PivotTable is a tool designed for analyzing data from various perspectives and meeting diverse requirements from a list or table. Starting from the initial massive data block, PivotTable can assist in grouping and condensing data according to your specifications.
This stands out as one of Excel's most valuable features. To delve deeper into PivotTable, refer to the examples below.
Suppose we have the following data table:
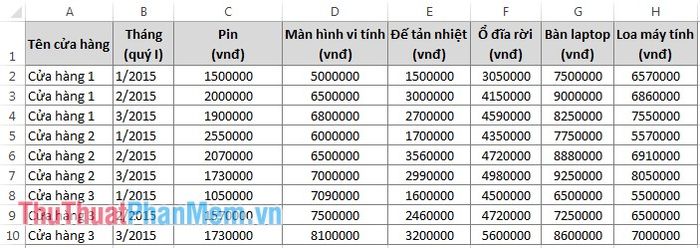
Utilizing PivotTable for Simple Analysis
Example 1: Use PivotTable to analyze the revenue of Computer Monitors at each Store using the provided data table.
Step 1: Start by placing the mouse cursor in any cell within the data range (alternatively, select the entire data range). Then, go to the Insert tab -> PivotTable.
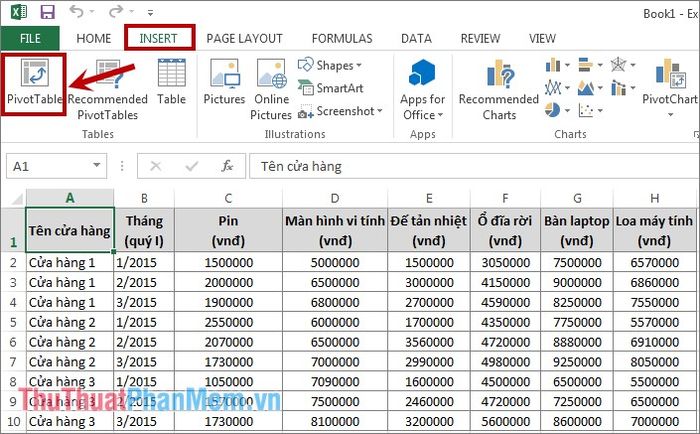
Step 2: The Create PivotTable dialog box appears. In the Table/Range section, the address of the data-containing range is displayed. In the Choose where you want the PivotTable report to be placed section, select the location for the PivotTable report.
New sheet: Place it in a new sheet.
Existing sheet: Position it in the current sheet. If you choose this option, you need to select the location address for placing the PivotTable in the Location box.
Afterwards, click OK to create the PivotTable.
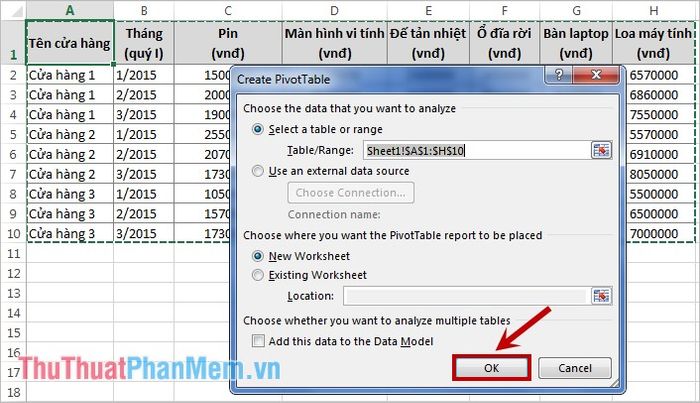
Step 3: At this point, the spreadsheet interface will display the PivotTable Field List dialog box on the right side of the screen. In this section, there are two parts: Choose fields to add to report – select data fields to add to the PivotTable report, Drag fields between areas below – four areas to drop fields dragged or selected from the choose fields to add to report section (report filter – data filtering area, column labels – column names, row labels – row names, values – values to be displayed).
As per the example's request, analyze the revenue for Computer Monitors in each store. Select both Computer Monitors and Store checkboxes.
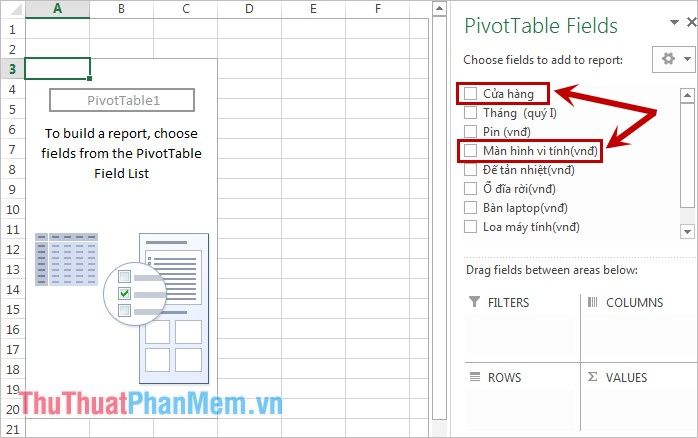
- If Computer Monitors are displayed in the ROWS section, hover over that cell, drag it to the VALUES section.
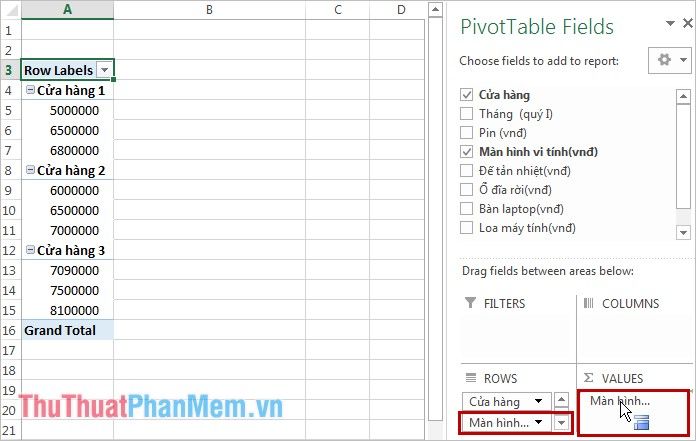
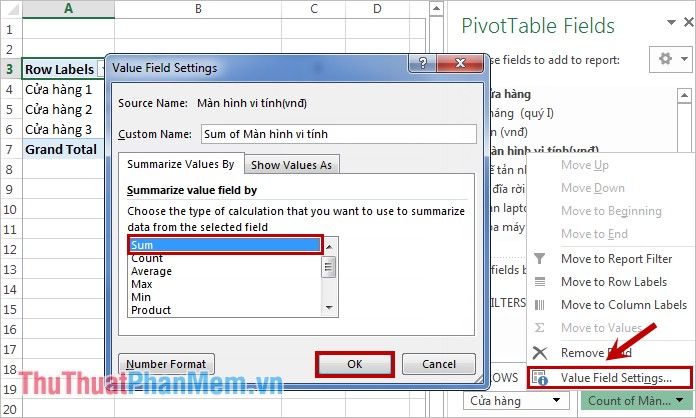
Then click on the dragged cell, choose Value Field Settings, and select the calculation method as Sum to meet the specified requirements. For different needs, choose a different calculation method accordingly.
- If Computer Monitors are shown in the VALUES section as illustrated below, you have successfully compiled the statistics.
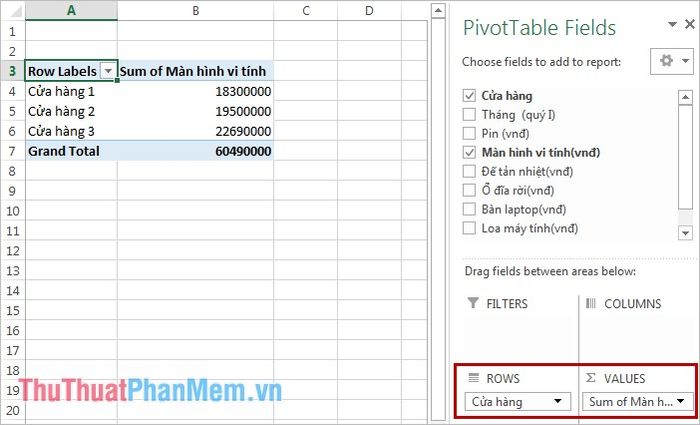
Note: You can also click and drag the data above directly into the four areas below. In the example, click and drag the Store cell down to the ROWS area, and do the same for the Computer Monitors cell into the VALUES area.
Utilize PivotTable to analyze data from multiple columns.
Example 2: Use PivotTable to display the revenue of Computer Monitors across Months for each Store in the given data table.
First, create a PivotTable as in Steps 1 and 2 in the previous example. Then, in the PivotTable Field List dialog, mark the three items: Store, Month, Computer Monitors (or you can drag Store and Month into the ROWS area, Computer Monitors into the VALUES area). The result will be as follows:
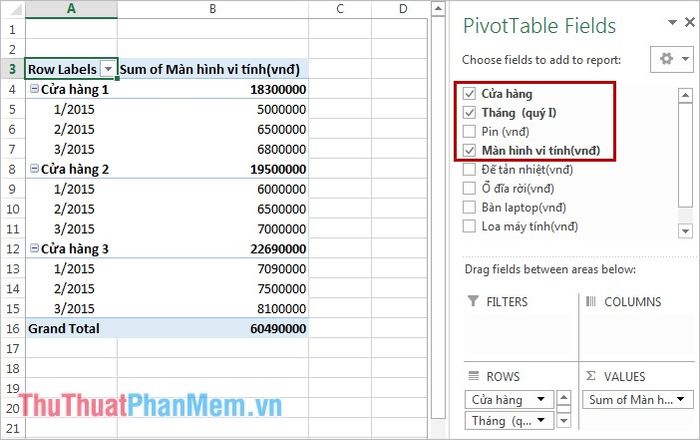
If you want an easier comparison, you can shift the Month cell to the COLUMNS area by left-clicking on the Month cell in the ROWS area and dragging it to the COLUMNS area. Alternatively, left-click on the Month cell in the ROWS area and select Move to Column Labels.
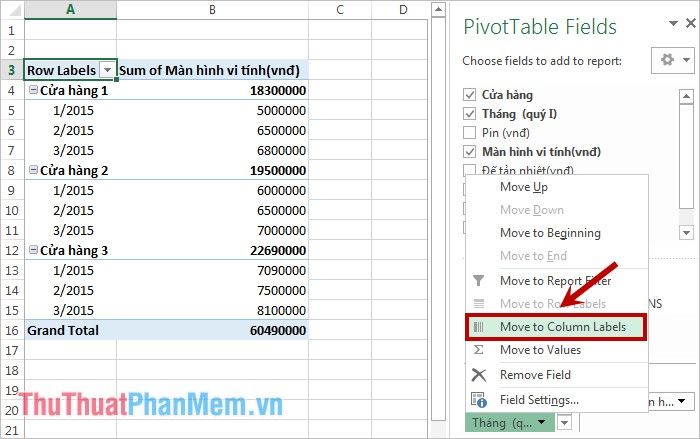
The result will look like this:
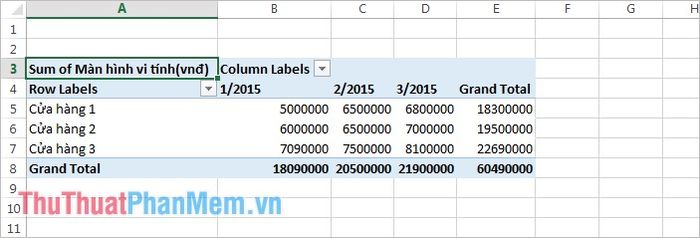
Thus, by utilizing PivotTable, you can swiftly process and consolidate data from both basic and complex requirements. Wishing you success in your endeavors!
