In a computer system, there are two types of graphics cards: dedicated GPUs (like AMD, NVIDIA) and integrated GPUs (built into the CPU). There are various methods to determine whether your computer uses an onboard or dedicated card. This article explores alternative methods beyond physical inspection of the machine.
1. Checking the graphics card using the 'dxdiag' command on Windows.
Step 1: Open the Run dialog by pressing Windows + R, then type 'dxdiag' and press OK.
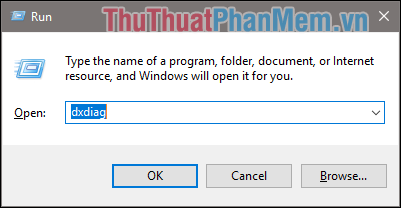
Step 2: A dialog box will appear, switch to the Display tab under Device and you will see information about the graphics card.
In the image below, the displayed graphics is Intel(R) HD Graphics 630, indicating an onboard card.
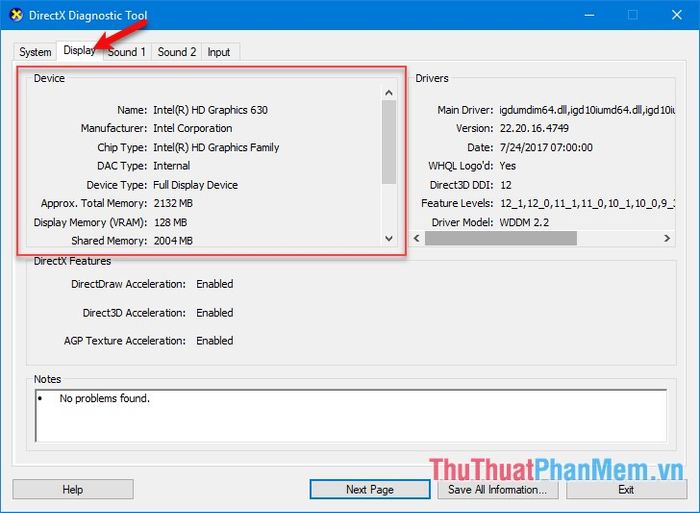
If it shows ATI, AMD, or NVIDIA as below, it's a dedicated graphics card:
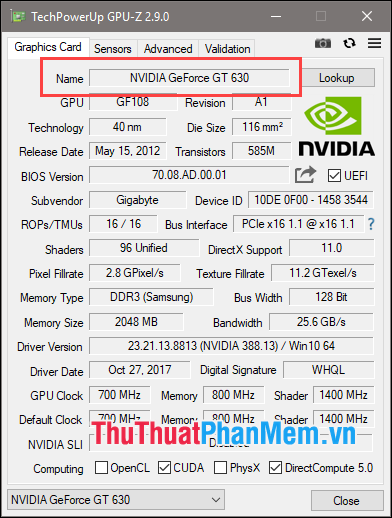
2. Checking the graphics card using GPU-Z software.
This software is specialized in providing detailed specifications of the graphics card, including monitoring its operational status.
Step 1: First, download the GPU-Z software from here:
http://www.guru3d.com/files-get/gpu-z-download-techpowerup,12.html
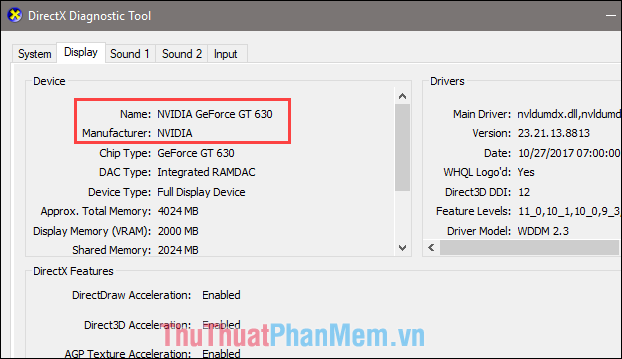
Step 2: Install the software, then run it. The interface will appear as follows:
Here, the displayed graphics card name is Intel(R) HD Graphics 630, indicating an onboard card.
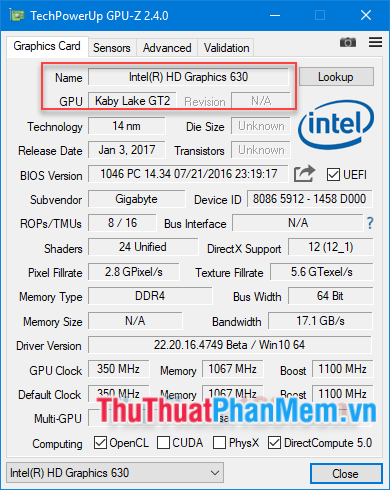
If it displays ATI, AMD, or NVIDIA as below, it's a dedicated graphics card:
Above is a guide on how to check whether your computer's graphics card is dedicated or onboard. We hope you find this article helpful. Thank you for reading!
