Proper sex education is crucial for promoting mental and physical well-being. Teaching this subject can pose challenges, particularly if you're unsure where to begin or what to cover. Fortunately, there are numerous approaches for educating young children, adolescents, and even adults.
Key Steps
Understanding Sex Education Curricula

Familiarize yourself with local sex education regulations. Each school, state, province, or country will have its own guidelines for teaching sex education. Typically, professional educators must adhere to specific curricula. For instance:
- In the United States, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services identifies 28 evidence-based curricula for use. Schools or programs often provide materials from these curricula.
- The Public Health Agency of Canada offers guidelines for sexual health education, covering topics such as health, sexuality, and sexual rights.
- In the United Kingdom, sex education is mandatory for those aged 11 and above, focusing on reproduction, sexuality, and sexual health. It forms part of the national curriculum under the Personal, Social, and Health Education (PSHE) framework. Detailed guidelines are available on the UK government website.

Evaluate Feasibility of Sex Education Delivery Ensuring the possibility of teaching sex education varies based on cultural, religious, and educational contexts. In areas where it's not mandatory, challenges may arise. Before initiating:
- Consult local authorities for support.
- Compile evidence supporting the necessity of sex education.
- Engage with advocacy groups.
- Design a tailored curriculum if resources are limited, involving extensive research and professional collaboration.

Explore Diverse Sex Education Approaches In North America, comprehensive sexual health education dominates, covering a wide range of topics like contraception, gender, and STIs. Other approaches include family life education, population education, medical/disease education, fear-based strategies, abstinence-based education, and sexuality education.

Develop Customized Curriculum While some sex education programs offer structured lesson plans, others require educators to create their own. It's advisable to adhere to established and tested curricula tailored to your setting, leveraging insights and strategies from experienced educators and considering the needs of diverse groups.
Preparing for Sex Education Instruction

Equip Yourself with Knowledge on Sex and Sexual Health To effectively address learners' questions, it's crucial to have a deep understanding of the subject matter. Resources from libraries, bookstores, and online platforms, as well as courses from various organizations, can aid educators in enhancing their knowledge. Key points include understanding beyond sexual behaviors, debunking myths, and fostering comfort in discussing sensitive topics.

Know Your Audience Tailoring sex education to learners' ages is vital. While some may hesitate to introduce such topics to young children, age-appropriate information can alleviate concerns. Understanding the developmental stages of learners facilitates providing suitable information and avoiding overstepping boundaries.

Define Teaching Goals Setting clear objectives guides the organization and delivery of lessons. Common goals include mitigating negative consequences of sexual behaviors, imparting decision-making skills, fostering self-confidence, promoting positive relationships, providing accurate information, and respecting individual beliefs.

Create a Safe Learning Environment for Discussing Sex Whether in a classroom, community center, or home setting, fostering a safe environment encourages open dialogue and inquiry. This environment should cultivate positivity, avoid judgment, discourage censorship, and promote honesty.

Prepare to Address Complex Topics like Gender and Sexuality Understanding the distinctions between gender, sex, and sexuality is crucial in supporting learners, particularly those with non-normative identities. Engage with LGBTQ+ organizations, advocate for inclusive policies, collaborate with experts, and ensure curriculum sensitivity to diverse beliefs and cultures.

Practice Conversing about Sexual Health If discussing sex education feels uncomfortable, practice with peers or friends to build confidence and refine teaching skills. This exercise aids in avoiding common pitfalls like criticism, discomfort, and condescension.

Engage Parents or Guardians in the Sex Education Process Maintaining parental involvement is essential, particularly for younger learners. Provide detailed information on the curriculum, allowing parents to opt out or offer feedback. Utilize resources such as sample letters and respect individual preferences.
Teaching Infants and Toddlers

Recognize the Importance of Early Sex Education While formal programs for infants may be scarce, caregivers play a vital role in laying the foundation for healthy sexual development. By fostering body awareness and promoting positive relationships, caregivers support infants in developing a healthy understanding of themselves and others.

Teach Children Proper Terminology for Body Parts Early introduction to correct anatomical terms for genitalia fosters body awareness and encourages proactive health habits. Utilize everyday routines like bath time to initiate discussions, promoting comfort and understanding.

Discuss Privacy Guidelines with Children Establishing boundaries around bodily autonomy and recognizing appropriate behavior ensures children's safety and well-being. Educate children about personal boundaries, recognizing good and bad touches, and understanding the difference between secrets.

Observe and Support Children's Gender Expression Acknowledging and supporting children's gender exploration fosters self-discovery and confidence. Address misconceptions, encourage individuality, and provide reassurance in the face of external judgment.

Introduce Reproduction Basics Addressing children's inquiries about reproduction with age-appropriate information promotes understanding and demystifies natural processes. Use clear and accurate language to explain concepts such as pregnancy and family creation.
Teaching Elementary-Aged Children
Explain Puberty to Children Inform children about the physical and emotional changes associated with puberty, fostering understanding and preparedness for the transition. Address topics such as physical growth, sexual feelings, and emotional changes, promoting comfort and awareness.
Address Exploratory Behaviors in Children Recognize and guide elementary-aged children as they navigate intimacy and emerging sexuality. Emphasize the importance of consent, educate on protection and STIs, and reinforce body autonomy to foster healthy relationships.

Support Children's Challenges during Puberty Acknowledge and address children's struggles with body image, sexuality, and gender identity during puberty. Provide resources and comfort to navigate issues such as sexual orientation, gender identity, masturbation, family dynamics, and body image.
Teaching Adolescents

Promote Understanding of Consent Educate adolescents on the significance of consent in sexual interactions to foster healthy relationships and prevent sexual violence. Emphasize the principles of voluntary and enthusiastic consent, mutual communication, and the importance of respecting boundaries.
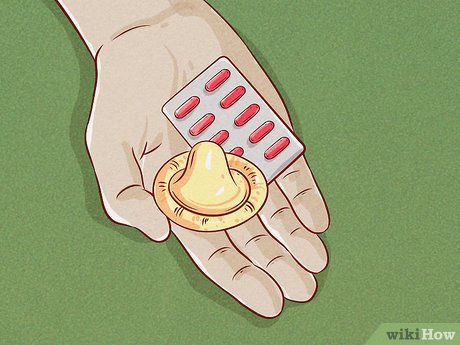
Educate Children on Protection and Contraceptives Provide children with comprehensive education on protection and contraceptives, including demonstrations and discussions on their benefits and effects to promote informed decision-making and sexual health awareness.
Utilizing Varied Teaching Approaches

Familiarize Yourself with Program-Specific Teaching Strategies Learn and apply teaching strategies tailored to your program, ensuring effective delivery of sex education content. Collaborate with educational institutions and organizations to enhance teaching methodologies.

Encourage Cooperative Learning Activities Foster cooperative learning environments through activities like inquiry-based, problem-based, and project-based learning. Engage students in collaborative investigations and problem-solving to deepen understanding and critical thinking skills.

Utilize Visual Aids and Media Enhance teaching effectiveness by integrating visuals and media into lessons. Utilize diagrams, videos, and demonstrations to illustrate concepts such as human anatomy, reproductive processes, and contraceptive use, promoting engagement and comprehension.

Promote Reflective Practice with Journal Writing Encourage students to engage in journal writing to reflect on their health learning experiences. Maintaining a health care journal enables individuals to monitor their health, track medications, and gain insights into their overall well-being.

Assess Student Learning After delivering lessons, employ various methods to assess student comprehension and engagement. Conduct comprehension checks, observe student behavior, and utilize rubrics to evaluate projects and assignments.
Effective Classroom Management

Set Ground Rules Establish clear ground rules before commencing lessons to foster a safe and respectful learning environment. Encourage active listening, mutual respect, and confidentiality among students.

Respect Student Privacy Communicate to students your commitment to respecting their privacy during discussions on sexual health. Refrain from sharing personal experiences unless it significantly contributes to the lesson and maintains learner comfort.

Promote Critical Thinking and Open-Mindedness Encourage critical thinking and open-mindedness among students by maintaining an unbiased stance, valuing their opinions, inviting discussions, and being flexible in addressing their queries.

Connect with Prior Knowledge Initiate lessons by inviting students to share their existing knowledge about sexual health topics. This approach fosters active participation and helps instructors tailor their teaching to address misconceptions effectively.

Offer Anonymous Questioning Cater to the needs of shy or uncomfortable learners by providing access to external resources, offering confidential guidance, and allowing anonymous submission of questions. This inclusive approach ensures all students can seek clarification without hesitation.
Managing Student Inquiries

Guide Questioning Reinforce the distinction between appropriate and inappropriate questions while encouraging a respectful learning environment. Empower students to seek clarification privately for unanswered queries, promoting a conducive classroom atmosphere.

Validate Students' Concerns Acknowledge students' questions or comments with affirmations, requests for clarification, or by addressing associated emotions. Normalize queries without labeling them as 'normal' to ensure an inclusive learning environment.

Respond Honestly to Questions Be transparent about your knowledge limitations while affirming students' inquiries. If uncomfortable, communicate this sentiment respectfully to maintain a conducive learning atmosphere.

Handle Personal Behavior Questions Establish clear boundaries regarding discussions on personal behaviors, redirecting students to appropriate resources or addressing inquiries privately to ensure sensitivity to diverse beliefs and values.

Address Shocking Questions Reframe provocative questions with professionalism, emphasizing respectful dialogue and guiding discussions toward educational outcomes. Address underlying concerns to foster constructive engagement in the classroom.
Teaching in Traditional Communities

Adhere to Community Policies Respect and adhere to community policies while delivering sex education, seeking guidance from leaders and organizations within the community to ensure effective communication and management of potential controversies.

Address Opposition to Sex Education Approach individuals opposing sex education with understanding and information, addressing concerns about program implementation, distress, misconceptions about its effects, and conflicts with moral or cultural beliefs with patience and clarification.
Useful Tips
- Engage Parents and Community
- Avoid Inappropriate Content
- Promote Natural Discussions
