
Considering a new laptop? Learn about the crucial differences between Core i5 and Core i7 CPUs.
Unleash the power of Intel Core i5.

Developed and manufactured by Intel, Core i5 is a dual-core or quad-core processor used in both desktops and laptops. The first Core i5 processor was released in September 2009, and subsequent generations have remained popular and in production to this day.
Core i5 processors come in various speeds ranging from 1.90 GHz to 3.80 GHz, with cache sizes of 3 MB, 4 MB, or 6 MB. The most common RAM type for Core i5 processors is DDR3 1333 or DDR3 1600. However, higher-performance RAM can also be used if supported by the motherboard.
In light tasks, Core i5 consumes relatively little power, but with more demanding software, power consumption can increase significantly.
The Mighty Intel Core i7

Intel Core i7, a powerhouse in the CPU realm, typically boasting four or six cores, clocking in speeds ranging from 2.6 GHz to 3.7 GHz. First released in November 2008, Intel Core i7 processors, alongside Core i5 and i3, remain the cornerstone of the brand.
Prominent features of the i7 series include high performance, energy efficiency for both desktop and laptop usage. Designed with robust graphics support, it excels in tasks demanding precision, including running graphically intense games, video editing, and audio rendering.
Dive into the Price Arena: Core i5 vs. Core i7
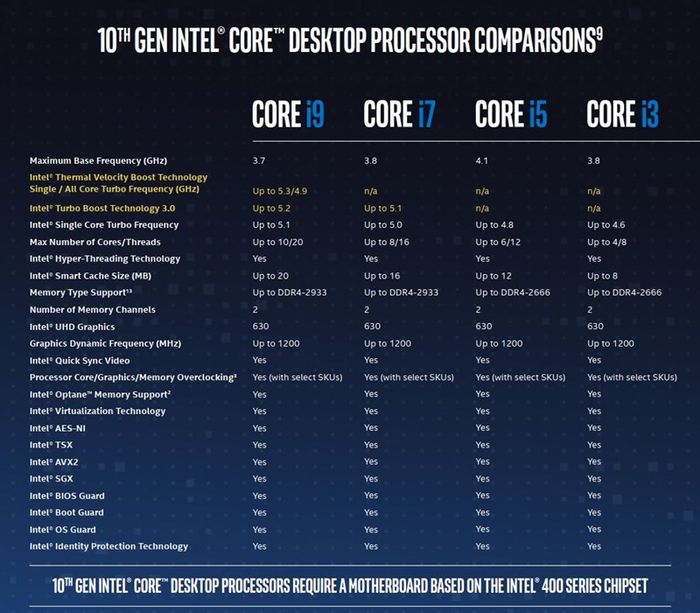
Enhanced Performance with Turbo Boost and HyperThreading

Turbo Boost is a cutting-edge feature integrated into Intel processors. Essentially, it allows certain cores of the chip to run faster than their base clock speeds. Both Core i5 and Core i7 processors utilize this feature, with Core i7 Turbo Boost often achieving higher clock speeds.
However, this performance boost isn't always guaranteed, as it depends heavily on specific design and PC cooling capabilities, among other factors.
Conversely, Intel's Hyper-Threading is an optional feature. It employs multithreading technology to make the operating system and applications believe that a processor has more cores than it actually does. This hyper-threading technology is used to enhance performance on multitasking tasks.
Of course, a CPU supporting Hyper-Threading within a specific product line will likely outperform one that doesn't. This means it's easy to understand that a Core i7 with Hyper-Threading will perform better than a similarly used Core i5 chip. However, this isn't a feature present in every product, which adds another layer of choice regarding multithreaded processing. On one hand, you have the option of a quad-core Core i5 chip with hyper-threading, as opposed to a six-core Core i7 chip without equivalent functionality.
What's the Right Choice for You?

On desktop computers, Intel's Core i5 primarily serves mainstream users concerned with performance, while the Core i7 is tailored for enthusiasts and high-end users. However, in the laptop market, the difference in performance between these two chips is very close. Broadly speaking, you can categorize them as follows:
Core i5 is intended for mid-range laptops requiring more power than Core i3 models. If you're someone with regular usage needs, or if you don't have overly complex requirements for graphics or heavy gaming, you can absolutely opt for this processor.
Core i7: This is the high-end CPU line, often used for business laptops, ultrabooks, or high-performance gaming laptops. It allows you to notice the difference compared to lower-tier chips when handling heavy tasks: rendering videos, running graphically demanding games, ... and of course, it still performs well in everyday tasks. To obtain this feature, you'll have to trade it for a higher price, whether the improved performance is significantly enhanced or not depends heavily on the laptop you're using.
Above are some differences you can notice between the Core i5 and Core i7 processors. However, to choose the best CPU for yourself, it's essential to observe your current personal needs to avoid wasting too much money. So, according to you, what's the most suitable choice for your work needs? Leave your comments below!
References: PCMag, Digital Trends, Intel.
