Alligators and crocodiles are frequently mistaken for each other, and the terms are often used interchangeably. Despite their similarities, there are distinct physical characteristics that can assist you in distinguishing between crocodiles and alligators.
Procedures
Noting Their Physical Differences
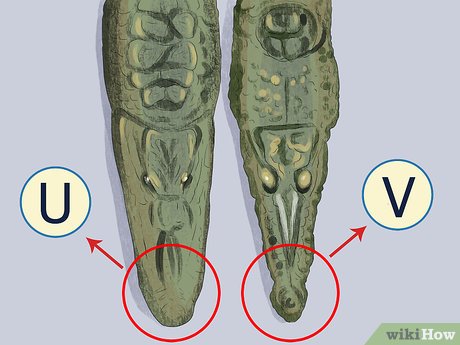
Examine the snout. The simplest method to differentiate between crocodiles and alligators is by examining their snouts. Alligators possess wide, rounded, 'U'-shaped snouts with larger noses, whereas crocodiles have longer, thinner, pointed 'V'-shaped snouts and smaller noses. Additionally, alligator snouts are shorter than those of crocodiles.
- The broad snouts of alligators provide them with greater strength than crocodiles. They can more easily crush hard-shelled prey, such as turtles, compared to crocodiles. Crocodiles, on the other hand, have a tendency to consume more fish and mammals.
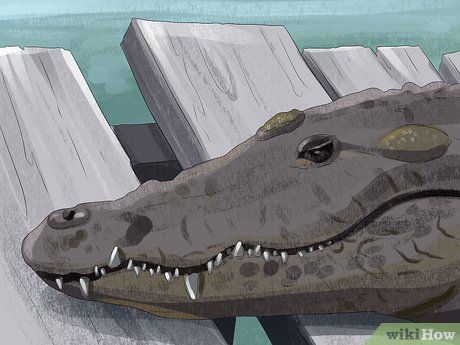
Examine the teeth. Crocodiles typically have upper and lower jaws of nearly equal width, resulting in exposed teeth along the entire jawline even when the mouth is closed. Conversely, alligators possess a wider upper jaw, causing the lower jaw teeth to fit into sockets in the upper jaw, concealing them from view. Only the upper jaw teeth are visible along the lower jawline.
- Alligators' upper jaws are wider than their lower jaws, causing the upper jaw to overlap the lower jaw. As a result, lower jaw teeth are hidden when the mouth closes.
- Crocodiles' upper and lower jaws are roughly the same width, leading to interlocking teeth when the mouth shuts. This exposes some of their teeth when closed, giving them a 'smiling' appearance, with the fourth tooth on each side of the lower jaw protruding over the upper lip.

Observe their physical appearance. Alligators typically possess darker skin compared to crocodiles, which usually exhibit lighter skin tones, often in shades of olive green or brown. Alligators tend to have darker, blackish-grey skin, and crocodiles are generally longer than alligators. On average, adult crocodiles measure 5.8 meters, while adult alligators reach lengths of 3.4 meters.
- Adult alligators typically weigh between 800-1,000lbs, whereas crocodiles can grow larger, weighing between 1,000-2,000lbs.
- Alligators have an average lifespan of 30-50 years, while crocodiles can live 70-100 years.
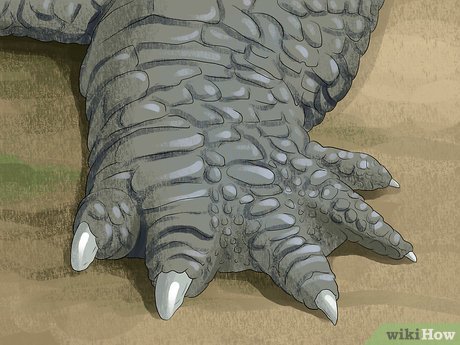
Consider their limb and foot differences. Most crocodiles feature a fringe-like appearance on their hind limbs and feet, which is absent in alligators. Additionally, alligators possess webbed feet, while crocodiles do not.
Examining Their Native Environment

Assess the habitat's water source. Alligators typically inhabit freshwater environments due to their low tolerance for salt. They may also reside in brackish water (a mixture of saltwater and freshwater). Alligators are commonly found in swamps, marshes, rivers, lakes, and other small bodies of water. While they prefer warmer temperatures, they can endure freezing conditions.

Assess whether the creature inhabits tropical climates or saltwater environments. Unlike alligators, crocodiles possess adapted salivary glands on their tongues, aiding them in tolerating saltwater. Crocodiles typically dwell near lakes, rivers, wetlands, and certain saltwater regions, favoring tropical climates due to their cold-blooded nature and inability to produce internal heat.
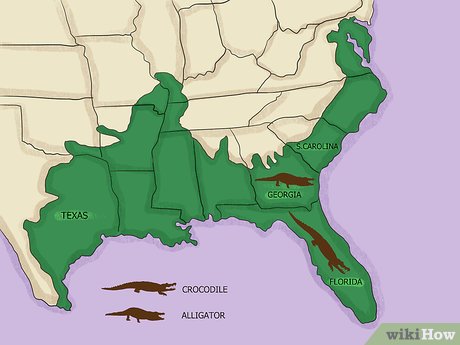
Consider the geographical distribution of the creature. Crocodiles are primarily found in the tropical regions of Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Americas, while alligators inhabit the southern United States and China. The United States is the sole country where both alligators and crocodiles coexist.
- American alligators are predominantly located in Florida and Louisiana, with less frequent sightings in Alabama, Georgia, South Carolina, Mississippi, and Texas.
- American crocodiles are typically sighted in Florida.
Assessing Their Demeanor

Observe their aquatic activity levels. Crocodiles exhibit significantly more aquatic activity and spend extended periods in water compared to alligators, while alligators prefer resting in mud or vegetation surrounding marshes and lakes.
- Alligators typically nestle their eggs within vegetation mounds surrounding freshwater areas.
- Crocodiles opt for slightly drier locations such as mud or sand for egg-laying.

Observe their aggressiveness. Crocodiles tend to display more aggression than alligators, often initiating attacks without provocation when approached, whereas alligators are more prone to attacking when hungry or threatened.
- In both their natural habitats and captivity, crocodiles exhibit notably more aggression towards humans than alligators.
Assess their velocity. Both crocodiles and alligators are exceptionally swift swimmers, capable of reaching speeds of up to 20 mph in water. On land, their pace slows a bit, typically reaching speeds of up to 11 mph. Due to their smaller size and lower fatigue levels, alligators can sustain running for longer durations compared to crocodiles.
Pointers
Cautions
- If you plan to enter the habitat of an alligator or crocodile, ensure you do so cautiously to avoid provoking aggression. Keep in mind that male aggression tends to increase during the spring mating season.
- Do not approach an alligator or crocodile without the presence of a professional handler, as they can exhibit highly aggressive behavior.
