A Comprehensive Guide to Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Side Effects
Key Considerations
- To initiate testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), consultation and a prescription from your physician are imperative.
- TRT is indicated for individuals with abnormally low testosterone levels, certain medical conditions, or those undergoing gender transition.
- The approximate cost of TRT is $150-200 per dose, with potential side effects including reduced sperm count, skin irritation, urinary issues, and hair loss.
Procedure
Obtaining a Prescription for Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)

Consult Your Physician for a TRT Prescription: TRT medications require a prescription from a physician. Arrange a consultation with your doctor to discuss the possibility of TRT and determine its suitability for your condition. TRT is commonly prescribed for individuals experiencing:
- Testosterone levels below 300 nanograms per deciliter
- Klinefelter syndrome (an extra X chromosome in males)
- Testicular damage due to cancer or injury
- Individuals transitioning from female to male
- Various symptoms related to low testosterone, such as diminished libido or hair loss
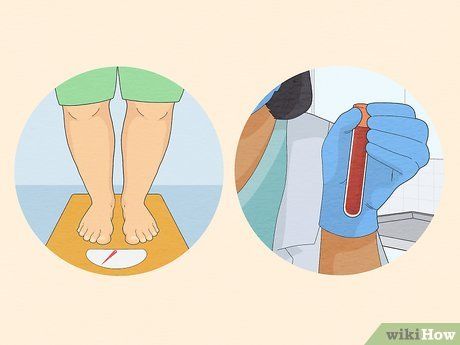
Undergo Physical Examinations and Blood Tests: Prior to commencing TRT, your doctor may conduct physical assessments and blood work to evaluate your suitability for treatment. These evaluations may include BMI measurement, testicular health checks, blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring, and testosterone level assessments. Blood tests may also assess other blood conditions like prolactin or hemoglobin levels, providing insights into your overall health status.
- Your doctor may request an MRI scan to examine your pituitary gland, responsible for testosterone regulation.
- Information about past medical conditions, surgeries, and specific symptoms will aid in accurate diagnosis.

Discuss Treatment Options with Your Physician: TRT offers various forms of administration, each with its unique advantages and considerations. Your doctor will discuss these options with you to determine the most suitable form of treatment based on your preferences and ease of use.
- Cost of TRT: Treatment expenses typically range from $150 to $200 per dose, influenced by medication type, supplier, and insurance coverage.
- TRT often requires ongoing treatment with regular checkups every 6-12 months.
- Individual responses to TRT vary, with noticeable changes potentially occurring within a week of treatment initiation.
Types of TRT

Topical Application: Referred to as 'transdermal,' this method involves using patches, gels, or creams applied to the skin. Typically worn for 4 days and may be covered with a bandage for enhanced efficacy.

Injectable: Administered by injecting testosterone under the skin using a syringe. Injections can provide short-term or long-term effects and are usually self-administered weekly, biweekly, or monthly based on individual requirements.

Oral Administration: Available in the form of an ingestible patch placed on the gums, releasing testosterone into the bloodstream over 12 hours. This method may be gentler on the liver but could lead to headaches or gum irritation.

Intranasal Application: Involves using a gel pumped into the nose via an applicator, typically done around 3 times daily. Some individuals may find this method uncomfortable and may opt for an alternative TRT form.

Pellet Implants: This involves the insertion of pelletized testosterone just beneath the skin of the buttocks or hip, often administered with numbing anesthesia for comfort. These pellets release testosterone gradually over 3-6 months, providing a long-term solution. They are commonly administered via injections.
Advantages, Side Effects, and Dangers of TRT
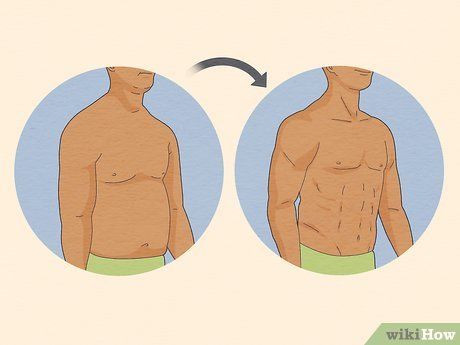
TRT could potentially alleviate various symptoms associated with low testosterone levels. Testosterone replacement therapy has the potential to alleviate or reverse many symptoms associated with testosterone deficiency, such as hair loss. Additionally, it may enhance libido, improve mood, reduce depressive symptoms, and boost overall energy levels. Furthermore, TRT may aid in increasing muscle mass and bone density if these are compromised due to low testosterone levels.
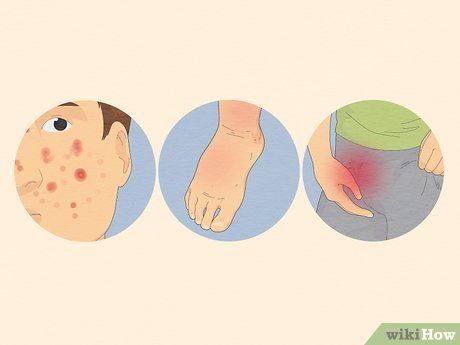
TRT may lead to adverse effects such as acne or exacerbation of sleep apnea. Despite its benefits, TRT carries certain risks. Some individuals experience adverse side effects during treatment, prompting them to discontinue TRT if these effects become severe. Other potential side effects of TRT include:
- Decreased sperm count or infertility
- Skin irritation
- Thinning hair
- Feelings of anxiety or irritability
- Swelling in the ankles or fluid retention in the joints
- Urinary issues resulting from prostate enlargement
- Enlarged or tender breasts
- Diminished testicular size
- Reduced sperm production
Avoid TRT if you have a history of prostate cancer or certain other medical conditions. If you have a history or increased risk of prostate cancer, your doctor may advise against TRT due to the potential exacerbation of this condition by elevated testosterone levels. Additionally, TRT may elevate the risk of certain diseases, particularly if you have a history of complications, including:
- Breast cancer
- Polycythemia (excess red blood cells)
- Urinary tract issues
- Heart failure
- Liver dysfunction
Indications and Origins of Low Testosterone
Signs of low testosterone encompass erectile dysfunction and hair loss. Testosterone plays a vital role in regulating numerous bodily functions, disruptions of which can occur due to low testosterone levels (also termed “hypogonadism'). To qualify for TRT, individuals typically need to exhibit low testosterone levels along with one or more symptoms associated with hypogonadism. Symptoms of hypogonadism may include:
- Diminished libido
- Episodes of hot flashes
- Decreased testicular size
- Low sperm count or infertility
- Memory impairment or difficulty concentrating
- Feelings of depression
- Enlarged breast tissue
- Increased body fat
- Loss of muscle mass or strength
- Reduced endurance
Hypogonadism may arise from disease or advanced age. Low testosterone is commonly categorized into “primary hypogonadism,” which involves physical abnormalities in the testicles affecting testosterone production, and “secondary hypogonadism,” which entails testosterone deficiency resulting from abnormalities in the hypothalamus or pituitary glands, responsible for hormone production and regulation. Prior to initiating treatment, your physician will ascertain the underlying cause of your hypogonadism. Notably, these conditions may stem from:
- Absence of testicles, or undescended testicles
- Various diseases, such as Leydig cell hypoplasia or Noonan syndrome (which causes delayed puberty)
- Testicular injury
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Sleep apnea
- Use of certain medications like psychoactive drugs or estrogen supplements
Natural Methods to Regulate Testosterone

Maintain balanced testosterone levels through a nutritious diet. Achieving natural testosterone balance is facilitated by maintaining a well-rounded diet, ensuring optimal bodily function to regulate testosterone effectively. Experts recommend consuming five servings of fruits and vegetables daily, complemented by starchy foods like potatoes, bread, or pasta. These should be supplemented with proteins such as beans, meat, or eggs, and small amounts of unsaturated oils like olive oil.
- Additionally, ensure adequate hydration by drinking at least 6-8 glasses of water daily to support optimal functioning of your endocrine system.
- Augment your diet with vitamin D and zinc supplements, adhering to your physician’s or the product’s dosage recommendations.
- To sustain healthier eating habits consistently, preplan your meals weekly, assigning specific recipes to each day and procuring groceries in advance to avoid reliance on takeout or less nutritious options.

Obtain a minimum of 5 hours of sleep per night to maintain favorable testosterone levels. Your body’s testosterone production is influenced in part by your sleep patterns. Research indicates that individuals sleeping less than 5 hours nightly may experience a 10-15% reduction in testosterone levels. Some experts recommend that adults aged 18 and above aim for 7-9 hours of nightly sleep to ensure adequate restfulness.
- To enhance sleep quality, consider indulging in a relaxing bath before bedtime or ingesting melatonin supplements in capsule or syrup form approximately 30 minutes before bedtime, adhering to the dosage instructions on the packaging. Melatonin, a natural sleep aid, is available over-the-counter.
Incorporate regular exercise or achieve weight loss to enhance testosterone levels. Studies indicate that testosterone levels are elevated following moderate- to high-intensity workouts. Furthermore, individuals with lower body weight often exhibit higher testosterone levels. Strive for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly, including activities like running, cycling, swimming, or engaging in active sports.
- To reduce body weight without exercise, endeavor to enhance your daily activity level by incorporating small, active movements throughout the day, such as opting for stairs over elevators, standing at your desk instead of sitting, or taking short 15-20 minute walks every few hours.
Minimize stress levels and refrain from drug or alcohol use. During periods of stress, the body prioritizes the production of certain hormones while suppressing others, including testosterone. Practice daily stress-relief techniques such as meditation or daily yoga. Moreover, prolonged alcohol consumption has been linked to decreased testosterone levels. Opt for non-alcoholic beverages and abstain from psychoactive drugs to maintain hormone balance.
Recommendations
-
Note that TRT is generally not prescribed to address natural age-related symptoms in otherwise healthy men, such as diminished muscle mass, decreased fertility, reduced libido, or hair loss.
