The liquid in lead-acid car batteries gradually diminishes over time, resulting in decreased battery performance and a shorter lifespan for your vehicle's battery. Monitoring your car battery's liquid levels and replenishing them when necessary is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Note that only distilled or deionized water should be used for refilling, as adding sulfuric acid can cause excessive corrosion.
Steps
Inspecting Water Levels

Put on protective eyewear and gloves. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working on your car battery. Use eyewear that fully shields your eyes, such as safety glasses or goggles, and gloves that provide complete hand protection, such as latex gloves or heavy-duty work gloves. Note that only maintainable batteries are refillable, so check the warning labels to ensure yours is not maintenance-free. If labeled 'DO NOT OPEN,' do not attempt to refill the battery. Perform this task with the car turned off, and exercise caution around hot engine components.
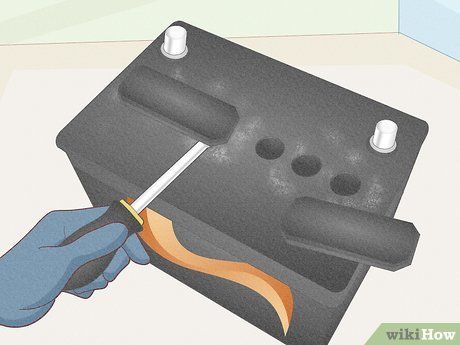
Lift up the 2 rectangular cell port covers using a flat-head screwdriver. Insert the flat edge of the screwdriver beneath one cover and lever it to remove the cap. Repeat this for the second rectangular cover. Each rectangular cover conceals 3 cell ports, which are used to check water levels inside.

Remove the 6 round cell port covers by twisting them off. Begin at one end of the row of cell ports and rotate the cap counterclockwise until it loosens. Repeat this process for each of the remaining 5 cell port covers. Car batteries with round covers have the same number and type of cell ports as those with rectangular covers; only the style of cover differs.

Clean the area around the cell ports with a damp cloth. Drench a clean cloth in water and squeeze out excess moisture until it's damp. Wipe the cloth over the battery surface around the cell ports to remove accumulated dirt and grime. Cleaning the battery surface helps prevent corrosion and keeps debris from entering the cell ports during refilling.
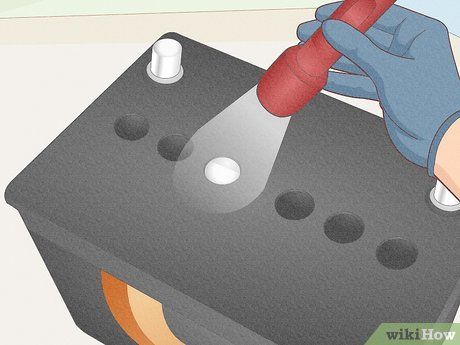
Inspect each cell to ensure the metal plate is submerged in water. Examine each cell port carefully and refill any cells where the metal plate is exposed. The standard water level is approximately 3/4 below the top of the cell. If all plates are submerged, there's no need for immediate refilling. Use a flashlight for better visibility inside the cells if needed.
Adding Water

Ensure your car battery is fully charged before adding water. This prevents overfilling the cells. Run your car for approximately 30 minutes or use a charger to fully charge the battery. Keeping your lead-acid car battery charged also extends its lifespan. Remember to turn off your car before adding water.

Use only distilled or deionized water to refill your car battery. Avoid tap water as it contains minerals that can harm your battery. Distilled and deionized water are mineral-free and safe for batteries. Never add sulfuric acid to your battery, as it disrupts the balance and causes rapid corrosion.

Refilling a car battery is straightforward yet essential. Always use distilled or deionized water to prevent damage. Ensure your car is turned off before starting. Utilize a turkey baster or funnel to add sufficient water to cover the exposed plates in each cell. Never attempt to add sulfuric acid.

Cover each exposed plate with water using a turkey baster or small funnel. Extract water from your bottle of distilled or deionized water using a turkey baster and add just enough to cover the plate in each battery cell. Alternatively, insert a funnel into each cell port and pour in enough water to cover the plate. Avoid overfilling the cells, as this can lead to leaks and corrosion. About 3/4 of the way down from the top of the cell is the ideal water level. If you overfill, use a turkey baster to remove the excess.
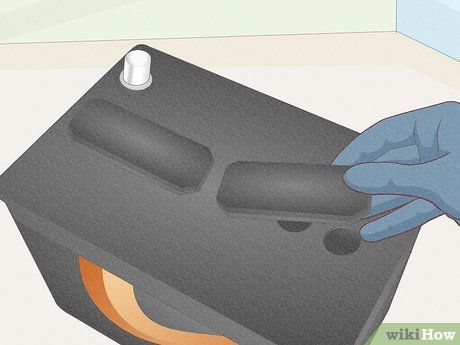
Replace the cell port covers. Snap rectangular caps securely over 3 cell ports or twist round caps over each cell port until tight. Double-check that all caps are firmly in place before starting your car.
References
- ↑ https://www.crownbattery.com/news/watering-your-lead-acid-battery-the-basics
- ↑ https://images.homedepot-static.com/catalog/pdfImages/bb/bbdc5178-a8c3-4815-9eaa-b65509a1b713.pdf
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3BUHnykZvU&feature=youtu.be&t=113
- ↑ https://www.autoblog.com/2016/04/08/how-to-check-electrolyte-levels-in-your-battery/
- ↑ https://northeastbattery.com/water-battery-basics/
- ↑ https://antiquecars.info/how-to-check-old-classic-cars-battery-water-levels-refill/
- ↑ https://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/water_loss_acid_stratification_and_surface_charge
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pesiwyi9uWk&feature=youtu.be&t=73
- ↑ https://www.autoblog.com/2016/04/08/how-to-check-electrolyte-levels-in-your-battery/
- ↑ https://www.popularmechanics.com/cars/car-technology/a26549/car-battery-how-to/
- ↑ https://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/water_loss_acid_stratification_and_surface_charge
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pesiwyi9uWk&feature=youtu.be&t=90
- ↑ Jason Shackelford. Auto Technician. Expert Interview. 11 June 2019.
Tips
-
Reviving an aging car battery by topping it up with water might offer a temporary solution, but it's often a sign that a replacement is imminent.
Warnings
- Never introduce sulfuric acid to your car battery as it disrupts the battery's equilibrium and accelerates corrosion.
- Ensure to refill your car battery on a level surface to ensure proper water level distribution.
- Diagnosing battery issues at home can be challenging and unreliable. Most auto parts stores and some repair shops offer complimentary battery testing services.
Things You’ll Need
- Protective eyewear
- Gloves
- Turkey baster or funnel
- Distilled or deionized water
- Flat-head screwdriver
- Flashlight (optional)
