Pharmacology delves into understanding the intricate relationship between drugs and the human body's response to them. Whether you're aiming to become a doctor, nurse, or pharmacist, pharmacology will likely be a pivotal aspect of your studies. While pharmacology poses challenges due to the vast array of drugs to cover, there exist numerous proven study techniques to help you excel. Stay organized, prioritize your topics, and engage with peers to conquer that daunting pharmacology exam.
Key Points to Remember
- Review your notes regularly after each lecture to gradually expand your understanding. Focus on one topic at a time to prevent overwhelm.
- Create flashcards containing drug names, categories, dosages, interactions, and side effects to enhance recall.
- Participate in group study sessions to streamline preparation. Collaborating with classmates enables mutual learning and reinforces understanding through teaching.
Study Approach
Effective Study Techniques for Pharmacology

Review your material after each lecture. Avoid cramming as it exhausts you and hampers exam performance. Instead, study regularly after lectures to gradually build knowledge and alleviate exam stress.
- Allocate study time equivalent to class hours to maintain pace and avoid last-minute cramming.

Focus on one topic per study session. Prevent confusion and maximize efficiency by dedicating each session to a specific drug class. Take breaks between sessions to recharge.
- Commit to studying one topic, such as Beta blockers, per session to maintain clarity.
- Utilize short breaks to refresh before the next session.

Create flashcards. Manage information overload by using flashcards for drug details. Regularly quiz yourself to reinforce learning.
- Consider purchasing pre-made flashcards for convenience.
- Carry flashcards for quick study during downtime, like while commuting.
Utilize visual aids like graphs or flowcharts. Enhance comprehension and organization by creating visual study guides.
- Design graphics depicting drug hierarchies for quick reference.
- Explore online resources for additional study aids, ensuring accuracy.

Utilize mnemonic devices. Mnemonics are helpful phrases or sayings used to memorize complex information, commonly employed by medical students for drug and anatomy memorization. Create your own mnemonic phrases tailored to aid your understanding.
- For instance, associate the drug Prazosin ending in “sin” with its classification as an Alpha blocker, where Alpha represents the opposite of sin.
- If creating your own mnemonics seems daunting, seek inspiration from online resources or classmates.
Enhancing Pharmacology Learning Through Collaboration

Form study groups. Collaborate with classmates to share study materials such as graphs and flashcards, reducing individual workload and fostering a sense of community during study sessions.
- Regularly convene study group meetings to engage in quizzing sessions and collaborative exam review.

Engage in peer teaching. Reinforce comprehension by teaching topics to peers, assessing your understanding and communication skills.
- While practicing with study group members is beneficial, teaching individuals outside your pharmacology program offers a fresh perspective and tests your ability to simplify complex concepts.

Seek guidance from professors. Leverage the expertise of your professors for study advice and strategies, recognizing their wealth of knowledge and experience in the field.
Strategizing Drug Categorization

Categorize drugs into broader classes. Begin your pharmacology study journey by organizing drugs into larger categories before delving into specifics. This approach helps prevent overwhelm and facilitates gradual learning.
- For instance, instead of tackling individual antibiotics, group them under the umbrella term “Antibiotics” and progressively refine your understanding.
- Explore comprehensive drug class lists at https://www.drugs.com/drug-classes.html.
Examine drug class interactions with the body. Understand the physiological effects of each drug class. Grasp general concepts such as mechanisms of action and therapeutic indications for each drug set.
- For example, antibiotics combat bacterial infections, not viral infections, highlighting a crucial distinction.
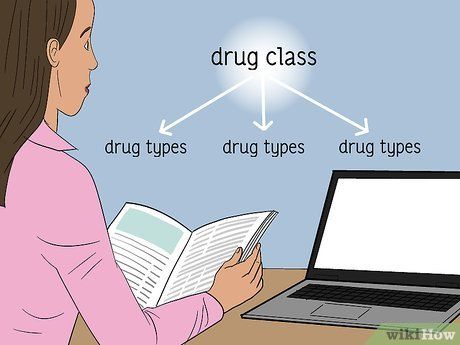
Progress to studying specific drug types. Once familiar with broad drug classes, focus on individual drug types within them. Identify nuances distinguishing each type to enhance comprehension.
- Within antibiotics, variations exist in efficacy against different infections and associated side effects, warranting focused study.
Emphasize unique side effects. Prioritize learning distinctive side effects over common ones shared among drugs. Focus on peculiarities to develop a comprehensive understanding.
- For instance, if insomnia is a unique side effect of a drug class amidst common side effects like nausea and diarrhea, prioritize memorizing this distinction.

Decipher drug suffixes. The suffix of a drug name often hints at its function or category. Understanding these suffix meanings can help identify a drug's purpose even without prior knowledge of it.
- For instance, drugs ending in “-pril” are ACE inhibitors, affecting the heart and kidneys, while those ending in “-olol” are Beta blockers, impacting the heart, lungs, GI tract, and kidneys.
- Find a comprehensive list of drug suffixes on the US National Library of Medicine portal: https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/jsp/drugportal/DrugNameGenericStems.jsp.

Utilize a spreadsheet for organization. Given the vast amount of information, maintaining organization is crucial. Create a spreadsheet to compile all drug-related details, ensuring easy access during study sessions.
- Include drug class, interactions, side effects, dosage, etc., in your spreadsheet.
- Refer to this spreadsheet as your central resource while creating study materials like flashcards and guides.
