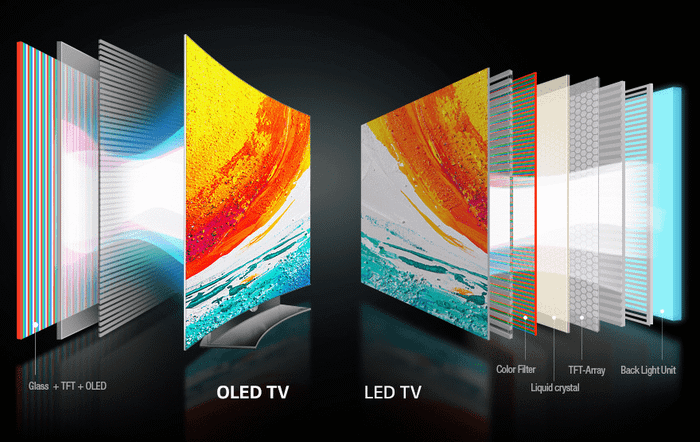
This marks the beginning of a series exploring TVs, one of our most familiar electronic devices. When it comes to TVs, our immediate association is often with their types: LCD/LED and OLED. The nomenclature essentially originates from the panel technology they use, which is the topic I want to share with you.
1. [Exploring TVs] Common Panel Technologies
This marks the beginning of a series exploring TV, one of our most familiar electronic devices. When it comes to TVs, our immediate association is often with their types: LCD/LED and OLED. The nomenclature essentially originates from the panel technology they use, which is the topic I want to share with you.
Liquid Crystal Display Panel ( LCD)
The most commonly used panel type on TVs (and arguably on all current consumer electronics) is the Liquid Crystal Display, abbreviated as LCD. Due to its affordability and excellent image quality, it has virtually dominated the TV market in recent years, surpassing Plasma and CRT.
Basic Operating Principle
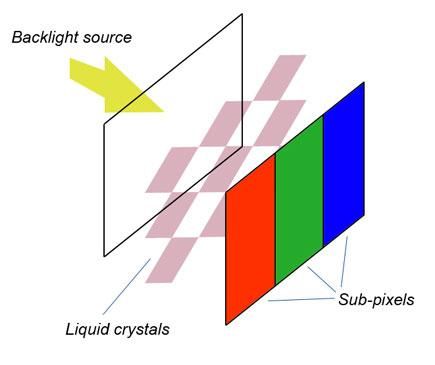


Quantum dot technology is a groundbreaking innovation related to backlighting.
In 2013, Sony introduced the Triluminos technology using quantum dot-shaped tubes around green LED backlights. However, by 2014, the Japanese electronics company discontinued the use of quantum dot technology while retaining the Triluminos brand to signify the color performance of high-end Sony Bravia TVs. In 2016, Sony claimed that Triluminos technology delivers image quality equivalent to quantum dots, leaving uncertainty about whether Sony utilizes quantum dots in their TVs. Meanwhile, since 2016, Samsung and LG TVs (SUHD and Super UHD) have been incorporating thin film quantum dot layers in their displays.
LCD panel types
When examining the liquid crystal display panel of a TV, it can be categorized into three types: IPS, VA, and TN. However, due to the requirements for high color reproduction, wide viewing angles, and relatively less emphasis on response time, TVs typically use IPS and VA.

LG TVs utilize IPS LCD panels
IPS and VA refer to the arrangement of liquid crystals. IPS is known for wider viewing angles, while VA is recognized for superior black performance but narrower viewing angles. In reality, from the mid-range segment (Sony Android TV 4K, Samsung series 6, LG UHD and above), supporting technologies make the performance of TVs virtually indistinguishable, whether they use IPS or VA technology. Currently, Sony and Samsung, popular TV brands in Vietnam, employ VA panels for their TV series, whereas IPS panels are used in LG, Panasonic, and Sharp TVs.
OLED Display Panel
Commercialized by LG in 2014, OLED display panel is a new technology that combines the advantages of both LCD and Plasma. At the time of this article, OLED appears only in high-end TV models with prices comparable to or higher than even the most premium LCD TVs. However, compared to the initial generations, the price of OLED TVs is gradually decreasing.
Operating Principle
Essentially, current OLED TVs are a variation of OLED called WRGB. It combines the operational method of LCD TVs and the characteristics of organic diodes, allowing LG to reduce the cost of OLED TVs while maintaining the characteristics of OLED technology. This is also the only commercially viable OLED technology in TVs.
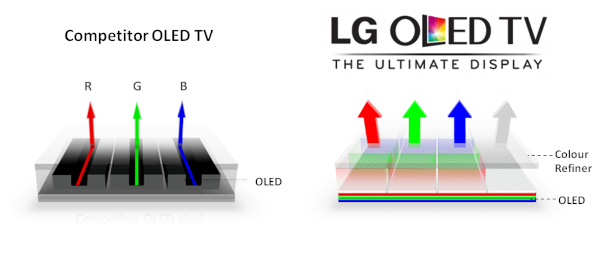
The most crucial factor that enables OLED to have better image quality than LCD is that when displaying black, its pixels completely turn off, achieving the deepest black. In principle, the liquid crystals on an LCD panel will block all light to display black. However, in reality, no liquid crystal panel can achieve this, and a small amount of light always passes through, preventing black from being as deep as expected. Therefore, OLED TVs always have much deeper black than LCD TVs, leading to higher contrast (the difference between the brightest and darkest points).
Comparison Between OLED and LCD Technologies in TVs
Since surpassing CRT TVs for the first time in 2007, LCD technology has dominated the TV market until now. Continuously improving, LCD technology, however, is reaching its limits. That's why companies are racing to find new display technologies to replace it. The emerging display technology is OLED. It's important to note that OLED TVs have only been commercialized for about 3 years, and there is still much room for improvement.

Advantages of LCD Technology
- Affordable
- Higher maximum brightness
- Diverse designs
Currently, LCD TVs are still the most popular type on the market. There is a wide range of models suitable for users from ordinary to high-end, except for the most demanding. A highlight of today's high-end LCD TVs is their very high maximum brightness, reaching up to 1000 nits in the 2016 top models (as announced by the manufacturer and UHD Premium certified). Combined with quantum dot technology, the color reproduction capability of LED TVs is also competitive with OLED. However, due to lower contrast, the overall image quality of LED TVs is still inferior to OLED TVs.

Advantages of OLED Technology (LG WRGB)
- Absolute black color representation
- Highest image quality
- Allows for ultra-thin TV designs
- Energy-efficient (depending on the case)
OLED TVs have only been commercially available for about 3 years, and there is still much room for improvement. OLED TVs typically have lower brightness than LCDs, except for the ultra-premium G6 series, which claims to reach 1000 nits like LCDs. Therefore, the superiority in image quality is sometimes evident only in certain cases. Depending on the displayed content, the power consumption of OLED TVs also varies, possibly higher or lower than LCD TVs. However, it's undeniable that the image quality of OLED TVs is higher than that of LCD TVs, which is crucial for high-end users. Given the current prices, it's easy to see that OLED TVs are targeting high-end users who want to own a TV with the best image quality and the most impressive design. Can the average user experience OLED TVs? With the current pace of technological development, the answer is yes; the only question is how soon.
