Ear reflexology, though less familiar than foot or hand reflexology, offers relief from stress and pain. It involves massaging specific pressure points on the ear to alleviate discomfort throughout the body. Note that while reflexology can help, it's not a substitute for medical treatment, especially for chronic conditions. Always consult a doctor if needed.
Steps to Follow
Initiating the Reflexology Procedure
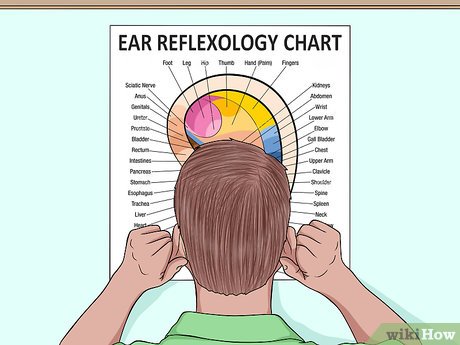
Refer to a reflexology chart if available. Having a reflexology chart handy can be beneficial as it allows you to quickly locate pressure points on the ears. If you forget any points, simply consult the chart. If you don't have a chart, you can easily print one from the internet. Keep in mind that these pressure points are consistent across individuals.

Find a comfortable spot. Choose a quiet room where you can relax without any interruptions. Pick a cozy chair or couch, and sit comfortably upright to begin ear reflexology.
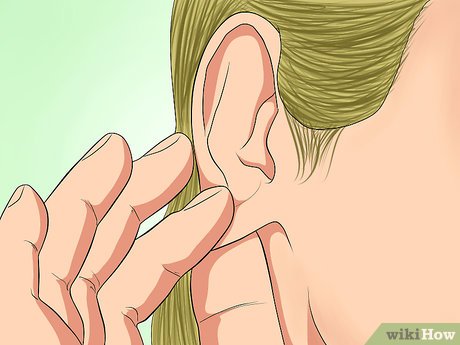
Prepare your ears for touch. Begin with your earlobes, gently pinching them between your thumb and index finger. Gently pull them downward while applying slight pressure. If you experience any discomfort, stop pulling immediately.

Check for sensitive spots. Before starting reflexology, ensure there are no tender areas on your ears. Run your fingers along your ears, noting any soreness, sensitivity, or injuries. Avoid massaging these areas during reflexology sessions as it should alleviate, not exacerbate, any pain or discomfort.
Applying Pressure to the Points
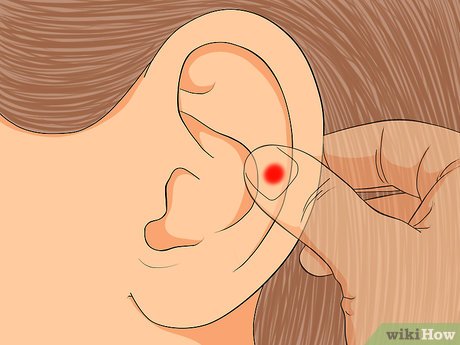
Target your upper body. If you're experiencing discomfort in your back and shoulders, focus on massaging the pressure points on the top of your ears near the tips. Massage these areas to help alleviate back and shoulder tension. Depending on the severity of your discomfort, you can massage for a few minutes to half an hour, giving extra attention to these points for more significant relief.
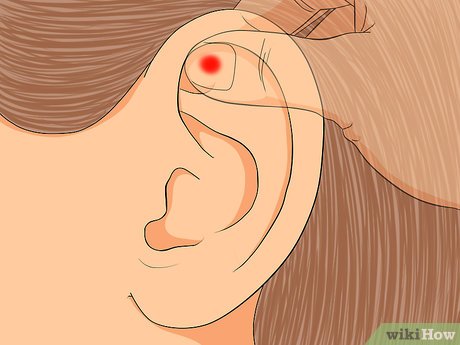
Manage joint pain. To alleviate joint pain, target the upper middle part of the ear with gentle massage. Apply pressure to this area for a few minutes daily to potentially ease discomfort.
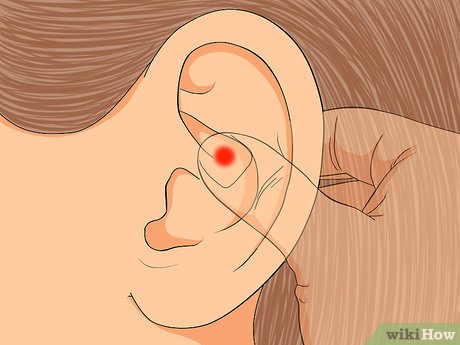
Address organ pain. While severe internal pain requires medical attention, reflexology may provide relief. Massage the area where the bridge of your ear meets the outer ear to help alleviate organ pain.
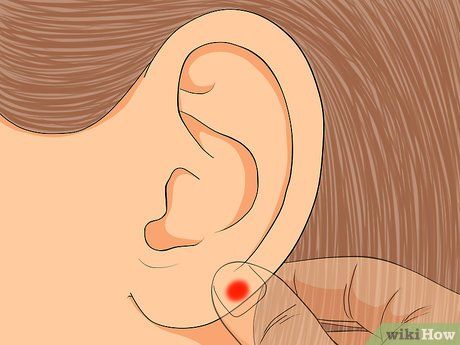
Relieve sinus and throat issues. Target the lower-inner portion of the ear to ease sinus and throat problems. Apply gentle pressure to this area to potentially facilitate clearer sinuses and easier breathing.
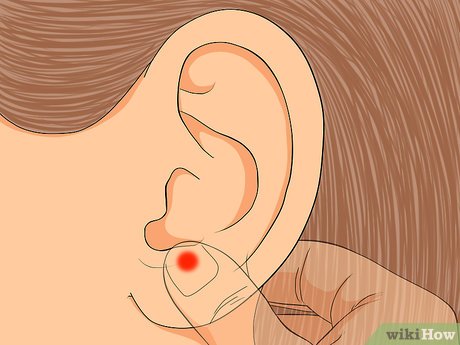
Alleviate digestive discomfort. Apply pressure just above the earlobe to aid digestion. Spend a few minutes massaging this area as digestive issues arise for optimal results.
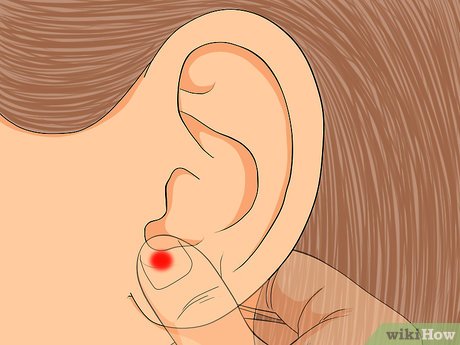
Focus on head and heart health. Massage the earlobes to potentially alleviate pressure headaches associated with the head and heart. For severe headaches or chest pains, seek medical attention.
Safety Measures
Avoid reflexology with certain health conditions. Reflexology may not be suitable for everyone. If you have conditions like deep vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, cellulite on your feet or hands, an infection, a high temperature, a high-risk pregnancy, or have had a stroke within the last two weeks, refrain from reflexology.
Consult a doctor for persistent symptoms. While reflexology may help manage minor aches and pains for some individuals, it's not a substitute for medical treatment. Any persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Realize reflexology isn't a cure. Reflexology is not a cure for chronic conditions. Conditions like chronic sinus issues will persist despite reflexology treatment. Consider reflexology as a way to alleviate symptoms rather than cure underlying medical issues.
Useful Advice
Important Notes
- You can utilize a small, blunt tool designed for reflexology to apply pressure to the inner ear reflex points. However, ensure the object is not sharp and avoid inserting it into your ear canal.
Materials Needed
- Ear reflexology chart
- Blunt stick (optional)
