
Understanding LOOKUP Function
LOOKUP is the tool for searching and referencing data based on a specific row or column in Excel. In simple terms, when you need to look up a value from a row or column, LOOKUP will find that value with just a simple formula.

Guide to Using LOOKUP in Vector Form
LOOKUP in Excel is divided into two different forms. In this section, let's explore the formula, notes, and examples of LOOKUP in Vector form together.
Formula for Vector LOOKUP Function
The Vector form of LOOKUP function is widely used to find a specific value within the range of a row or a column and then relocate the discovered value to another position in Excel. Typically, people apply the Vector form in cases where they want to determine the positions of values for comparison.
How to use the Vector Form of LOOKUP:
LOOKUP(LOOKUP_value, LOOKUP_vector, [result_vector])
Explanation:
- LOOKUP_value: the value to be searched, can be alphanumeric or logical.
- LOOKUP_vector: the range containing values (could be a row or a column). Values in the LOOKUP_vector must be alphanumeric or logical.
- Result_vector: can be a column or a row and must be of the same size as LOOKUP_vector.

Considerations when using Vector LOOKUP
- If LOOKUP_value (the value to be searched) is not available, Excel will automatically use the smallest value in LOOKUP_vector (the range containing values to be searched).
- In case LOOKUP_value is smaller than the smallest value in LOOKUP_vector, Excel will display the #N/A error.
Example of Vector LOOKUP Function
To better understand how the LOOKUP function operates, refer to the example below.
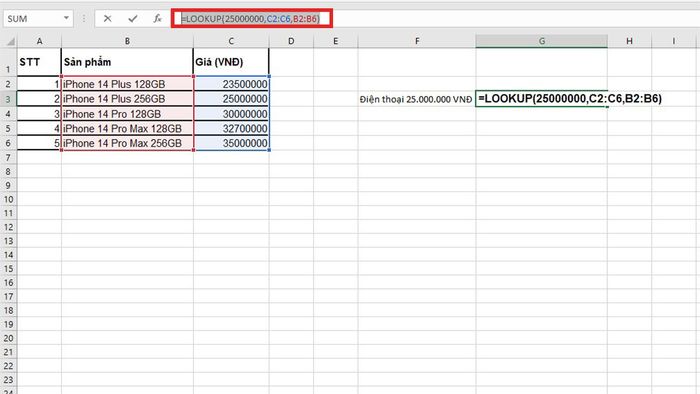
Imagine a customer looking for a genuine product priced at 25,000,000 VND at . To find a suitable product for the customer, you need to consult the table using the LOOKUP function in vector form as follows:
| STT | Sản phẩm | Giá (VNĐ) |
| 1 | iPhone 14 Plus 128GB | 23.500.000 |
| 2 | iPhone 14 Plus 256GB | 25.000.000 |
| 3 | iPhone 14 Pro 128GB | 30.000.000 |
| 4 | iPhone 14 Pro Max 128GB | 32.700.000 |
| 5 | iPhone 14 Pro Max 256GB | 35.000.000 |
In this case, you would use the LOOKUP function with the formula =LOOKUP(25000000,C2:C6,B2:B6)
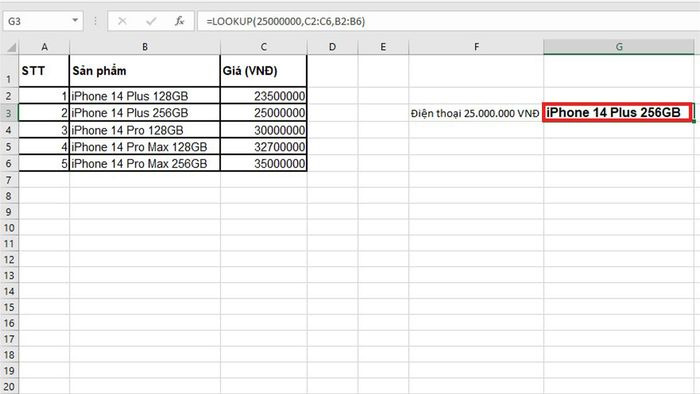
After using the LOOKUP function in vector form, we will obtain the result as iPhone 14 Plus 256GB
Guide to Using LOOKUP in Array Form
The previous section introduced LOOKUP in vector form. You need to grasp the formula and pay attention to usage nuances to avoid confusion with the LOOKUP formula in array form!
Formula for Array LOOKUP Function
The array LOOKUP is used to search or reference a value in a specific cell to an array of values in Excel. The obtained result will be displayed with the value in the same position in the column or row of the array.
The formula for the array LOOKUP function is as follows:
Use LOOKUP(LOOKUP_value, array)
Explanation:
LOOKUP_value: the value to search in the array. It can be text, number, name, or logical value.
Array: an array containing the values to search. The array must contain numbers, text, names, or logical values.

Considerations when Using Array LOOKUP
If the array LOOKUP function doesn't find a matching value, Excel will automatically take the smallest value in the search array.
- If the value we're looking for in the LOOKUP array function is smaller than the value in the array, Excel will immediately report the #N/A error.
Array LOOKUP Function Example
To understand more about using the LOOKUP array function, check out this example.
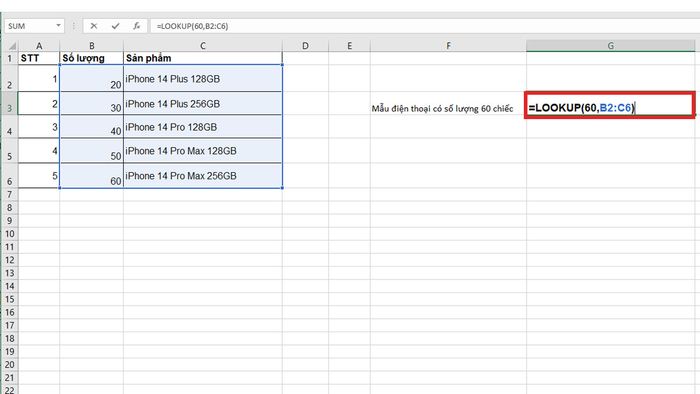
Suppose we need to find a phone with a quantity of 60 at Mytour according to the following table:
| STT | Số lượng | Sản phẩm |
| 1 | 20 | iPhone 14 Plus 128GB |
| 2 | 30 | iPhone 14 Plus 256GB |
| 3 | 40 | iPhone 14 Pro 128GB |
| 4 | 50 | iPhone 14 Pro Max 128GB |
| 5 | 60 | iPhone 14 Pro Max 256GB |
Based on the example requirements, we will execute the formula =LOOKUP(60,B2:C6)
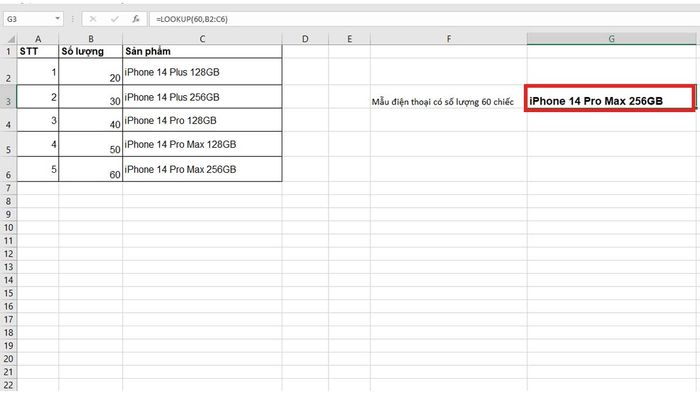
After applying the Array LOOKUP function, we get the following result:
Important Notes When Using LOOKUP Function in Excel
To effectively use the data lookup method with LOOKUP, individuals must grasp the formulas and considerations when applying both vector and array LOOKUP functions to various scenarios.
When encountering the #N/A error, check if the value to be searched is smaller than the values in the array.
Additionally, explore functions like VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, or IF with multiple conditions for more efficient and faster data retrieval.

Mytour's article guides you on using the LOOKUP function through practical examples. If you have any further questions, feel free to leave a comment below for Mytour's assistance. Thank you for reading, stay tuned to Mytour for daily updates on valuable knowledge!
