A bug making its way into your ear can provoke significant anxiety. Insects like moths, cockroaches, ladybugs, and beetles might find their way into your ear canal while you're asleep or engaging in outdoor activities. Entomologists suggest these intrusions might be motivated by a need for warmth or safety. Regardless of the cause, having a bug in your ear is far from pleasant. It's crucial to remove the insect promptly to prevent potential hearing loss, ear damage, or infection.
Essential Steps
Eliminating the Intruder
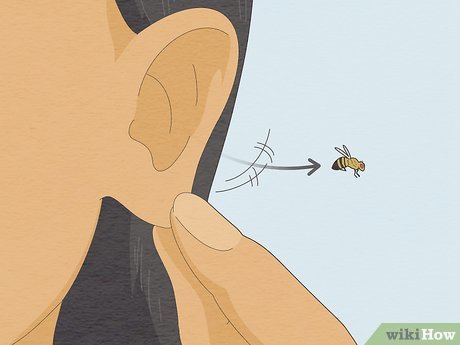
Adjust your head position and gently manipulate your ear with your fingers. One method to dislodge a bug from your ear involves utilizing gravity. Tilt your head towards the ground and gently wiggle your ear. Hold the outer part of your ear and give it a gentle shake. If the bug hasn't penetrated too deeply into your ear canal, it might dislodge on its own.
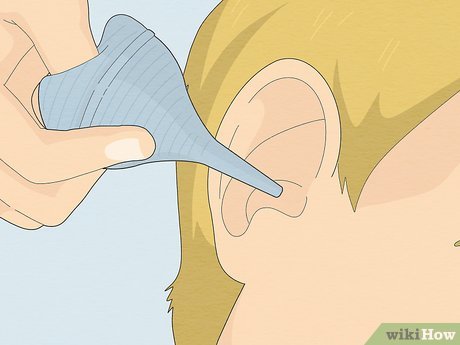
Flush the ear with warm water using a dropper or bulb syringe. Keep your head upright and gently pull the outer ear to straighten the ear canal. Administer a gentle stream of warm water into your ear. Tilt your head sideways to let the water drain out. Avoid irrigating your ear if you suspect a ruptured eardrum to prevent further damage.
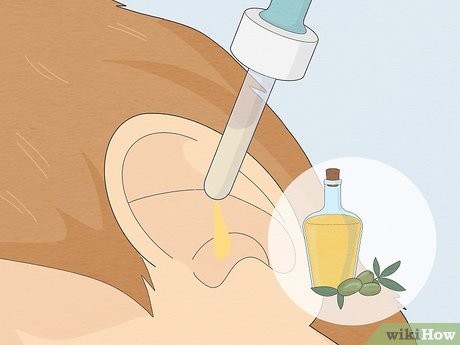
Utilize mineral oil to eliminate the bug. Apply a drop or two of mineral, baby, or olive oil into your ear canal to exterminate the insect. This can prevent irritation or potential eardrum damage caused by scratching or biting.
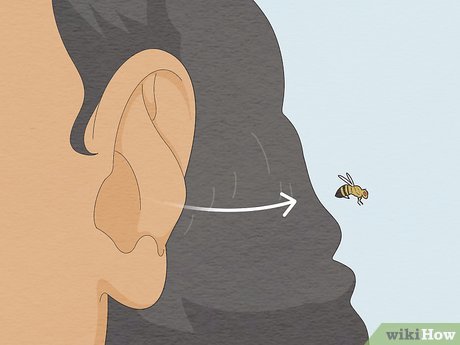
Allow the bug to exit naturally. If the bug is alive and not deeply lodged in the ear canal, it might exit on its own. Stay calm and refrain from inserting objects (such as fingers) into your ears; there's a chance the bug will find its way out on its own.

Seek medical assistance. A doctor will examine your ear closely using a specialized tool called an otoscope. Once the object is located, they may use a suction device, commonly employed for earwax removal, to extract the bug. Attempting this on your own could be risky, so it's essential to visit an emergency room or urgent care clinic and have a professional remove the bug.
Preparation
Determine if a bug has entered your ear. There are various reasons why your ears might feel sensitive, including allergies or weather changes. Symptoms of a bug in your ear may include pain, swelling, bleeding, or crackling sounds. You might also feel sensations of biting or stinging, along with potential hearing loss or dizziness.

Keep calm! While having a bug in your ear can be distressing, it's essential to remain composed. Being overly agitated could push the bug further into your ear, exacerbate the situation, or cause harm to the delicate inner ear or eardrum.
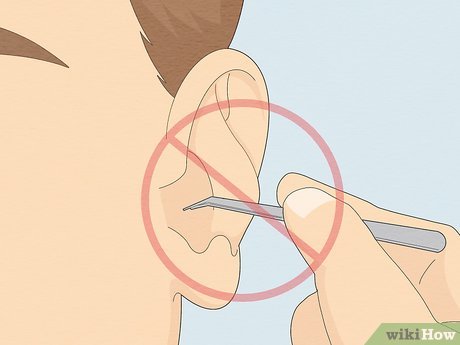
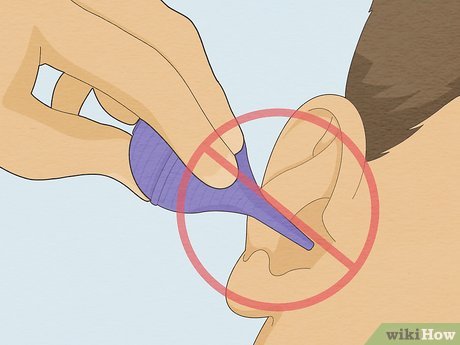
Avoid inserting objects into your ear. It's crucial not to push the bug deeper into your ear or risk accidental self-injury. The ear contains numerous nerve endings, and using tools like cotton swabs or tweezers can damage these nerves. Refrain from attempting to remove the bug forcibly.

Locate the bug. If the bug has reached your eardrum, it's advisable to seek professional help for removal. Ask someone to shine a flashlight or use a lighted magnifying glass to locate and identify the insect in your ear. This can aid in determining its precise location and species.
Adopt a comfortable position. Prior to removal, find a comfortable position. This could involve sitting in a relaxed manner with your head tilted to the side for easy access to the ear, or lying on your side with the affected ear facing upward for added comfort.
Recovery Process
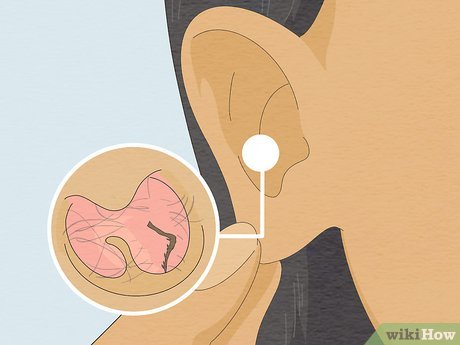
Examine the bug for any remaining parts. Ensure that you have extracted the entire bug from your ear. Leaving any remnants behind could lead to complications such as ear infections. Thoroughly inspect any objects removed from your ears.
Take it easy. The process of removing a live insect from your ear can be stressful. Flushing or suctioning your ears might induce slight dizziness due to pressure on the middle ear. Avoid sudden movements and strenuous activities for at least a day after the procedure.
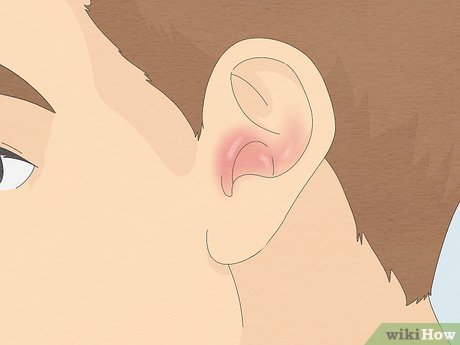
Be vigilant for signs of infection. The bug may have inflicted damage to your ear before its complete removal. Symptoms of an ear infection include pain, itching, swelling, and discharge. More severe indications may encompass dizziness, hearing impairment, and fever.

Schedule a follow-up appointment with a doctor. If you're uncertain whether you've eliminated the entire insect or concerned about infection, arrange a consultation with your primary care physician to ensure your well-being. They may refer you to an otolaryngologist, an ear specialist, for further diagnostic evaluation.
Useful Tips
Important Warnings
- Never attempt to remove an insect with tweezers, bobby pins, cotton swabs, or any other object. Doing so will only push the insect deeper into the ear canal, complicating removal further. It can also cause damage to the eardrum, resulting in permanent hearing loss.
