While the PRODUCT() function helps you multiply values, the DPRODUCT() function helps you multiply values based on specified conditions.

This article describes the syntax and usage of the DPRODUCT() function in Excel.
Description
DPRODUCT() returns the result as the value of multiplying values in a column of a list or a database based on a specified condition.
Syntax
=DPRODUCT(database,field,criteria)
Where:
- database: is a series of cells forming a list or database containing the data to be processed by the DPRODUCT() function, including field names (Column Headers).
- field: the data field (column) used in the function. You can write it in text form with column names enclosed in double quotes (e.g., 'Age', 'Salary'), the field can also be a number representing the column position (like 1 for the first column, 2 for the second column...) or you can directly enter the cell name containing the column header (A1, A5...).
- criteria: is the range of cells containing the conditions. You can use any range for criteria but it must contain at least one Column Header and one cell below containing the condition.
Note
- It's recommended to place the criteria range on a worksheet so that when adding data, the range containing the criteria doesn't change.
- The criteria range should be separate and not inserted into the list or database to be processed.
- Criteria must include at least one Column Header and one cell containing the condition beneath the column header.
Example
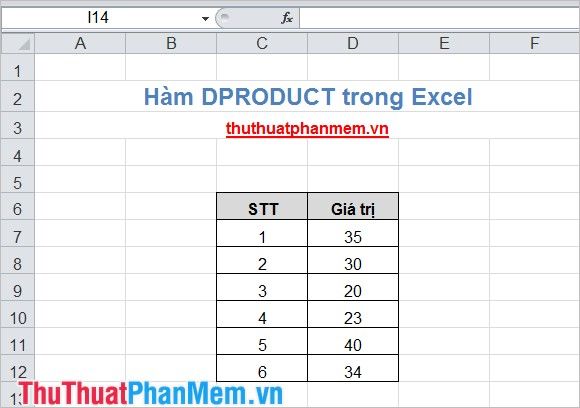
Calculate the product of numbers in the Value column with ID <=4.
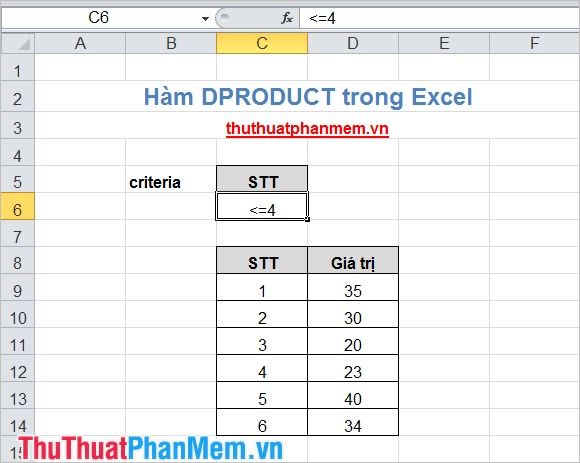
Create criteria:
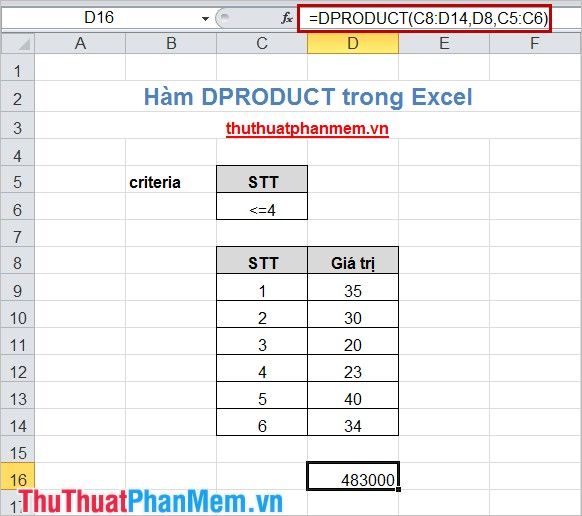
Apply the DPRODUCT() function: =DPRODUCT(C8:D14,D8,C5:C6)
C8:D14 represents the database table containing column headers as well.
D8 represents the column header name for calculation.
C5:C6 indicates the criteria range.
The result will be as follows:
Above, the article introduced the syntax and specific examples of using the DPRODUCT() function in Excel. Depending on the requirements of each problem, apply the function accordingly. Wishing you success!
