Heat dissipation plays a crucial role, designed for use in induction cooktops, electric stoves, and other electronic devices. Join us at Siêu Thị Mytour as we dive into the heat dissipation components of induction and electric stoves!

Exploring Heat Dissipation in Induction and Electric Stoves
Cooling systems in induction and electric stoves operate as follows:
Initially, operational components generate hot air, which is compressed by the cooling fins to convert electronic component heat into ambient air temperature.
Then, this hot air is expelled outside through the stove's vent slits by a fan, ensuring stable temperatures and preventing overheating.
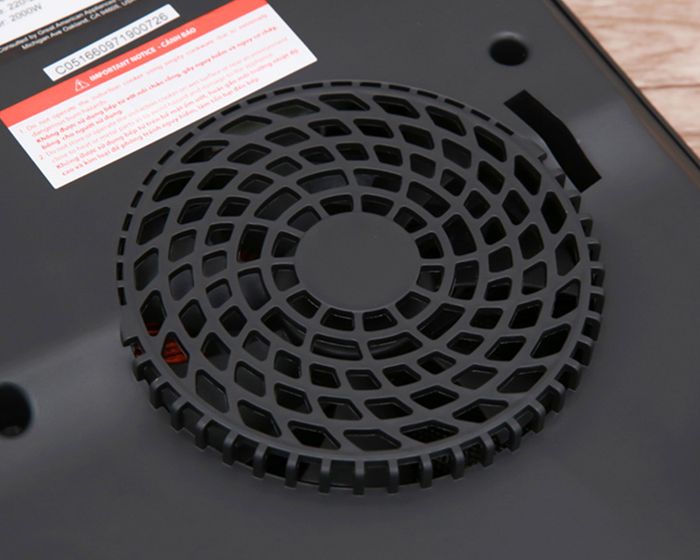

The mechanism of the cooling system's operation
Simultaneously, external air is drawn in by a fan, undergoing compression as it moves through the radiator, effectively drawing heat from components to cool them down.
This cycle repeats continuously while the stove is in operation and for a few minutes after it is turned off, ensuring the internal components do not overheat, maintaining stability and durability of the stove.
The cooling system for an induction stove consists of a cooling fan, radiator bars, and ventilation slots around the stove, working together to keep the internal components efficiently cooled.
2.1. Cooling Fan
The cooling fan is a key component in both induction and electric stove cooling systems. It circulates air to cool down components and the stove surface, ensuring optimal temperature management.
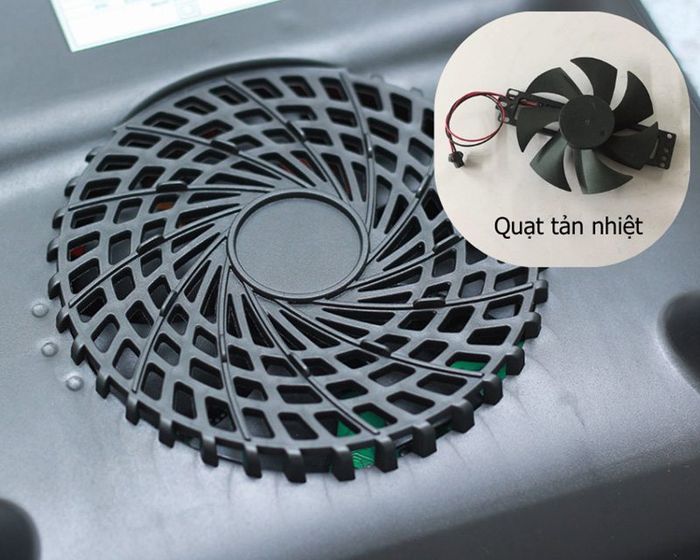
Cooling Fan
Placed strategically beneath the cooking surface, the cooling fan draws ambient air and pushes it underneath, creating a cooling airflow for electronic components and the cooking area.
2.2. Heat Sink
A heat sink is a component of the cooling system, designed to dissipate heat and cool electronic components. Typically made of metal like aluminum or copper, it features a large surface area to enhance air contact and heat transfer efficiency.
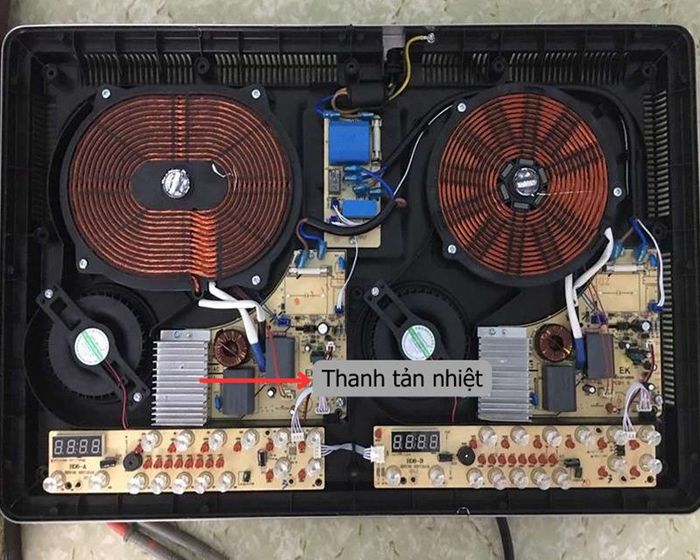

Heat Sink
The primary function of a heat sink is to transfer heat from electronic components to a broader surface, allowing for efficient and easy dispersion of heat through air. This process helps maintain stable temperatures and prevents overheating damage to electronic components.
2.3. Cooling Vents
Cooling vents, also known as ventilation slots, ensure ventilation and cool down electronic components in devices to extend their lifespan. These vents are typically positioned around the body of the stove, facilitating air circulation and heat dissipation during component operation to minimize temperature and prevent overheating.
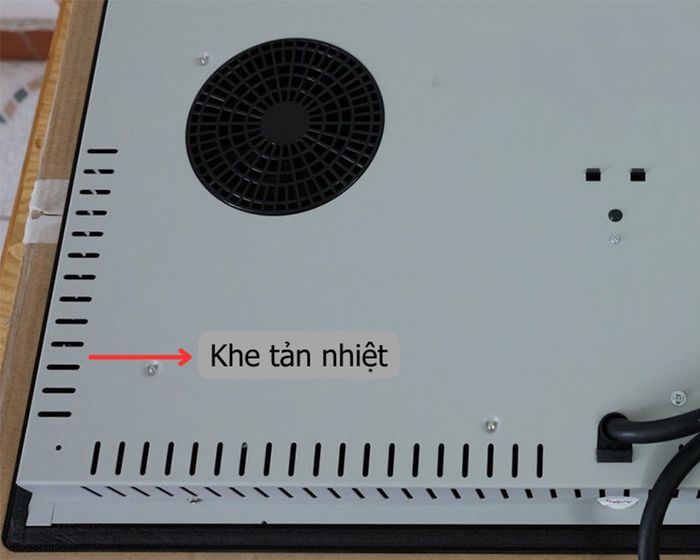

Cooling Vents
3. The Role of Induction Cooktop Cooling Systems
The cooling system in induction cooktops plays a critical role in maintaining the electronic components' temperature, ensuring stability and efficiency.
Cooling Down: By cooling the surface and internal electronic components, the system prevents overheating that could lead to damage or fire hazards.
Electronic Component Protection: Cooling extends beyond surface protection, safeguarding internal electronic parts from heat-induced damage.
Lifespan Extension for Induction Cooktops: Preventing overload and component damage, the cooling system increases the appliance's longevity, saving on replacement and repair costs.

The cooling system plays a pivotal role in induction cooktops
Energy Efficiency: Effective cooling ensures optimal performance of induction cooktops, leading to energy savings.
Prevention of Fires and Explosions: Overheated components within induction cooktops can cause fires or explosions. The cooling system helps mitigate these risks, ensuring user safety.
User Safety: The cooling system also lowers the surface temperature of the cooktop after cooking, preventing burns from accidental contact.
Discover insights on the essential cooling components in induction and electric stoves, aiming to enhance your usage experience for efficiency and smooth operation.
