Recall the nostalgic Red Ryder wagons of your childhood or envision crafting a versatile garden planter or outdoor toy for your kids. Regardless of your inspiration, this comprehensive tutorial will walk you through the steps to construct your very own children's wagon.
Instructions
Acquiring Materials
Gather the necessary materials and tools. For this project, illustrated with rough sawn treated yellow pine privacy fence boards, affordability and lightweight were prioritized. These materials are also resistant to rot and insects, ideal for constructing a planter box. Additionally, you'll require:
- Drill and circular saw
- Corrosion-resistant screws
- Basic hand tools
Constructing the Foundation

Begin by constructing the foundational platform for the wagon. The platform depicted in the illustrations measures approximately 18 inches (45.7cm) in width and 24 inches (60cm) in length. However, feel free to adjust the dimensions according to your specific requirements.

Create four wheels by bonding together two 1X6 boards perpendicular to each other. Proceed to outline a circle on them, then utilize a jigsaw or bandsaw to cut along the marked lines. Drill a 1/2 inch (1.2cm) hole at the center of each wheel for the mounting bolts (explained later).
Fabricating the Swiveling Front Axle

Fabricate the swiveling mechanism for the front axle by cutting two 2 X 2 inch (5cm x 5cm) boards to match the width of your wagon.

Drill a hole at the center of these two boards to accommodate the swivel pin. The illustrations demonstrate the use of a metal pipe measuring 3/4 inches (1.9cm) in diameter, thus a hole of the same size is drilled for this purpose.

Trim a segment of pipe (or wooden dowel, if preferred) to a length of 2 1/2 inches (6.3cm) to fit into the holes of the swivel assembly. Utilize a flat washer as a bushing to facilitate smooth movement of the swivel once assembled.
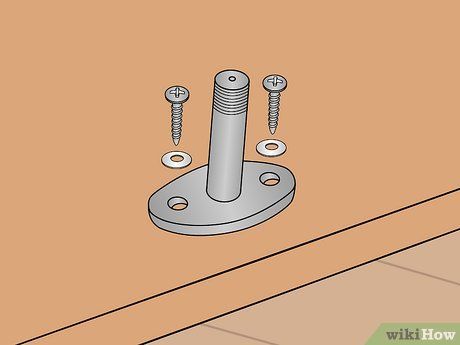
Secure the swivel in place using a large screw or lag bolt. If the depth of the hole is too great for the wood to hold the screw, you may require a large fender washer to enable the screw to tighten properly.

Drill the ends of the mobile section of the front axle swivel assembly for the wheel bolts. A 1/2 inch (1.2cm) steel bolt is ideal for this assembly. Drill through the center of each wheel, insert the bolt through, place a flat washer on the bolt, and then insert the bolt into the hole in the end of the axle assembly.
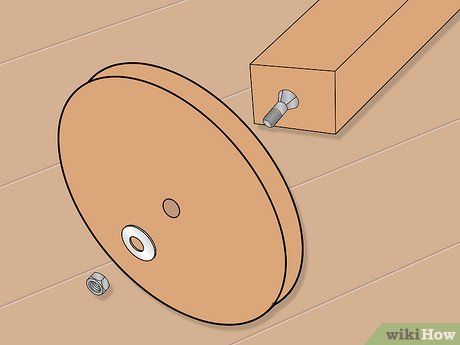
Drill a hole through both the axle assembly and the bolt that connects the wheel to the assembly. Secure it in place with a wood screw. Optionally, you may lubricate the bolt to ensure smooth wheel rotation and reduce wear on the surface. Alternatively, consider installing a metal bushing in the center of the wheel to further minimize wear.
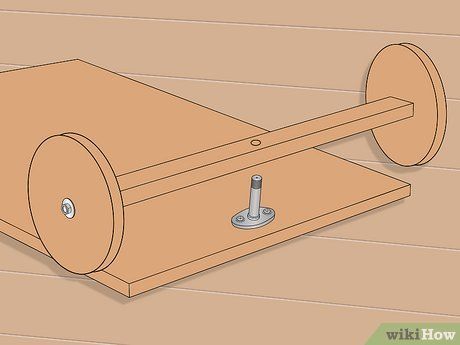
Secure the assembly to the underside of the initial wagon base.
Fixing the Handle
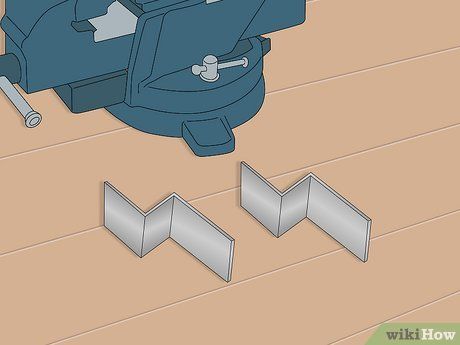
Create two angled clips for attaching the wagon handle. Opt for a 1 inch (2.5cm) by 1/8 inch (3.1mm) aluminum flat stock, which is easy to manipulate, drill, and resistant to weather and corrosion. Each side of the angle should measure approximately 4 inches (10cm) in length, and holes with a diameter of 3/16 inch (4.7mm) need to be drilled on one side of each piece for mounting screws.
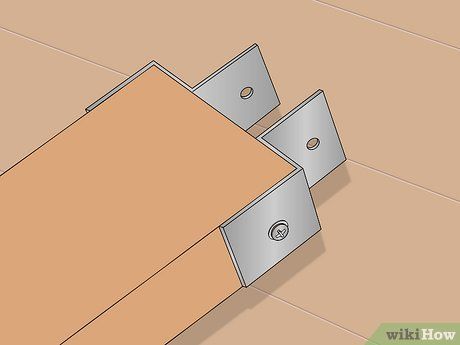
Position these brackets at the center of the swivel/axle assembly, ensuring ample space for the pull handle to move between them unrestricted. Consider ripping the stock (1 1/2 inches (3.8cm) square by 3 feet (91cm) long) prior to mounting the attaching brackets to ensure correct positioning.

Rip the stock (as described in the preceding step), sand the edges for smoothness, and place it between the brackets to accommodate the attaching bolt. Utilize a 1/4 inch (6.3mm) bolt measuring 2 1/2 inches (6.3cm) in length to secure this piece in place. To prevent loosening during use, you can create a dimple at the end of the bolt where the threads emerge from the nut.
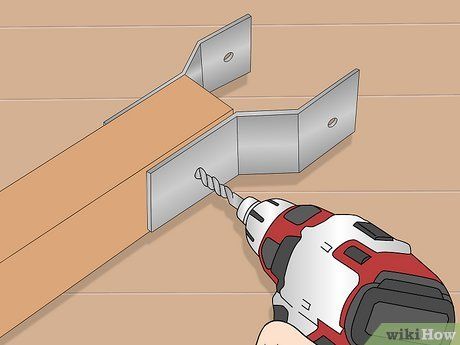
Construct the yoke responsible for securing the grip at the opposite end of the handle. Once again, utilize aluminum flat stock for this task, as it offers convenience. Shape two identical pieces into a squared 'zee' form (refer to the illustration), drill them for mounting screws, and use a file or sandpaper to smooth the edges to prevent potential scratches during handling.
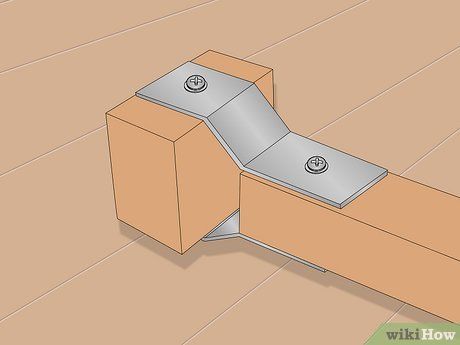
Insert a wooden block measuring 1 inch (2.5cm) square between the yoke ends. Proceed to drill the block at its center with a 1/4 inch (6.3mm) bolt hole (or all-thread rod) for attachment. Ensure the drilling is as centered as possible, using a sufficiently long bit to drill entirely through.
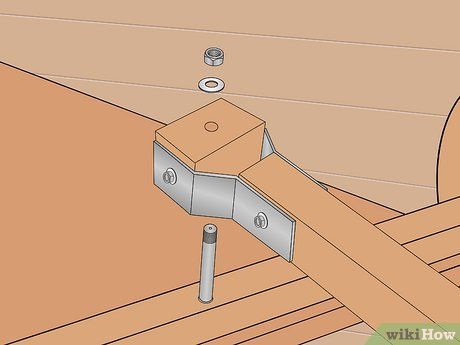
Pass the bolt or all-thread rod through the yoke, the wooden block, and out the opposite side of the yoke. Then affix a nut to the end (or both ends, if all-thread rod is utilized).
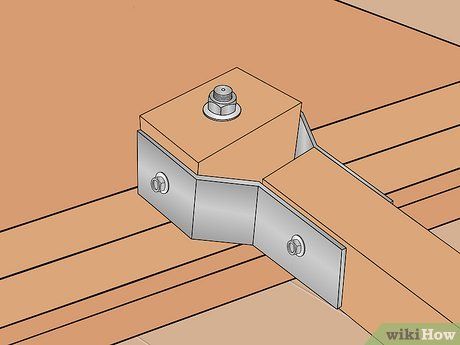
Secure the assembly firmly in place. Trim off any excess bolt threads and smooth out with a grinder to achieve a neat finish.
Constructing the Rear Axle

Construct the sturdy rear axle. Cut a board measuring 1 1/2 by 1 1/2 to match the width of your wagon, and create two spacer blocks to provide support and allow clearance for the wheels to rotate.
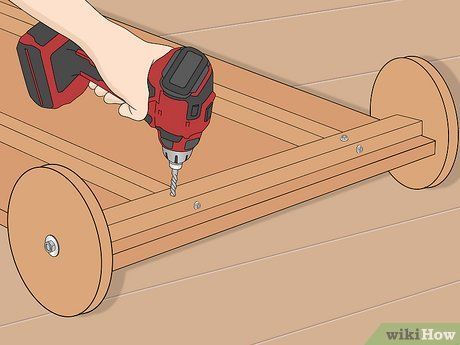
Secure the spacer blocks and rear axle in place using screws. Subsequently, drill the ends to accommodate the insertion of wheel mounting bolts. Proceed to secure these bolts in place using the same method employed for the swivel assembly.
Installing Sideboards and Final Touches
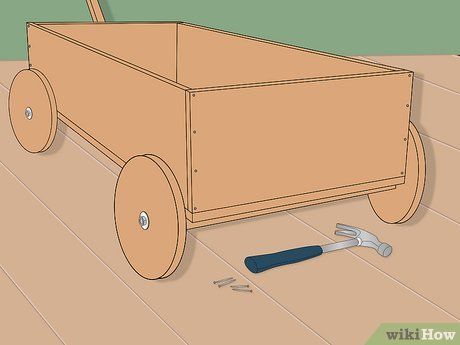
Trim and affix the sideboards onto the wagon platform. Utilize wood screws or brad nails for attachment purposes.

Smooth out any rough or splintered edges using a power sander or sandpaper. Exercise caution, especially if the wagon will be utilized by a child.
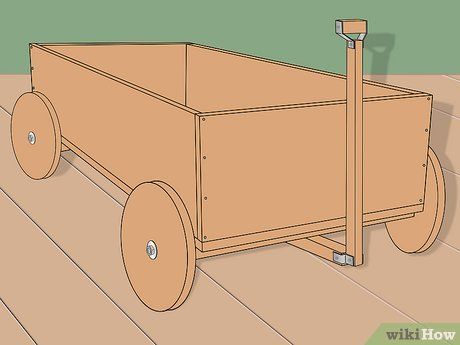
Completion.
Useful Tips
- Opt for rust-resistant fasteners (and waterproof glue, if preferred).
- Consider using chromed blind nuts or self-locking nuts for a more polished appearance (optional).
- Battery drills, power screwdrivers, or an impact driver can significantly simplify the assembly process.
Warnings
- Always wear safety glasses when drilling metal or sawing wood or metal.
- Be mindful of sharp edges or splinters in the final wagon, particularly if it will be used by children.
Materials Needed
- Wood, preferably cedar or redwood, but yellow pine is acceptable
- Screws, bolts, and nuts as outlined in the instructions
- Power and manual tools
