Beta signifies the volatility or risk of a specific stock concerning the overall volatility of the stock market. It serves as an indicator of a stock's risk level and aids in assessing its anticipated rate of return. Beta is a fundamental metric utilized by stock analysts in their stock selection process, alongside metrics like price-to-earnings ratio, shareholder's equity, debt-to-equity ratio, among others.
Procedures
Beta Estimator
 Beta Estimator
Beta EstimatorDeriving Beta Using a Simple Formula

Locate the risk-free rate. This represents the expected return on an investment with zero risk, such as U.S. Treasury Bills for investments in U.S. dollars and German Government Bills for investments traded in euros. This value is typically presented as a percentage.

Identify the respective returns for the stock and the market or suitable index. These returns are also expressed as percentages, usually calculated over multiple months.
- Either or both of these returns may be negative, indicating a loss if invested in the stock or the market (index) as a whole during the period. If only one of the returns is negative, the beta will be negative.

Subtract the risk-free rate from the stock's return. For instance, if the stock's return is 7% and the risk-free rate is 2%, the difference would be 5%.

Subtract the risk-free rate from the market's (or index's) return. If the market or index return is 8% and the risk-free rate is once again 2%, the difference would be 6%.
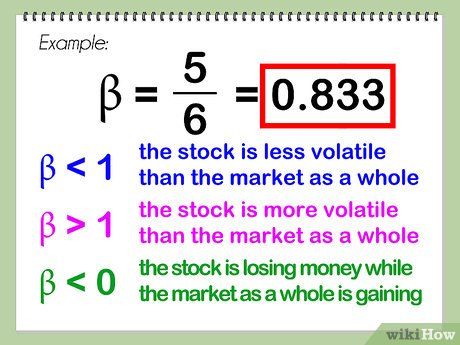
Divide the first mentioned difference by the second mentioned difference. This quotient represents the beta value, typically presented as a decimal. Using the example provided, the beta would be 5 divided by 6, resulting in 0.833.
- The market's beta itself (or the relevant index) is inherently 1.0, as the market is compared to itself, resulting in any number (except zero) divided by itself equaling 1. A beta below 1 indicates the stock is less volatile than the market, whereas a beta above 1 suggests the stock is more volatile than the market. A beta value less than zero suggests either the stock is losing money while the market is gaining (more probable) or the stock is gaining while the market is losing money (less probable).
- When calculating beta, it's customary, though not obligatory, to utilize an index that reflects the market in which the stock is traded. The S&P 500 is commonly used for U.S. stocks, though analyzing an industrial stock might be better served by comparing it to the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Other suitable indexes exist. For internationally traded stocks, the MSCI EAFE (representing Europe, Australasia, and East Asia) serves as a suitable representative index.
Utilizing Beta to Assess a Stock's Return Rate

Locate the risk-free rate. This value remains consistent with the description provided under 'Calculating Beta for a Stock.' For this section, we'll adhere to the same example rate of 2 percent as previously mentioned.

Identify the market's return rate or that of its representative index. In this instance, we'll maintain the same 8 percent figure as previously mentioned.

Calculate the product of the beta value and the disparity between the market's return rate and the risk-free rate. For this example, we'll utilize a beta value of 1.5. Given a 2 percent risk-free rate and an 8 percent market return rate, this yields a difference of 8 - 2, resulting in 6 percent. Multiplied by a beta of 1.5, this totals 9 percent.
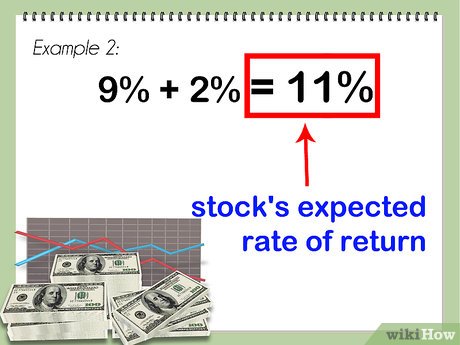
Combine the outcome with the risk-free rate. This yields a total of 11 percent, representing the anticipated rate of return for the stock.
- A higher beta value for a stock corresponds to a higher expected rate of return. However, this elevated rate of return comes with increased risk, necessitating a thorough examination of the stock's other fundamentals before deciding whether it belongs in an investor's portfolio.
Utilizing Excel Graphs for Beta Calculation
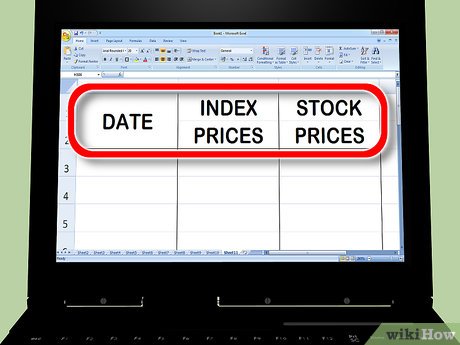
Create three price columns in Excel. The first column should consist of dates. In the second column, enter the index prices, representing the overall market against which you'll compare your beta. The third column should contain the prices of the stock for which you're calculating beta.
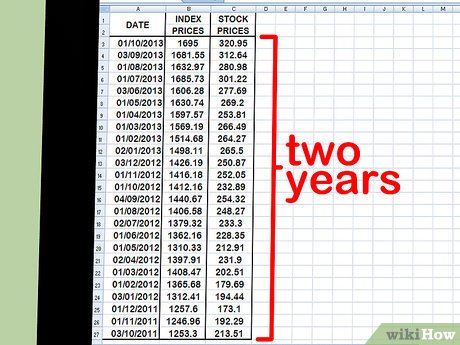
Input your data points into the spreadsheet. Start with one-month intervals. Choose a date, such as the beginning or end of the month, and input the corresponding values for the stock market index (consider using the S&P 500) and the stock price for that day. Select around 15 to 30 recent dates, possibly extending a year or two into the past. Record both the index price and the stock price for each date.
- The longer the time frame you select, the more accurate your beta calculation will be. Historical beta evolves as you monitor both the stock and the index over a longer period.
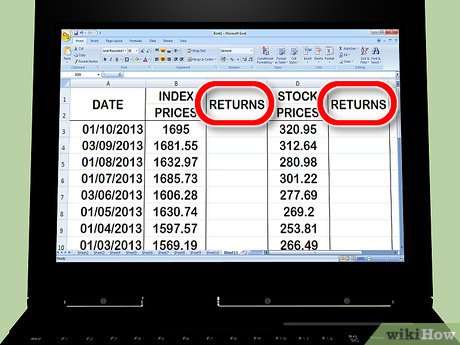
Establish two return columns adjacent to your price columns. One column should represent the returns of the index, while the other should depict the returns of the stock. You'll utilize an Excel formula to compute the returns, as explained in the subsequent step.
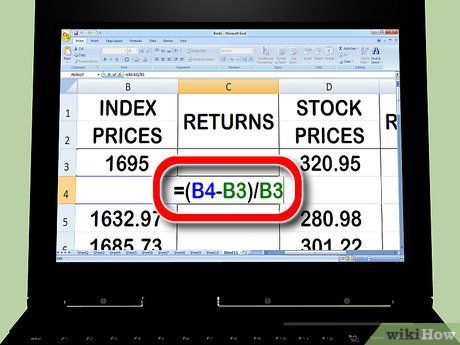
Commence calculating returns for the stock market index. In the second cell of your index-return column, input an '=' (equals sign). Click on the second cell in your index column, type a '-' (minus sign), and then click on the first cell in your index column. Next, type a '/' ('divide by' sign), and click on the first cell in your index column again. Press 'Return' or 'Enter.'
- Since return is a calculation over time, leave your first cell blank. You need at least two data points for return calculation, which is why you'll begin with the second cell of your index-returns column.
- This action involves subtracting the newer value from the older one and then dividing the result by the older value. This provides the percentage of loss or gain for that period.
- Your formula for the returns column might resemble this: =(B4-B3)/B3
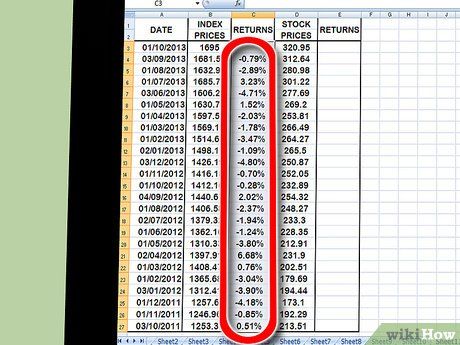
Utilize the copy function to replicate this process for all data points in your index-price column. Click on the small square at the bottom right of your index-return cell and drag it down to the lowest data point. This directs Excel to duplicate the same formula (above) for each data point.
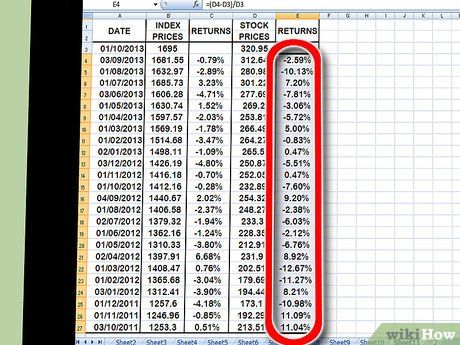
Repeat the same process for calculating returns, this time for the individual stock instead of the index. Upon completion, you'll have two columns, formatted as percentages, detailing the returns for both the stock index and the individual stock.
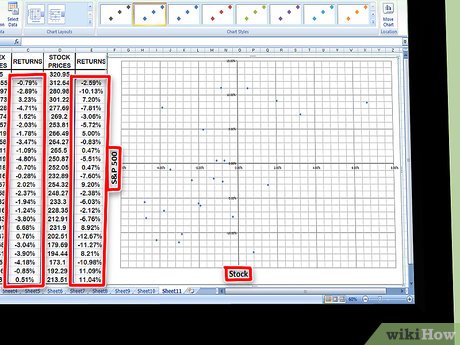
Generate a chart from the data. Highlight all data in the two return columns and click the Chart icon in Excel. Choose a scatter chart from the options list. Label the X-axis with the name of the index you're using (e.g., S&P 500) and the Y-axis with the name of the stock you're using.
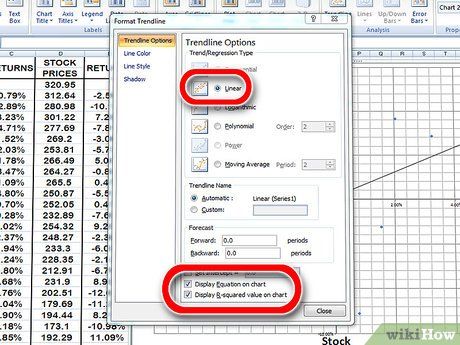
Incorporate a trendline into your scatter chart. This can be achieved by selecting the trendline layout in newer Excel versions or manually finding it by clicking in Chart → Add Trendline. Ensure to display the equation and the R2 value on the chart.
- Select a linear trendline, not a polynomial or moving average.
- The ability to graph the equation and the R2 value will vary depending on your Excel version. Newer versions allow you to display the equation and the R2 value by clicking on Chart Quick Layouts and selecting the equation R2 value layout.
- In older Excel versions, navigate to Chart → Add Trendline → Options. Then, check both boxes next to 'Display equation on chart' and 'Display R2 value on chart.'
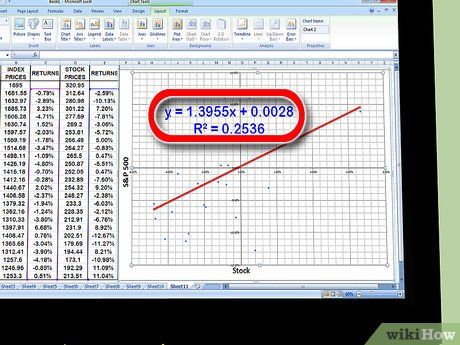
Determine the coefficient for the 'x' value in the trendline equation. Your trendline equation will be in the form of y = βx + a. The coefficient of the x value represents your beta.
- The R2 value indicates the relationship between the variance of stock returns and the variance of overall market returns. A high value, such as .869, signifies a strong correlation between the two variances. Conversely, a low value, like .253, indicates a weaker correlation.
Understanding Beta

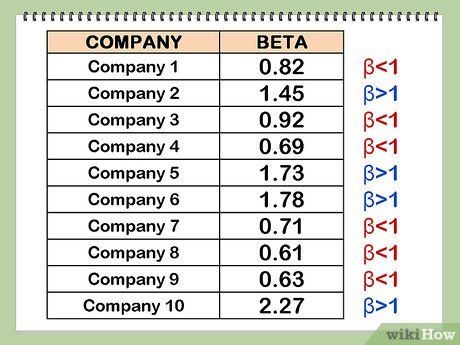
Interpret beta correctly. Beta reflects the risk an investor undertakes relative to the overall stock market by owning a specific stock. It's essential to compare a stock's returns to an index's returns, with the index serving as the benchmark. The index's risk is fixed at 1. A beta below 1 suggests the stock is less risky than the benchmark index. Conversely, a beta above 1 indicates the stock is riskier than the benchmark index.
- For instance, suppose Gino's Germ Exterminator has a calculated beta of .5 compared to the S&P 500. This implies it's half as risky as the benchmark. If the S&P drops 10%, Gino's stock price is likely to decline by only 5%.
- Another example: If Frank's Funeral Service has a beta of 1.5 compared to the S&P, expect Frank's stock price to fall more than the S&P, approximately by 15%, if the S&P falls by 10%.

Understand the relationship between risk and return. Generally, higher risk corresponds to higher potential returns, while lower risk results in lower potential returns. A stock with a low beta won't experience losses as substantial as the S&P during downturns but also won't enjoy gains as significant during upswings. Conversely, a stock with a beta exceeding 1 will incur greater losses than the S&P during downturns but will also achieve higher gains during upswings.
- For example, consider Vermeer's Venom Extraction with a beta of .5. If the stock market rises by 30%, Vermeer's gains only 15%. However, if the stock market declines by 30%, Vermeer's only drops by 15%.

Anticipate that a stock with a beta of 1 will mirror the market's movements. If your beta calculations reveal a stock with a beta of 1, it will exhibit the same level of risk as the benchmark index. If the market rises by 2%, your stock will rise by 2%; if the market falls by 8%, your stock will also fall by 8%.
Include both high- and low-beta stocks in your investment portfolio to ensure diversification. Having a balanced mix of high- and low-beta stocks can help mitigate the impact of any significant market downturns. However, it's important to note that while low-beta stocks tend to perform more steadily during bullish periods, a diversified beta portfolio may not yield the highest returns during bullish market phases.
Recognize that, like most financial forecasting tools, beta cannot reliably predict future performance. Beta measures a stock's historical volatility, which may not accurately forecast its future behavior. The beta value of a stock can undergo significant changes from one year to the next, making it an unreliable predictive indicator.
Insights
-
Take note that classical covariance theory might not be applicable due to the 'tail heaviness' of financial time series data. Additionally, the standard deviation and mean may not be well-defined for the underlying distribution. Thus, a modification using quartile spread and median instead of mean and standard deviation could be considered.
-
Beta evaluates a stock's volatility over a specific time frame, regardless of whether the market was in an upward or downward trend. Similar to other fundamental stock analyses, past performance assessed by beta does not guarantee future performance.
Cautions
- Beta alone cannot determine which of two stocks is riskier if the stock with higher volatility has a lower correlation of its returns to those of the market, and the stock with lower volatility has a higher correlation of its returns to those of the market.
