The survival strategies of creatures in nature are peculiar and diverse, and the animal kingdom is full of mysteries. An elephant can endure a broken leg, prompting questions about why a horse, too, succumbs to death with a similar injury.
Self-recovery capabilities and adaptive mechanisms in an elephant with a broken leg
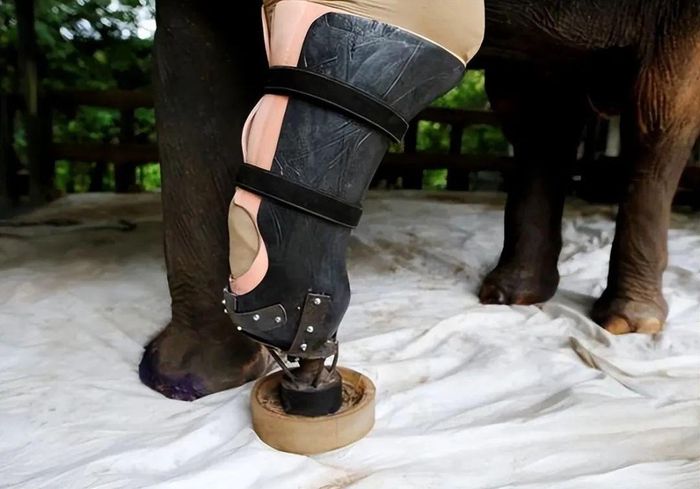
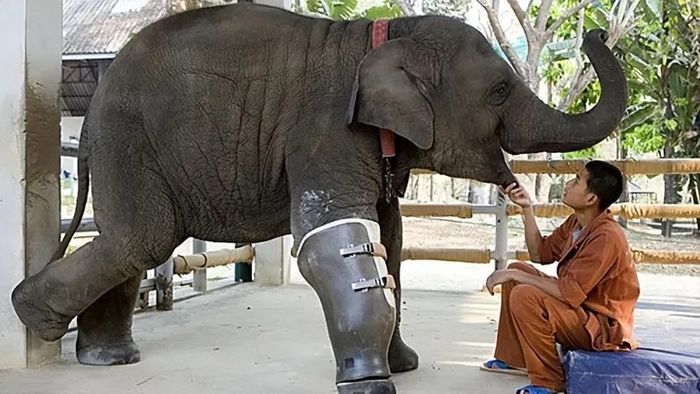
Being one of the largest land animals, elephants possess astonishing self-recovery capabilities and adaptive mechanisms, especially in cases of leg injuries or amputations.
The bone structure of an elephant serves as the foundation for its wound healing abilities. Elephant bones are sturdy and intricately designed, allowing them to better support their weight and reduce the burden on joints and other bones during severe injuries like a broken leg. Additionally, elephant bones are rich in calcium and minerals, accelerating the healing process of fractures.
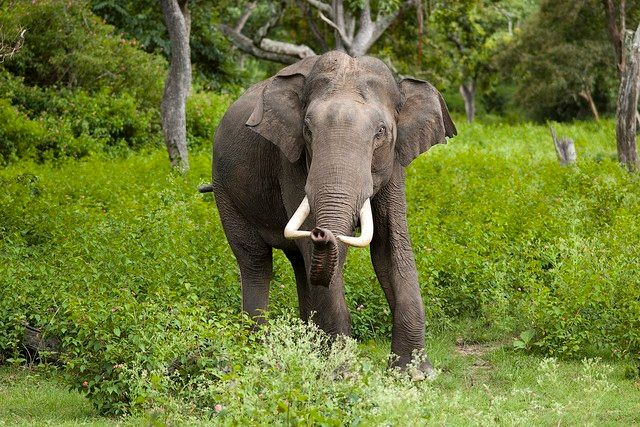

The muscular system of elephants also plays a crucial role. Elephants have thick and healthy muscles that provide enough strength to maintain balance and stability. When an elephant suffers a broken leg, the remaining three legs collectively bear the entire weight through flexible muscle movements, reducing pressure on the injured leg. Moreover, the elastic and resilient nature of elephant muscle tissue aids in a smooth recovery process.
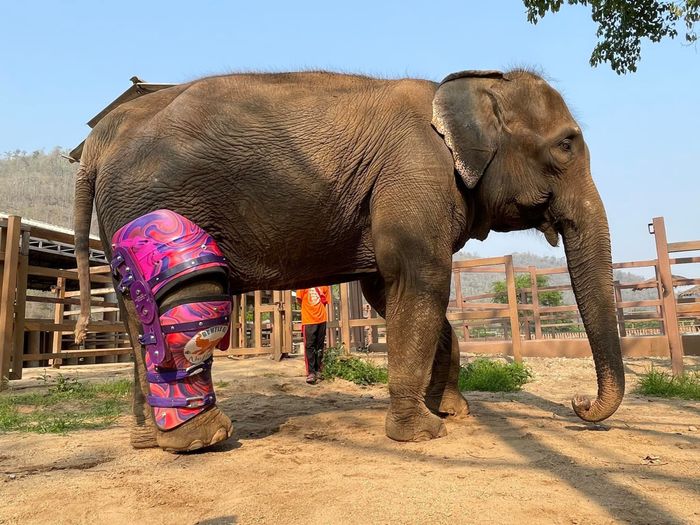



Horses, being herbivores, often need to run for extended periods to find food or escape predators. However, when a horse suffers a leg injury, it hampers their ability to run normally. The body's weight shifts to the remaining legs, causing additional pain and pressure. In such cases, the horse's body struggles to recover, leading to prolonged healing times.

Treating a leg fracture in horses typically demands significant resources, including finances, manpower, and medications. For farmers or regular individuals, investing such substantial resources in treating a horse with a broken leg is undoubtedly a hefty financial burden.
Currently, the technology for treating a horse with a broken leg is relatively limited, requiring a team of professional veterinarians for diagnosis and surgery. However, such specialized teams are not always readily available, especially in remote areas. Expensive advanced equipment and medications further restrict the effectiveness of treating leg fractures in horses.

Apart from the mentioned challenges, healing a fractured horse leg is complicated due to the constraint of time. Typically, treating a horse's broken leg should happen as quickly as possible to enhance recovery chances. However, external factors such as distance and economic constraints often lead to delays in treating a horse with a broken leg. This increases the risk of wound infections, prolonged recovery times, and difficult wound healing.
The difficulty in treating leg fractures in horses stems from a combination of factors such as the unique bone structure of horses, limited mobility, constrained resources, and time limitations.
Reference: Zhihu
