Ensuring seamless network connectivity on your Windows device is crucial. Fortunately, there exist several straightforward methods to achieve this task. For Windows 10 users, accessing the Network and Sharing Center is the key. As for other users, utilizing “netstat,” a command-line tool for network statistics, can unveil issues or provide insights into network traffic. Thankfully, employing this command involves only a few simple steps.
Procedures
Accessing the Network and Sharing Menu in Windows 7 to 10
Initiate by clicking Start.
Navigate to Settings.
Choose 'Ethernet' from the 'Network & Internet' options.

Access the Network and Sharing Center. This Windows 10 feature provides insights into your network status, connection type, ability to connect with other computers, and internet connectivity.
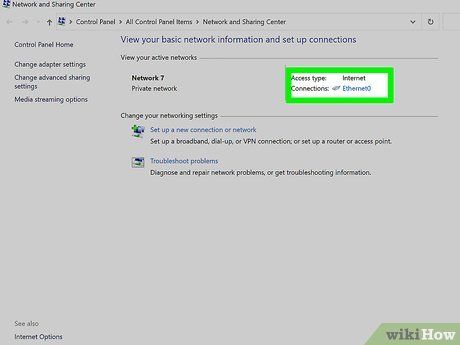
Click on the icon adjacent to 'Connections.' This icon corresponds to your connection type, such as an ethernet cable for 'Ethernet' or five bars for a wireless network connection.
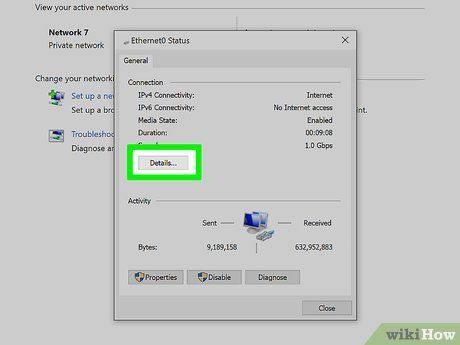
Select Details. This action triggers a window to appear, displaying the specifics of your network connection.
Utilizing the Network Connections Folder in Windows 7
Initiate by opening the Start menu.
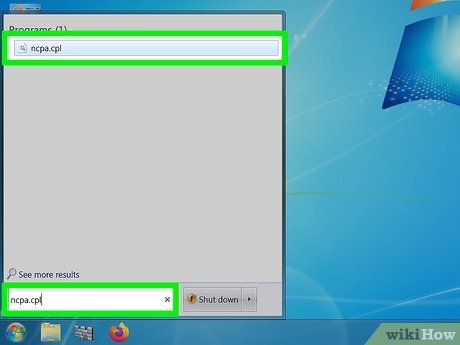
Type 'ncpa.cpl' (without quotes) into the search box.
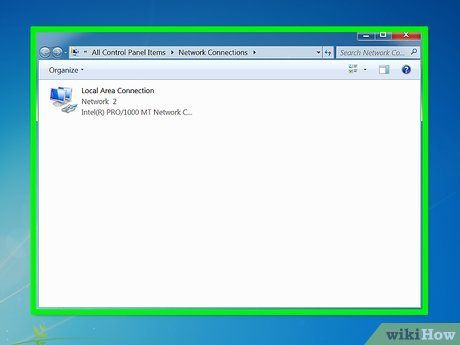
Wait for the Network Connections Folder to appear. It will present all available connections within your network.
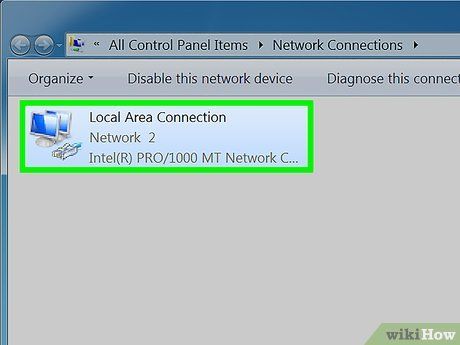
Simply right-click on your desired connection.
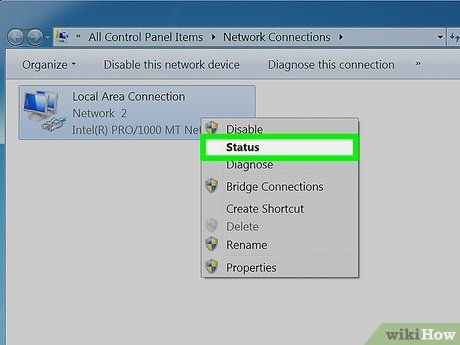
Opt for Status from the dropdown menu.
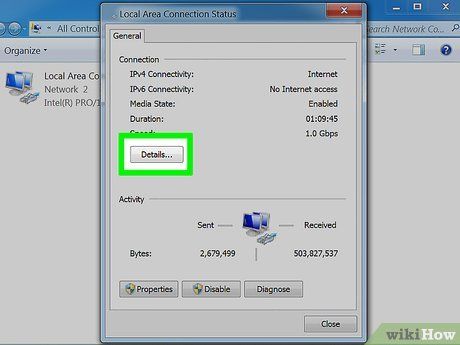
Wait until the Network Connection Status page is displayed. This page provides an overview of the network status, with the option to delve into further details by selecting 'Details'.
Utilizing the Netstat Command in Vista or Later Versions
Access the Start menu.

Lookup “cmd.” To open the command prompt on Vista or newer Windows versions, simply enter 'cmd' (without quotes) in the search box.
Be patient for a black window, or terminal, to emerge. This is where you'll input your netstat command. Here are a few options you can utilize, with some of the more popular ones listed below.
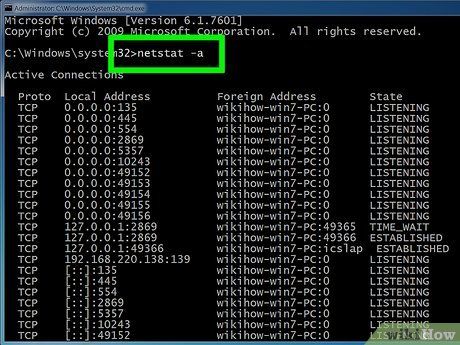
Type netstat -a to display current connections. This command presents a list of your ongoing TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections and ports. It includes the local computer name for local addresses and the host name for remote ones. Additionally, it indicates the port's state (waiting, established, etc…)
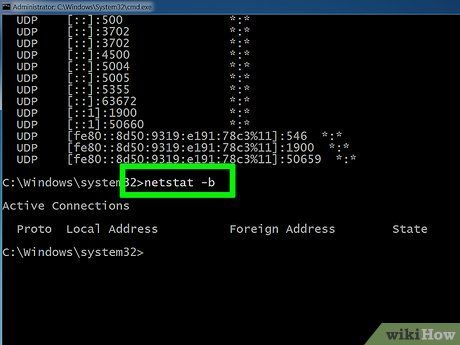
Type netstat -b to reveal programs utilizing connections. This command showcases the same list as netstast -a but also identifies the programs utilizing the connections/ports.
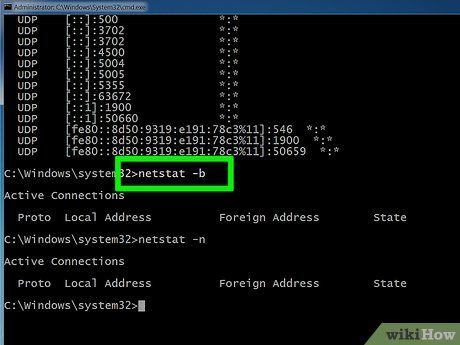
Type netstat -n to uncover IP addresses. This command shows the same TCP connections and ports list, but with numerical (IP) addresses instead of computer or service names.
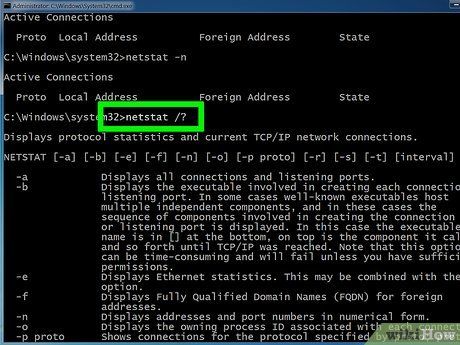
Type netstat /? to display available commands. This command furnishes statistics for all variations of the netstat protocols.
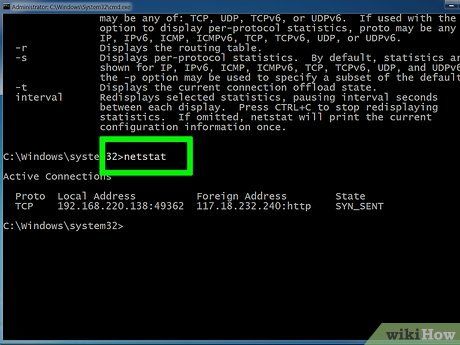
Verify active network connections. Once you input your netstat command, a roster of TCP/UDP connections along with IP addresses will display.
Utilizing the Netstat Command in Windows XP

Initiate by pressing Start.
Proceed to click 'Run.' This action triggers the appearance of a text box.
Enter 'cmd' (without quotes).
Anticipate a black window, or terminal, to materialize. This is where you'll input your netstat command. Here, I'll outline a few different options, including some of the more popular ones.
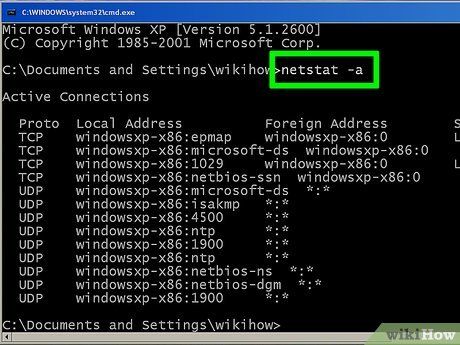
Type netstat -a to display ongoing connections. This command generates a list of your current TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connections and ports. It includes the physical computer name for local addresses and the host name for remote ones. Additionally, it provides information on the port's state (waiting, established, etc…)
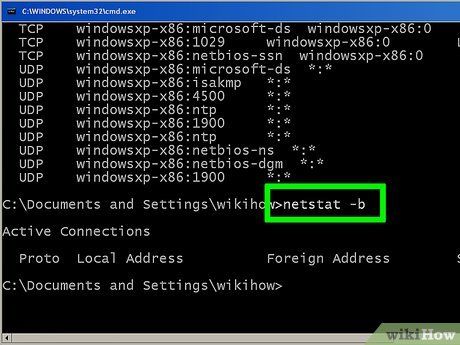
Input netstat -b to unveil programs utilizing connections. This command presents the same list as netstast -a but also indicates the programs using the connections/ports.
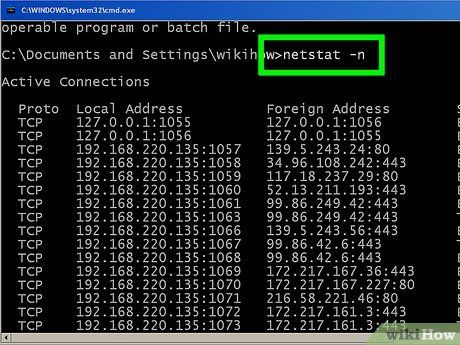
Key in netstat -n to reveal IP addresses. This command displays the same list of TCP connections and ports, but with numerical (IP) addresses instead of the actual names of the computers or services.
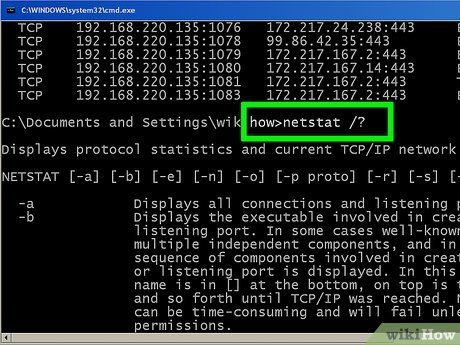
Execute netstat /? to display available commands. This command furnishes statistics for all variations of the netstat protocols.
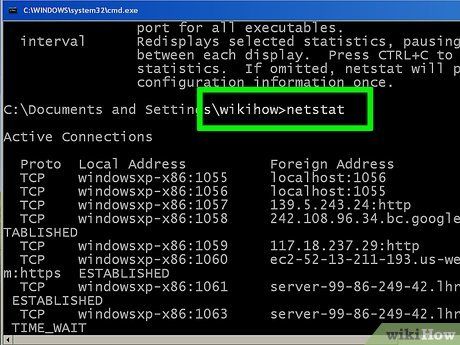
Verify active network connections. Upon entering your netstat command, a roster of TCP/UDP connections alongside IP addresses will be presented.
Suggestions
-
Explore - there's a plethora of UNIX commands available (such as 'netstat' mentioned earlier) - utilize your preferred search engine to discover them.
-
Alternatively, acquire TCPView from SysInternals.
-
Keep in mind that the netstat command is obsolete on Linux; hence, 'ip –s,' 'ss,' or 'ip route' may be utilized in its place.
