If you can't afford a professional tattoo or you don't have access to a tattoo parlor, you can give yourself a tattoo at home without a tattoo gun, using what is sometimes called the 'stick-and-poke' method. This process can be risky, but with proper precautions, you can achieve satisfactory results. Just ensure you're well-informed and adhere to all safety measures and hygiene standards before attempting this on your own.
Procedure
Preparing for Your Tattoo

Acquire or Assemble Your Own Home Tattoo Kit. Essential components include needles and ink. Only utilize unused tattoo needles and ensure the ink you use is specifically designed for tattooing. While tattoo ink is ideal, if unavailable, India Ink can be a substitute, though not recommended. Never resort to pen or marker ink!
- Home tattoo kits provide a secure and affordable option, offering both materials and instructions.
- Select a reputable brand of tattoo ink to guarantee its safety and absence of harmful substances.
- Avoid using sewing needles, straight pins, or safety pins, as they lack sterility and ink retention capabilities, posing significant health risks. Opt for professional-grade equipment for best results.
- Never reuse needles or share them, as doing so greatly increases the risk of infection. Always dispose of needles safely after use.

Prepare Your Workspace. Before beginning the tattooing process, ensure you have all necessary supplies ready. Gather cotton thread, a water cup, and rubbing alcohol.
- Keep a non-toxic marker nearby for sketching tattoo designs.
- Have ink caps, a shallow bowl, or saucer on hand to hold India ink. These items are cost-effective and aid in preventing ink wastage. Sterilize them using rubbing alcohol or hydrogen peroxide with a high alcohol content (91-99%).
- Thoroughly clean all utensils with hot, soapy water and alcohol or peroxide, then cover them with plastic wrap for added protection. When handling supplies, wear sterilized gloves and wash hands and gloves frequently throughout the process.

Prepare and Shave the Tattoo Area. Prior to tattooing, cleanse the chosen area with warm water and soap, followed by shaving the hair within an inch of the intended tattoo location.
- After shaving, sanitize the skin using rubbing alcohol. Apply it using a cotton ball and ensure it dries completely before proceeding.

Sketch Your Design. Outline or draw your desired tattoo directly onto your skin. Take your time to ensure accuracy, as this sketch will guide your tattooing process. Alternatively, utilize stencil paper and stencil gel for a more precise outline.
- Opt for easily accessible areas for self-tattooing, as you'll be working for several hours. Avoid difficult-to-reach or awkward spots, such as the chest or shoulder.
- For best results, stick to simple and small designs for stick 'n' poke tattoos. Complex designs are better executed by a professional tattoo artist.
Commencing Your Tattoo
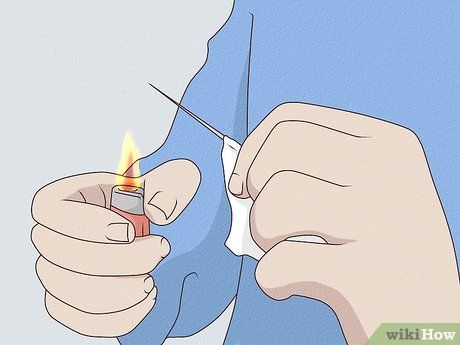
Sterilize the Needle. Ensure needle sterility by carefully heating it with a flame from a candle or lighter until it glows. Use tongs to avoid burns. Once sterilized, wrap the needle in cotton thread, starting about 1⁄8 inch (0.3 cm) from the tip, and wrap the thread back and forth approximately 1⁄4 inch (0.6 cm) up the needle to create an absorbent oval shape. This aids in ink absorption when dipping the needle into the ink source.
- Exercise caution and precision during the needle sterilization process to avoid injury or contamination.
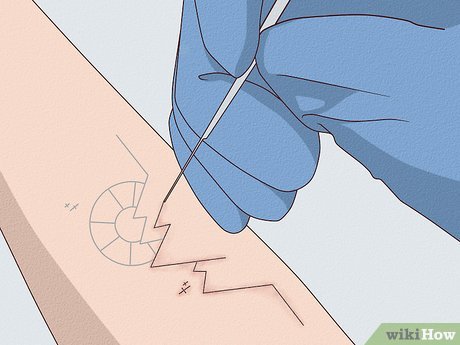
Commence Poking. Immerse the needle into India ink and proceed to puncture your skin, leaving small dots. While some blood may surface after multiple layers of poking, excessive bleeding indicates a need to cease immediately and sterilize the area. Apply a clean paper towel, avoiding cloth, to the tattoo until bleeding subsides.
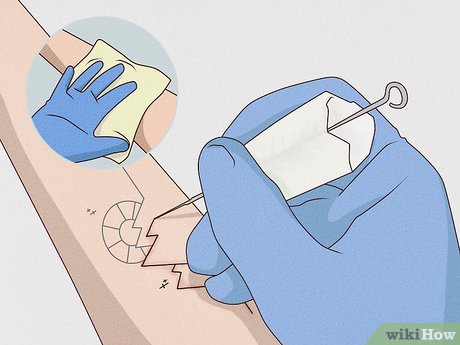
Begin Tracing the Lines. Follow the outline of your tattoo design, filling it in with small punctures. Utilize a cotton swab or rag to remove any blood or excess ink.
- Expect some swelling of the skin during the process, which may result in a patchy appearance. Touch-ups may be necessary once swelling diminishes for smoother lines. However, wait until the tattoo is fully healed, a process that may take up to two months, before performing touch-ups.
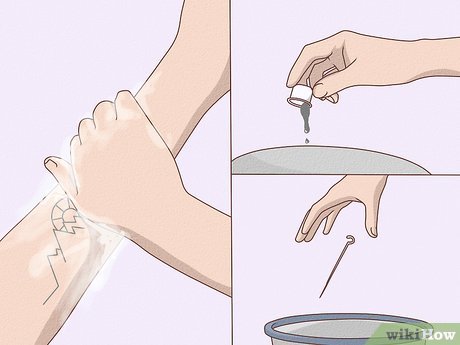
Sanitize the Tattooed Area. After completing the tattoo, cleanse the area with soapy water. Dispose of any leftover India ink and needles, as they are no longer sterile. For future touch-ups, utilize new needles and fresh ink saucers.
- Avoid using alcohol to clean a fresh tattoo; opt for soap and water instead.
Tattoo Aftercare

Secure Your New Tattoo with Plastic Wrap. Avoid using cloth or bandages, as they may absorb ink and hasten fading. Refrain from applying ointments or lotions during the first week of healing, as they can clog the tattoo and increase infection risk.
- Leave the plastic wrap on for 1-3 hours, but no longer than 6.
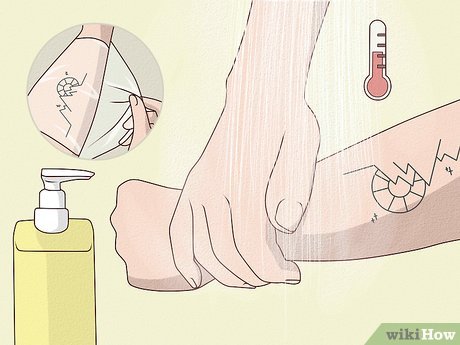
Maintain Tattoo Hygiene. Unwrap the initial covering and delicately cleanse the area with warm water and unscented soap. Refrain from vigorous scrubbing and ensure your hands are clean while washing.
- Avoid immersing your tattoo in water or exposing it to hot water, as this can cause discomfort and compromise ink retention.
- Avoid picking at the tattoo to prevent ink leakage, which can lead to blurred lines and potential scarring.
- Remove the bandage after a few hours and cleanse the tattooed area.
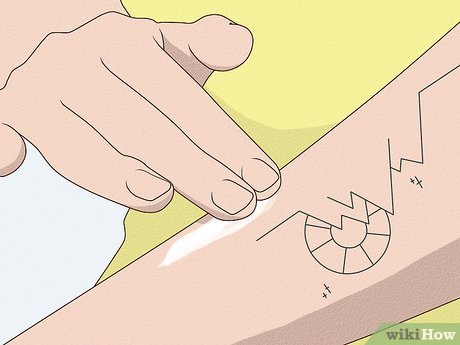
Apply Moisturizer to Your Tattoo. Once swelling subsides and the skin begins to scab, switch to a plain, unscented lotion such as Lubriderm or Aquaphor. Apply thin layers to allow proper healing and skin respiration.
- Moisturize your tattoo 3-5 times daily, adjusting frequency based on tattoo size. If your skin appears dry, apply a small amount of lotion.
- Avoid excessively greasy products like vitamin E, aloe, or Vaseline.
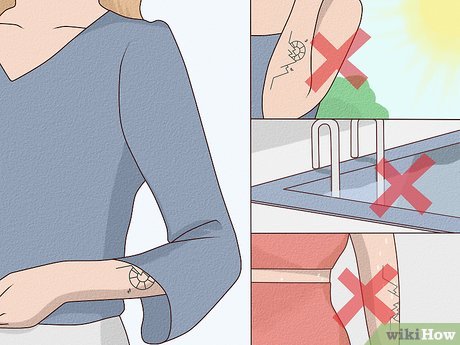
Allow Your Tattoo to Heal. During the initial week, take extra care to keep your tattoo clean as it scabs over. Avoid direct sunlight, water exposure, high-contact activities, and tight clothing to promote optimal healing.
- Avoid exposing your tattoo to direct sunlight to prevent fading and discomfort.
- Avoid swimming in pools, hot tubs, or natural bodies of water to minimize the risk of infection from bacteria.
- Avoid vigorous physical activities that induce sweating and wear loose clothing to allow your tattoo to breathe.
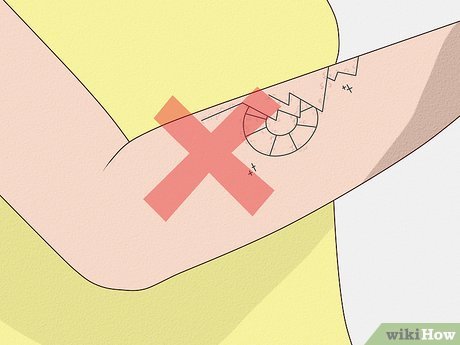
Monitor for Signs of Infection. Be vigilant for redness, excessive scabbing, oozing, or swelling around your tattoo, as these may indicate infection.
- Maintain cleanliness of supplies and proper tattoo care to minimize infection risk. If infection is suspected, consult a physician promptly.
- Avoid picking or scratching your tattoo, as this can introduce bacteria and hinder healing.
Recommendations
Precautions
- Use only tattoo ink or India ink as other types can be hazardous and pose serious risks.
- Always use new, sterile needles, and ensure they are properly sterilized before use. Never share or reuse needles.
- The safest method for getting a tattoo is through a professional tattoo parlor. Avoid self-tattooing if you're uncomfortable with associated risks.
- Home tattooing carries the risk of severe infections and may be prohibited in certain areas. Familiarize yourself with the risks beforehand.
- Sharing needles increases the risk of contracting diseases such as HIV, Hepatitis, Staph infections, MRSA, and others.
