Elevate the appearance and durability of your kitchen or bathroom cabinets by crafting your own cabinet doors. The key lies in the craftsmanship and quality materials used for construction.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Constructing a Slab or Flat Panel Door

Decide which type of door to construct. You'll typically choose between two main types: slab and flat panel doors, based on factors such as construction speed, durability, and ease of maintenance.

Choose the appropriate material for your doors. Slab doors are commonly crafted from plywood, while MDF (medium density fiberboard) can be used for a wood grain appearance when painted or covered.
 Opt for solid wood when constructing a panel door.
Opt for solid wood when constructing a panel door.



Constructing a Raised Panel Door
 For a sophisticated appearance, opt for a flat (raised panel) door.
For a sophisticated appearance, opt for a flat (raised panel) door.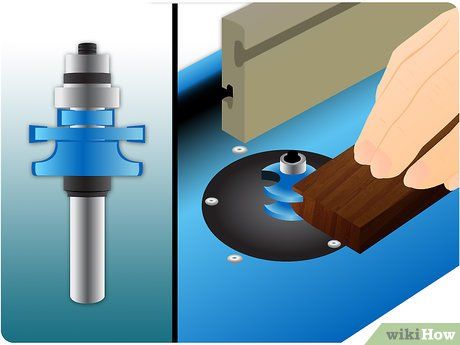
Switch to a coping or stick bit. The coping bit ensures a snug fit between the rail and stile. Proceed to run the rail ends through the bit.

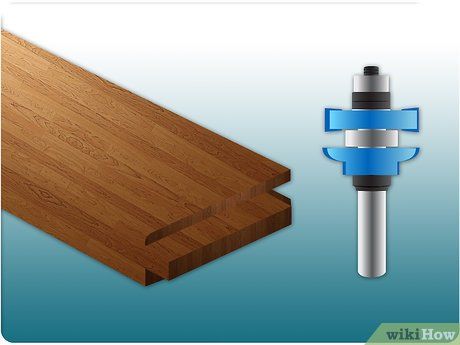
Determine the panel dimensions. Measure from the outer edges to the beginning of the roll-over or bead. Deduct this measurement from the total door height and width. Typically, a flat door panel is crafted from .25-inch (.6 mm) plywood, matching the cabinet's wood type.
- Cut the door panel insert slightly smaller than required to accommodate wood expansion and contraction, typically the width of a table saw blade.
- Commence door assembly. Apply glue to the inside of the stile where the rail fits and insert the rail tenon.
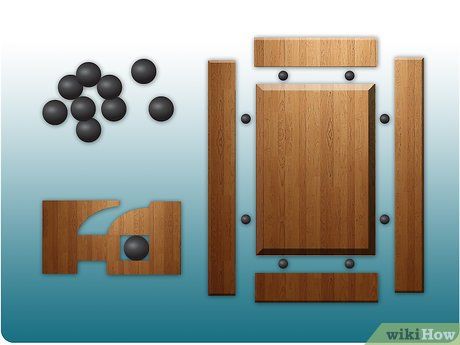
Acquire rubber space balls, commonly found at woodworking supply stores. Insert the balls into the groove created by the router-style bit. Then, insert the panel.

Apply adhesive to the rail tenon. Insert the second stile and secure the pieces with clamps while allowing the adhesive to set.

Smooth the door surface and apply desired finish. Proceed to attach the hardware and hang the newly crafted cabinet door onto the cabinet frame.
Useful Tips
-
You have various options for the style of panel cabinet doors, ranging from flat to raised or glass panel doors. Your decision should align with the desired aesthetic outcome.
-
When referring to 4/4, it indicates wood thickness of .25 inches multiplied by 4. For instance, 3/4 wood equals .75 inches, while 6/4 equals 1.5 inches.
-
Elevate the appearance of slab cabinet doors by incorporating molding along the edge or offset from it.
Warnings
- Building a flat or raised panel door without a router table is not recommended. Achieving the necessary precision is difficult without one.
Essential Tools
- Sheet goods .75 inches (2.0 cm) thick for slab doors
- .25-inch (0.5 cm) plywood for flat panel door
- .75-inch (2.0 cm)wood for stiles and rails
- Hinges
- Door knobs
- Adhesive
- Brushes for applying adhesive
- Router table
- Router
- Stile and coping router bits plus cabinet door bits
- Round-over bit
- Table or circular saw
- Bar clamps
- Space balls for panel spacing
- Stain or paint
