An art critique involves in-depth analysis and assessment of an artwork. While each person's reaction and interpretation may differ, there are key steps to follow for a thoughtful and comprehensive critique. The essential components of an art critique include description, analysis, interpretation, and evaluation.
Steps to Follow
Describing the Artwork
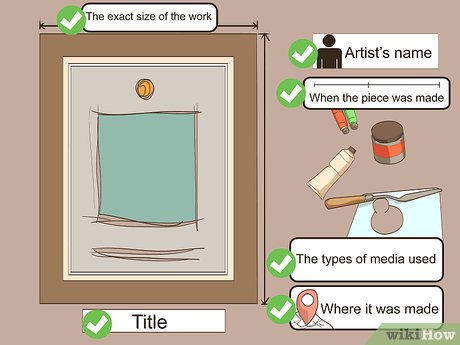
Obtain essential details about the artwork. This information is typically found in museum or gallery labels, or art book captions. Understanding the background of the piece significantly influences interpretation and comprehension. Begin your critique by providing the following details:
- Title of the artwork
- Name of the artist
- Date of creation
- Place of creation
- Medium used (e.g., oil paint on canvas)
- Dimensions of the artwork

Observe and describe. Using objective language, portray the artwork. Your portrayal should encompass aspects like the structure and size of the piece. If the art features figures or objects rather than abstract forms, elucidate what is being depicted.
- For instance, you could state, “This artwork comprises a petite-scale portrait depicting a young lady, displayed from the mid-torso upwards, set against a somber backdrop. She clasps her hands in front of her chest, gazes upwards and slightly to the right of the viewer. She dons a pink attire and a lengthy veil cascading behind her head.”
- Avoid employing subjective terms such as “beautiful,” “ugly,” “good,” or “bad.” At this stage, focus solely on describing what you perceive, without passing judgment on the art!
Analyze the components of the piece. Delve deeper into the artwork's intricacies. Discuss how the art utilizes the fundamental elements of art and design: line, color, space, light, and shape.
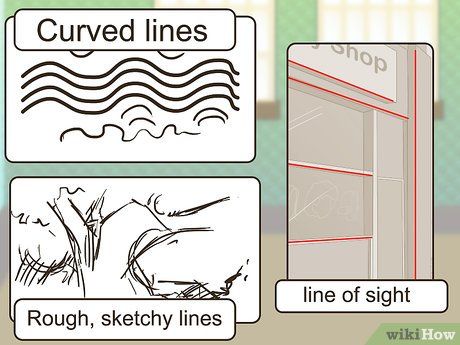
Examine the role of line. Lines within art can be either explicit or implied. Various types of lines can evoke different emotions or impressions. For instance:
- Curved lines can instill a sense of tranquility, whereas jagged lines might evoke a more rugged and dynamic feel, or convey a sense of vigor.
- Loose, sketchy lines can suggest movement and spontaneity, while smooth, solid lines impart a sense of stability and meticulous planning.
- A directional line of sight or action may be implied by the arrangement of figures and objects within the composition. For example, a group of figures all facing or gesturing in the same direction can establish an implied line that guides the viewer's gaze through the artwork in a specific direction.
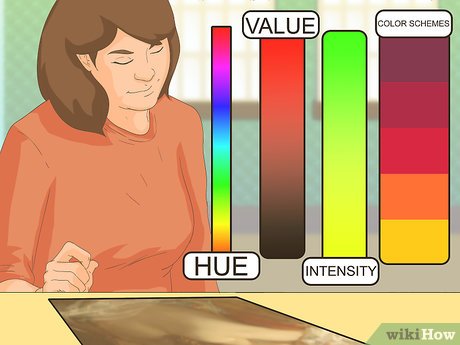
Discuss the utilization of color. Take note of attributes such as hue (e.g., red, green, blue), value (lightness or darkness), and intensity. Observe overall color schemes and contemplate how the colors interact.
- For instance, do the colors clash, or do they harmonize? Does the artwork employ a diverse range of colors, or does it stick to a monochromatic palette (e.g., various shades of blue)?
Explore the use of space within the artwork. “Space” refers to the areas surrounding and between elements in a piece. When discussing space, pay attention to factors like depth and perspective, object overlapping, and the balance between empty and detailed spaces.
- If you're describing a two-dimensional artwork, like a painting, consider whether the piece creates the illusion of three-dimensional space and depth.

Examine the utilization of light in the artwork. Light within art can convey warmth or coolness, brightness or dimness, naturalness or artificiality. Take a moment to discuss the role played by light and shadow in the artwork.
- If discussing a two-dimensional piece, like a painting, focus on how the artist creates the illusion of light.
- For a three-dimensional piece, such as a sculpture, consider how actual light interacts with the artwork. Does the surface reflect light? Are there interesting shadows cast by the sculpture? Are certain areas more shadowed or well-lit than others?
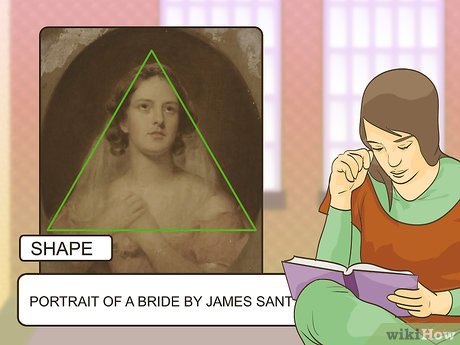
Observe the use of shape in the artwork. Are the shapes within the artwork geometric, characterized by straight lines and smooth curves, or do they appear more organic? Does any particular type of shape dominate the artwork, or do you notice a variety of shapes?
- Shapes play a significant role in both abstract and representational artworks. For instance, in James Sant's portrait of a bride, triangular shapes are evident in the drape of the veil around her shoulders and the positioning of her clasped hands.
- Once you identify a shape in a painting, look for any repetitions elsewhere in the artwork.
Examining the Artwork
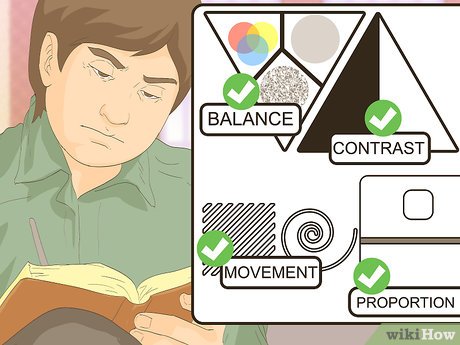
Analyze how the artwork employs compositional principles. After describing the artwork, delve into its analysis and discuss how all elements come together. Begin by examining how the artwork is composed, considering a few key concepts such as:
- Balance: How do colors, shapes, and textures interact to create a sense of balance or harmony in the piece? Is there any imbalance present?
- Contrast: Does the artwork utilize contrasting colors, textures, or lighting? Contrast can also be seen in the use of different shapes or outlines, like sharp versus curved lines or geometric versus organic shapes.
- Movement: How does the artwork create a feeling of movement? Does your eye naturally follow a particular path through the composition?
- Proportion: Do the sizes of elements in the artwork appear realistic, or do they surprise you? For example, in a depiction of a group of people, are any figures disproportionately larger or smaller than expected?
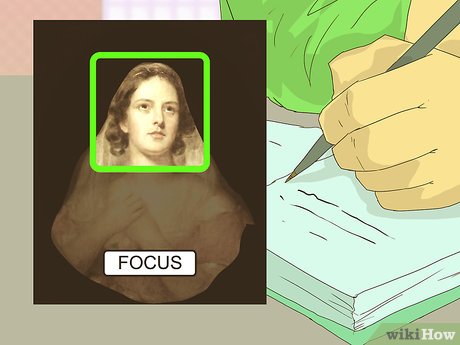
Identify the focal point(s) of the artwork. Most artworks have specific points designed to capture attention and guide the viewer's gaze. In portraits, this could be the face or eyes of the subject. In still-life compositions, it might be a centrally positioned or well-illuminated object. Try to pinpoint which areas of the artwork are emphasized.
- Observe the artwork and note which features immediately draw your attention or repeatedly attract your gaze.
- Consider why certain features stand out. For instance, if one figure in a group catches your eye, is it due to their larger size? Proximity to the viewer? Brighter illumination?

Explore thematic elements within the artwork. Identify key themes and analyze how the artist utilized design elements (color, light, space, shape, and line) to convey these themes. Themes could encompass:
- The use of color schemes to evoke specific moods or meanings, as seen in Picasso's Blue Period paintings.
- Symbolism through religious or mythological imagery, such as Botticelli's use of classical mythology in 'The Birth of Venus.'
- Recurring images or motifs across the artwork or a series of works, similar to Frida Kahlo's incorporation of plants and flowers in many of her paintings.
Interpreting the Art

Uncover the purpose behind the artwork. Attempt to discern what message the artist intended to convey with the piece. Why did they create it? Summarize your interpretation of the artwork's overall meaning.

Share your personal response to the artwork. Transition into a subjective viewpoint and reflect on your emotional response while observing the artwork. Consider the overall mood and any associations it triggers (such as ideas, experiences, or other artworks).
- Utilize descriptive language to articulate your emotional reaction. Does the artwork evoke feelings of sadness, hope, or peace? Would you characterize it as beautiful or unattractive?

Substantiate your interpretation with evidence. Provide examples from your analysis and description of the artwork to support your thoughts and emotions about the piece.
- For instance, 'I interpret James Sant's portrait of a young bride as a portrayal of her spiritual devotion. This is evident from the composition's upward line, guiding the viewer's gaze along with the subject's upward gaze. Additionally, the warm light from above suggests a spiritual aura surrounding the young woman.'
Evaluating the Artwork

Determine the level of success of the artwork. Your aim here is not necessarily to label the art as “good” or “bad.” Instead, focus on whether you consider the work to be “successful.” Consider the following:
- Does the artwork effectively convey the artist's intended message?
- Did the artist skillfully utilize tools and techniques?
- Is the artwork innovative, or does it replicate other works?

Describe the criteria for evaluating the artwork. After selecting specific aspects of the artwork for evaluation, clearly outline the areas you will focus on during your assessment. For instance, you could mention that your evaluation will consider the organization, technical execution, and successful portrayal of mood or themes.

Provide a summary of why you believe the artwork is successful or unsuccessful. In a brief statement, justify your assessment of the artwork. Support your judgment with specific reasons based on your interpretation and analysis of the piece.
- For example, “I find this artwork successful because the cohesive use of light, shape, gesture, and line effectively conveys the intended mood of the subject.”
Helpful Tips
-
Keep in mind, there isn't a single correct method for critiquing artwork. Your objective isn't to determine whether the art is good or bad, but rather to clearly convey your understanding of and response to the art.
