Leap years help maintain the accuracy of our calendar. With approximately 365.24 days per year, we insert an extra day every 4 years to compensate for the fractional day. This additional day ensures that our calendar remains synchronized with the astronomical year. While calculating leap years is straightforward, there are specific rules to consider. If you prefer, you can simply refer to a calendar instead of performing the calculations manually.
Steps to Follow
Utilizing Division

Identify the Year for Evaluation: To determine leap years, you must select a specific year for examination. This could be a past, present, or future year. For example, you might choose to analyze 1997 or 2012 for the past, 2019 for the present, or 2025 or 2028 for the future.

Determine if the number is divisible by 4. When dividing the year by 4, if you obtain a whole number without any remainder, then the year is a leap year. Otherwise, it is not.
- For instance, dividing 1997 by 4 results in 499.25, indicating it's not a leap year due to the decimal remainder.
- On the other hand, dividing 2012 by 4 gives 503, signifying that it's likely a leap year.

Verify the number is not divisible by 100. If a year is divisible by 4 but not by 100, it's a leap year. If divisible by both 4 and 100, further calculation is needed.
- For example, 2012 is divisible by 4 but not 100, making it a definite leap year.
- However, 2000 is divisible by both 4 and 100, implying it might not be a leap year and requires additional assessment.
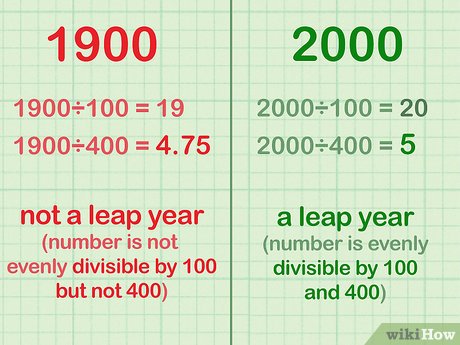
Ensure divisibility by 400 to confirm a leap year. If divisible by 100 but not by 400, it's not a leap year. If divisible by both 100 and 400, it is a leap year.
- For instance, 1900 is divisible by 100 but not 400, making it not a leap year.
- Contrarily, 2000 is divisible by both 100 and 400, confirming it as a leap year.
Pro Tip: Utilize online leap year calculators if manual division isn't your preference or if you're uncertain about your calculations. They provide accurate results without the need for manual computation.
Consulting a Calendar

Find the desired year on a calendar. Begin by locating the specific year you want to investigate on a physical or online calendar. Ensure the calendar allows you to navigate a few years backward or forward.
- For instance, to determine if 2016 was a leap year, refer to that year's calendar.
- To check if 2021 is a leap year, access the corresponding year's calendar online.

Check February for a 29th day. Leap years add an extra day to February, the shortest month. Refer to February in the calendar and verify if February 29th is present. Its presence confirms a leap year.
- If February ends on the 28th, it is not a leap year.

Anticipate the next leap year in 4 years. Since each year is roughly 365 days and a bit less than 6 hours, these extra hours accumulate to an additional day over 4 years, resulting in leap years almost every 4 years. Count forward 4 years from the last leap year to predict the next one.
- For example, if 2016 was a leap year, you could foresee 2020 as the next leap year by counting ahead 4 years.
Pro Tip: Note that occasionally, there may not be a leap year for 8 years due to a slightly less than 6 extra hours each year—precisely 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 46 seconds. Therefore, performing calculations is beneficial instead of solely relying on a leap year every 4 years.
Leap Year Calculator and Reference
 Leap Year Estimation Tool
Leap Year Estimation Tool Leap Year Reference Diagram
Leap Year Reference Diagram