Dealing with water or fluid in the ears can be bothersome, but solutions exist to address this issue. Although fluid typically drains naturally, you can expedite the process using simple techniques. Clear the fluid by performing easy maneuvers that you can do independently. Alternatively, dry the fluid using ear drops or a hairdryer. However, if you suspect an infection, seek medical treatment from a doctor.
Steps
Drying Up Ear Fluid
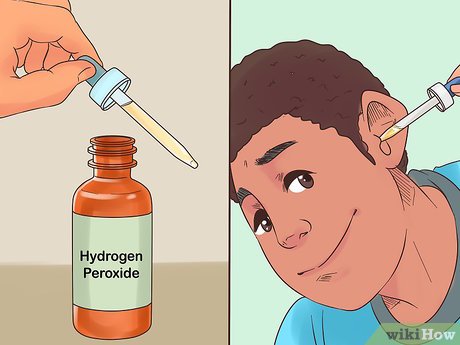
Pro Tip: Using hydrogen peroxide can aid in evaporation of fluids while also cleaning out any ear wax that might be trapping the fluids.
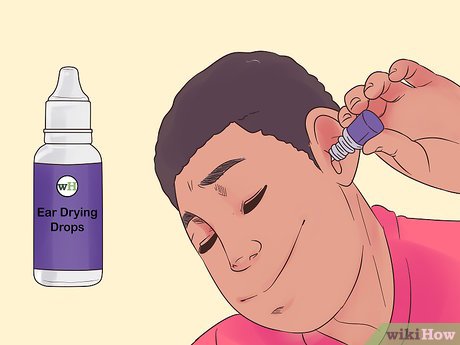
How to Apply Ear Drops
Adjust to room temperature: Ear drops that are too hot or cold can cause dizziness. Place your ear drops in your pocket for 30 minutes and move around to reach the proper temperature.
Review the instructions: Always read the package instructions, including any potential side effects.
Check the expiry date: Do not use expired drops.
Seek assistance: Applying ear drops on your own can be challenging, so ask for help.
For adults and teenagers: Lie down with your affected ear facing up on a towel. Have someone gently pull your earlobe up and outward, then administer the correct number of drops into the ear canal. Press on the ear flap to distribute the liquid, and wait for 1-2 minutes.
For children: Have the child lie down with their affected ear facing up on a towel. Gently pull their earlobe out and downward to straighten the auditory tube, then apply the appropriate number of drops. Press on the ear's flap and wait for 2-3 minutes.
If both ears have fluid: Wait about five minutes or plug one ear with a cotton ball before treating the second ear.
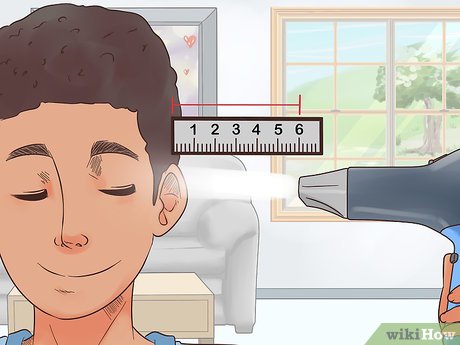


Dislodging Fluid
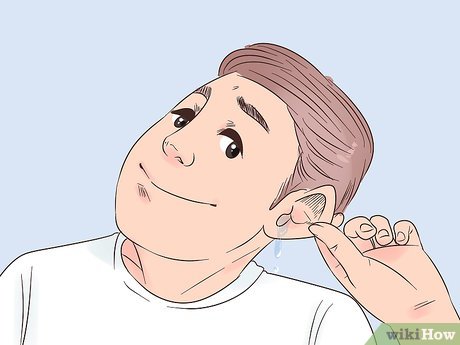
- This method is effective for removing water post-swimming or showering.


- Avoid this maneuver if you suspect an ear infection.
- Blow gently; excessive force may result in a nosebleed.



- You can also try sucking on hard candy for a similar effect.
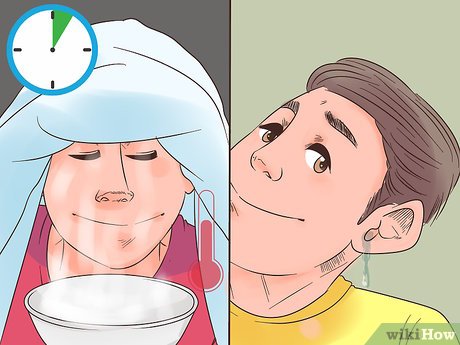
Home Steam Treatment
Fill a bowl with steaming hot water. Optionally, add a few drops of anti-inflammatory oils like chamomile or tea tree. Cover your head with a towel and lean over the bowl, inhaling the steam for 5-10 minutes. Afterward, tilt your affected ear to let the fluid drain into the bowl.
Caution: Always be cautious with steam as it can be very hot. Test the temperature by placing your hand over the steam before exposing your face to it.
Managing Medical Issues

Decongestants: Not Suitable for Everyone
Unfortunately, decongestants may not be safe for certain individuals. If you or someone you know falls into these categories and requires a decongestant, consult a doctor first.
Pregnant and nursing women: While many decongestants pose no known risks for short-term use during pregnancy or breastfeeding, not all are equally safe. Seek advice from your doctor regarding the most suitable decongestant for you.
Individuals on other medications: There's a possibility of adverse interactions between decongestants and other medications.
Diabetics: Decongestants can lead to elevated blood sugar levels.
Individuals with high blood pressure: Decongestants work by constricting blood vessels to reduce nasal swelling, but this can impact other blood vessels and cause a rise in blood pressure. Consider using a cold medication specifically designed for those with high blood pressure.
Individuals with hypo- or hyperthyroidism: Pseudoephedrine, found in many decongestants, can exacerbate symptoms of both hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
Individuals with glaucoma: While decongestants generally have minimal effects on open-angle glaucoma (more common), caution is advised for individuals with closed-angle glaucoma as decongestants can lead to pupil dilation and angle closure.
- This pill reduces inflammation in your Eustachian Tubes, allowing fluid to drain naturally.

- The screening involves a visual examination of your ear, blood tests, and if a growth is suspected, a tissue sample may be taken for testing after administering a local anesthetic. MRI scans might also be used.
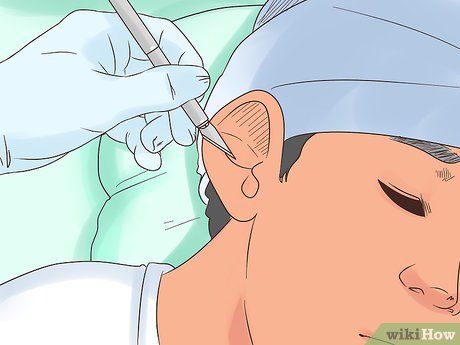
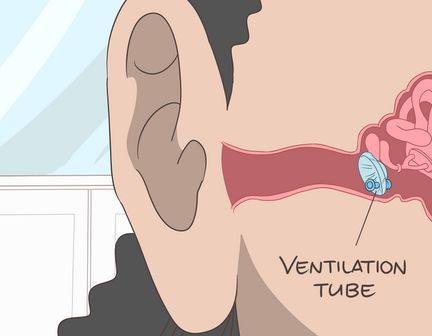
- Children may require ear tubes for 4 to 6 months, while adults may need them for 4-6 weeks only.
- The initial surgery is performed under anesthesia at a hospital as an outpatient procedure. Tubes often fall out naturally or can be removed without anesthesia during a doctor's visit.
Expert Advice: Clearing Sinuses


Useful Tips
-
Usually, fluid will naturally drain from your ears. If it persists beyond 3-4 days, consult a doctor as stagnant fluid can lead to ear infections.
-
If you suspect your child or infant has ear fluid, seek medical attention for proper treatment.
- Try hopping on one foot with the affected ear facing downward. When you hear a popping sound, it indicates success.
- Avoid completely cleaning ear wax as it plays a vital role in preventing infections.
- After swimming, tilt your head and wait for a minute or two.
Cautions
- Inserting cotton swabs or other objects into your ears can harm the eardrum and potentially lead to hearing loss.
