordPerfect or OpenOffice.
To access the File menu, first locate and click on the 'File' tab situated in the upper-left corner of your screen.
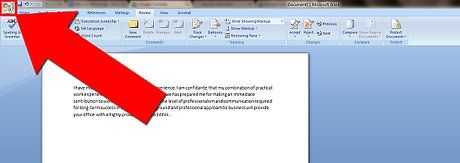
Within Word, navigating to the 'File' menu is essential. Look for a distinct button, often marked with a stylized 'F', usually positioned at the top-left corner of the interface.
After accessing the 'File' menu, proceed by selecting the 'Save As' option from the available choices.
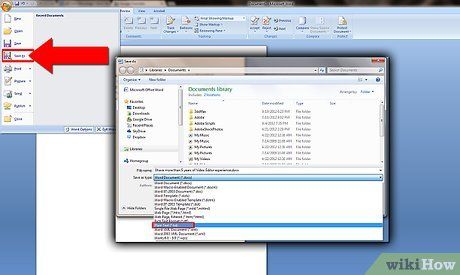
Upon selecting 'Save As', the application prompts you to provide a name for the document you wish to create.
Take a moment to assign an appropriate name to your document before finalizing the saving process.
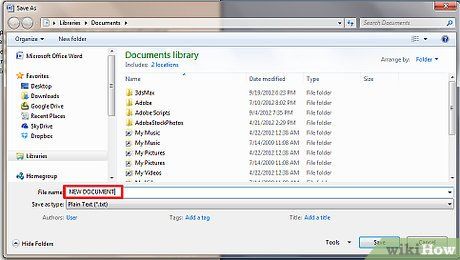
When renaming your file, consider choosing a distinctive name. Although it can match the previous document's title, ensure it bears a new file extension.
Opt for saving the document in plain text format to maintain simplicity and compatibility across various platforms.
When prompted to specify the file type, opt for plain text options such as '.txt', 'text', 'plain text', 'ASCII', 'UNICODE', or similar, then proceed to click 'Save'.
Here are some additional tips to enhance your text document management:
- In Microsoft Windows, consider right-clicking and selecting 'New', then 'Notepad Document' to swiftly create a new text file.
