Losing a pet can be a frightening experience, but microchips offer a solution to locating them quickly. While microchips don't enable real-time tracking, they significantly increase the chances of reuniting lost pets with their owners, making them a worthwhile investment. Microchips facilitate identification for those who find your pet, but it's crucial to maintain up-to-date contact information in the registry. Additionally, you might consider employing a GPS tracker for pinpointing your pet's exact whereabouts.
Steps to Follow
Utilizing a Pet's Microchip for Locating a Lost Animal
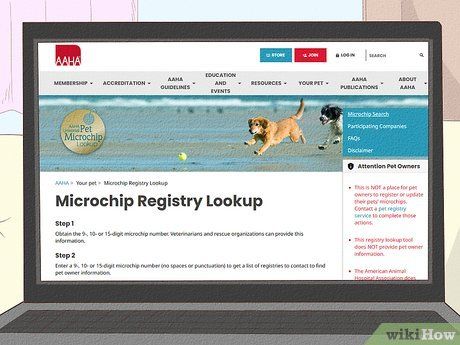
Register the pet’s microchip number in the chip registry. Ensure that your pet's microchip is registered in a reputable registry. While the manufacturer typically offers its registry, you can also opt for a universal registry. Options include platforms like https://www.aaha.org/petmicrochiplookup. If you've misplaced the number, contacting the veterinarian or clinic where the chip was installed may provide assistance in retrieving it.

Be patient for a notification once your pet's microchip is scanned. Waiting for updates on your lost pet can be challenging, but scanning the microchip is essential for the reunion process. Veterinary clinics or shelters typically scan lost pets to check for microchips. Once scanned, they can access your contact details and inform you about your missing pet.

Inquire with the shelter about your rescue pet's microchip status before adoption. Even if you didn't personally implant a microchip in your pet, it might already have one. Many shelters routinely chip pets prior to adoption. If your rescue pet goes missing, contact the shelter to confirm if this applies to your pet. If so, they can be contacted if your pet is found. Remember to inform the shelter of your desire to reclaim your pet and regularly follow up with them.

Gain insight into the functionality of microchips. Microchips are embedded under a pet's skin to facilitate easy identification if it gets lost. A veterinarian or shelter can scan the chip to retrieve the pet's ID number, which links to the owner's contact information. Some registries even allow entry of the pet's medical history. It's worth noting that not all scanners and chips are compatible, although universal scanners are increasingly common. Also, microchips do not function as GPS trackers, which offer real-time pet location tracking. GPS trackers are separate devices that can be attached to a pet's collar.

Allie Bender, Certified Dog Trainer
A microchip is a crucial tool for reuniting lost pets with their families. Implanted beneath the skin, it contains a unique ID number. When scanned by animal shelters or veterinarians, the chip's associated registry is contacted, providing registration information. Pet owners must ensure their contact details are up to date with the registry.
Implanting a Microchip and Enrolling Your Pet

Discuss microchip insertion with your veterinarian. Microchips can be easily inserted during a routine vet visit using a needle. Anesthesia isn't necessary, but insertion can also occur during procedures like spaying or neutering. Your vet can advise if a microchip is suitable for your pet's needs.

Have the microchip implanted by a veterinarian between your pet's shoulder blades. Professional insertion is crucial to avoid complications. The chip must be placed correctly and at the right depth for scanner detection. It's typically the size of a grain of rice.

Obtain an activation ID to register the microchip. Your vet should provide an activation code for registration, along with a contact number. Ensure you receive these before leaving the vet's office. If forgotten, contact the vet for the details.
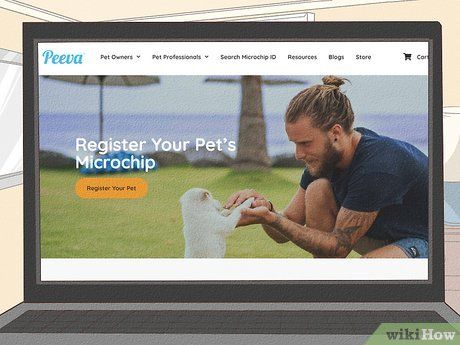
Complete registration of your pet's microchip with the appropriate registry. Registration is vital for the microchip's effectiveness. Provide the microchip number, your details, and your pet's information including breed, age, color, and gender. Some companies offer toll-free numbers for registration, while others allow online registration. Certain registries may also accept health information such as vaccinations and surgeries.
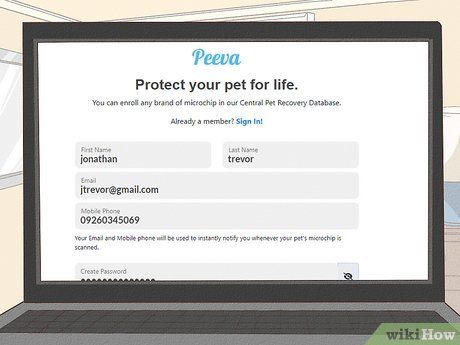
Maintain up-to-date contact details on the registry. Regularly update your contact information to ensure the microchip's efficacy. Contact the manufacturer's registration number to update details, providing the microchip ID and necessary information. Updates are necessary for changes in contact information or pet ownership. Some manufacturers offer online information updates.
Utilizing an External GPS Tracking Kit

Determine if a GPS tracking kit suits your pet's needs. Combining a GPS tracker with a microchip offers comprehensive tracking capabilities. GPS trackers provide real-time location data via an app, ensuring you can locate your pet wherever it ventures. However, subscription fees for GPS tracking services can make these devices costly. Some models include a handheld tracker for convenience, while others offer additional features like temperature monitoring and activity tracking.

Choose a GPS tracking device suitable for your pet's species. Select a GPS tracker designed for either cats or dogs, considering size and weight differences. Larger dogs may require models tailored for their size, while smaller pets benefit from lightweight options.

Secure the GPS tracker to your pet's collar or opt for an integrated collar. Ensure your pet wears the GPS tracker at all times. Some devices come with pre-attached collars, while others can be attached to existing collars. For cats, use cat-safe collars to prevent accidents, and consider breakaway collars for added safety.
Track your pet's whereabouts. Once the GPS tracker is in place, easily monitor your pet's location. Some trackers also offer historical location data, allowing you to track your pet's movements over time. Remember to replace the battery when it runs low.

Understand the limitations of GPS trackers. GPS trackers have certain constraints, including susceptibility to removal in accidents or thefts. They rely on batteries and require regular replacement. Moreover, they function only in areas with adequate GPS coverage. Some pets may find wearing GPS trackers uncomfortable or may attempt to remove them, leading some owners to opt for both a microchip and a GPS tracker.
Advice
- Microchips typically have a lifespan of up to 25 years, ensuring longevity for your pet's identification.
- Request your vet to scan the chip during pet visits to verify its functionality.
- GPS tracking kits may be less effective for indoor pets.
Cautions
- Ensure your pet wears identification tags at all times, even with a microchip, as they can sometimes migrate out of the body.
- In rare instances, injection sites may exhibit side effects like oozing or swelling. Seek immediate veterinary attention if observed.
