Refrigerators are indispensable appliances found in every household, serving the crucial purpose of preserving perishable food items for extended durations. Join Mytour on an exploration of the fundamental structure and operational principles of refrigerators!
Basic Structure of Refrigerators
A typical refrigerator comprises four essential components: the evaporator coil, compressor unit, refrigerant substance (gas), and condenser coil.
- Evaporator Coil:
This crucial component facilitates heat exchange between the refrigerant (cold gas) and the cooling environment (water or air). The evaporator coil's primary function is to release the heat from the condensing refrigerant into the surrounding environment. Typically constructed from materials like iron or copper, it features heat-dissipating fins.
Normally, the evaporator coil is installed with one end (inlet) connected to the compressor unit's discharge port, while the other end (liquid refrigerant outlet) is linked to the filter dryer before connecting to the capillary tube.

The Compressor Unit (Block) is an indispensable component of refrigerators.
- Compressor Unit (Block):
Refrigerators are often equipped with single or dual-piston compressor units, employing a mechanism that converts rotary motion into reciprocating motion of the pistons.
The Compressor Unit (Block) extracts the refrigerant vapor generated at the evaporator coil, simultaneously maintaining the necessary pressure for vaporization at low temperatures. Another key role is compressing the vapor from evaporative pressure to condensing pressure and delivering it to the condenser coil.
- Refrigerant Substance (Gas):
Acts as a liquid easily vaporized within the refrigerator to create cold temperatures. Many advanced systems use pure ammonia as the refrigerant. The vaporization temperature of the refrigerant is approximately -27 degrees Celsius (about -32 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Evaporator Coil:
The evaporator coil in a refrigerator is considered a heat exchange device between the refrigerant on one side and the environment requiring cooling on the other. The evaporator coil is responsible for absorbing heat from the cooling environment to allow the refrigerant to boil at low temperatures. This component is installed after the capillary tube or expansion valve, ahead of the compressor in the refrigeration system.

4 Fundamental Operating Steps of a Refrigerator
Operating Principles of Refrigerators
Refrigerators utilize dry steam to absorb heat. The operation of a refrigerator involves a fairly intricate mechanism, with various components playing crucial roles in the refrigeration cycle.
The operating principles of a refrigerator involve 4 steps:
Step 1: Compression of gas (refrigerant) at the compressor unit:
The refrigerator is equipped with a compressor (position 4 in the diagram) used to compress the refrigerant to high pressure and high temperature, at which point the refrigerant is in a gaseous state.
Step 2: Condensation at the condenser coil (1):
After passing through the compressor, the refrigerant is directed to the condenser coil (position 1 in the diagram). Here, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant is cooled by ambient air and condenses into a liquid with high pressure and low temperature. Simultaneously, this is where the heat dissipation process occurs during condensation. Hence, if you touch the side of the refrigerator where the condenser coil is located, you will feel warmth.
Step 3: Expansion (2):
Next, the liquid refrigerant at high pressure passes through the expansion device (position 3 in the illustration) (Expansion Valve). Under the action of the expansion valve, the refrigerant transforms from high pressure and low temperature to low pressure and low temperature.
Step 4: Vaporization at the evaporator coil (3):
Here, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air inside the refrigerator to vaporize. During the vaporization process, the refrigerant extracts heat from the air inside the refrigerator, cooling the environment within. After vaporization, the refrigerant (gaseous state) returns to the compressor to start a new cycle.
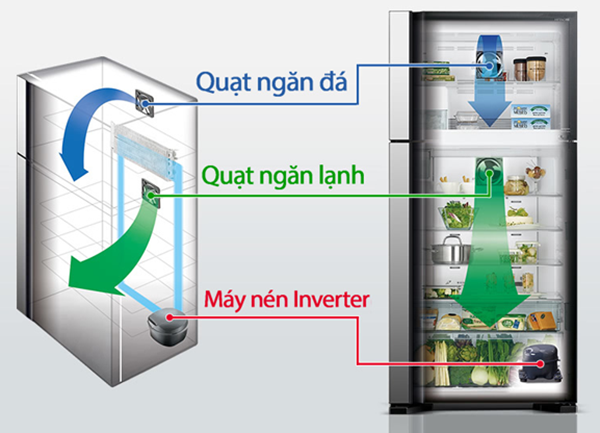
Refrigeration system of the Hitachi Inverter 339-liter refrigerator r-fg450pgv8(gbk)
Mytour has introduced to you the fundamental operating principles of refrigerators. However, each brand and type of refrigerator may modify or incorporate additional technologies and features into the operating process. If you're looking to purchase a high-quality and reasonably priced refrigerator, visit Mytour or place an online order at https://dienmaycholon.vn/ to enjoy exclusive promotions and attractive gifts.
Mytour
