Learn how to set up two different operating systems on your desktop or laptop.
Essential Information
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Follow These Steps
Learn the Art of Crafting Bootable Drives
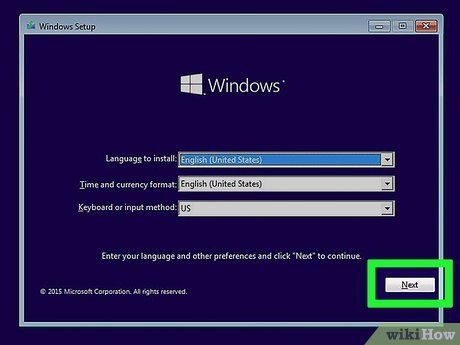
Initiate Windows Installation. Before delving into other operating systems, it's imperative to lay the foundation with Windows. Operating systems like Linux are designed to complement Windows seamlessly. For a smooth experience, prioritize Windows installation on your PC.
- An exception arises when aiming to dual-boot Windows with macOS on a Mac. Macs, with their unique architecture, usually ship with macOS pre-installed.
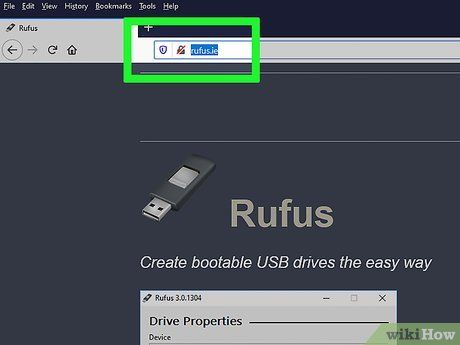
Visit https://rufus.ie/ using your preferred web browser. This website hosts Rufus, a utility instrumental in crafting USB install drives for operating system installations.
- You can also resort to official install CDs or DVDs.
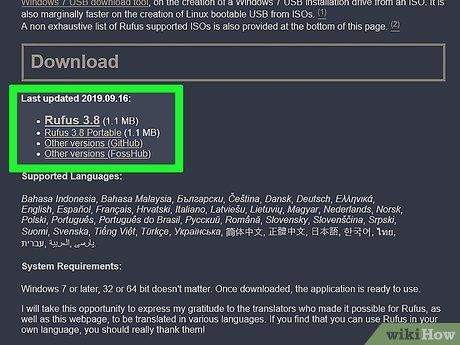
Fetch and Deploy Rufus. Follow these steps meticulously to acquire and deploy Rufus from the designated download page.
- Scroll and select Rufus 3.8
- Execute 'Rufus-3.8.exe' either directly from your browser or your Downloads directory.
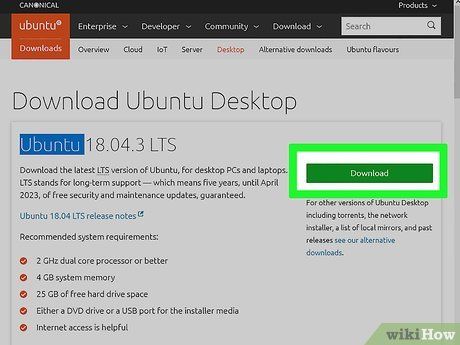
Acquire a Disk Image (ISO) for Your Desired Operating System. A disk image encapsulates data for an install disk, DVD, or USB drive. Visit the respective website of your chosen operating system to procure the ISO file. Below are some links offering operating system ISO images:
- Windows 10
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
- Ubuntu
- Linux Mint
- Debian
- Installing macOS on a non-Apple device presents complexities compared to other operating systems but remains plausible.
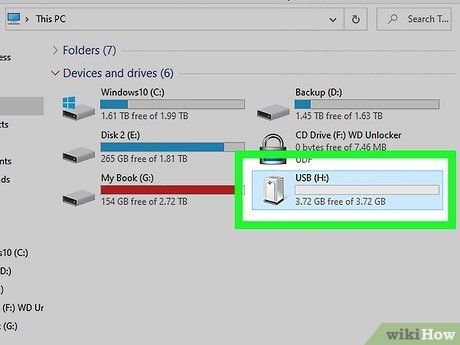
Prepare a Fresh USB Flash Drive.
Launch Rufus.
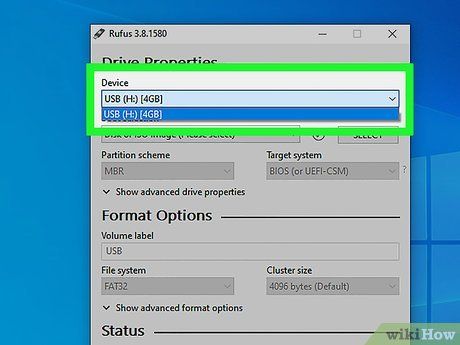
Designate Your USB Flash Drive.
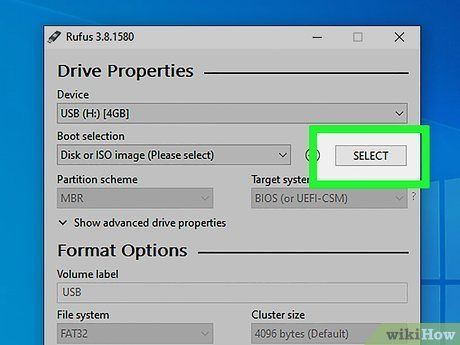
Tap on Choose.
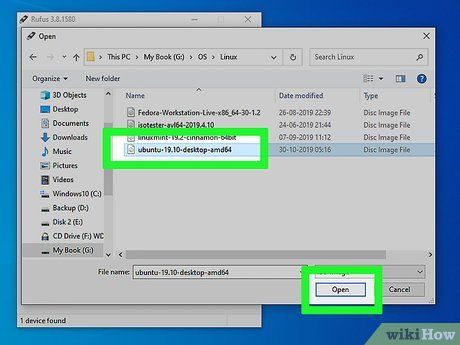
Select Your OS ISO and Hit Unveil.
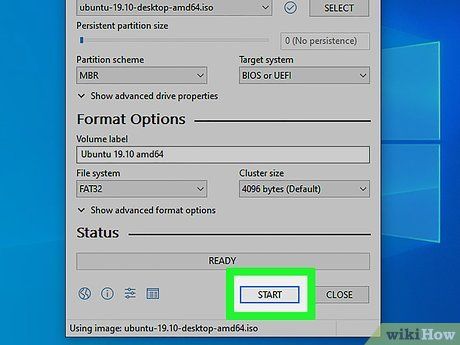
Initiate the Process by Clicking Start. Situated at the bottom right of Rufus, this action initiates the process of transferring the ISO file to the USB drive. Expect some waiting time for completion.
Initiate a New Partition
Secure vital data files. Although partitioning a disk drive and installing a new operating system typically preserve data, it's wise to create backups beforehand. This precaution ensures data safety in case of unforeseen mishaps.

Click on Access Disk Management. Locate this option by right-clicking on the Windows Start menu. It grants entry to the Disk Management window.
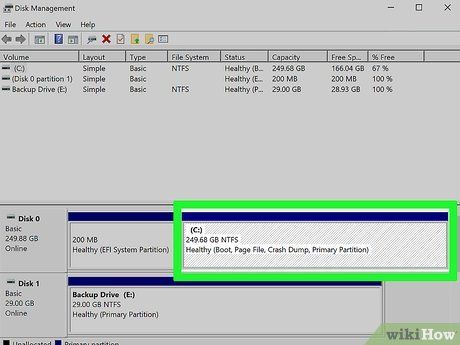
Right-click on your Windows system drive. Typically denoted as the 'C:' drive, this is where Windows is installed.
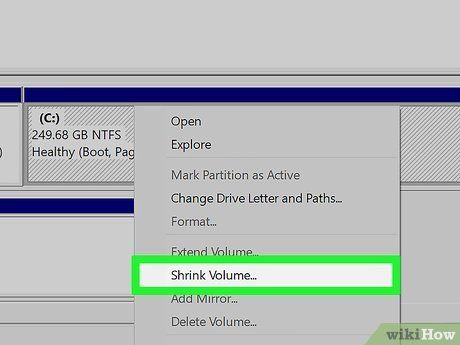
Opt for Shrink Volume. Locate this within the disk management menu, accessible via right-clicking on a disk drive.
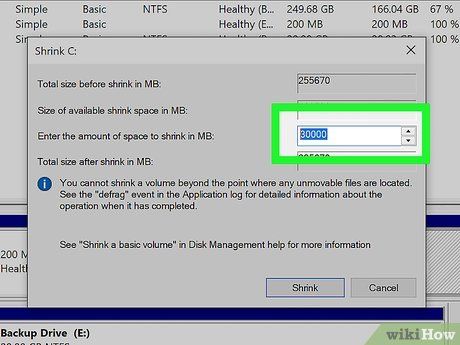
Specify the Allocated Space. Input the desired amount of megabytes (MB) for partitioning, ensuring it meets the minimum requirement for the new OS installation.
- To convert GB to MB, multiply by 1000. For instance, 40 GB equals 40,000 MB.
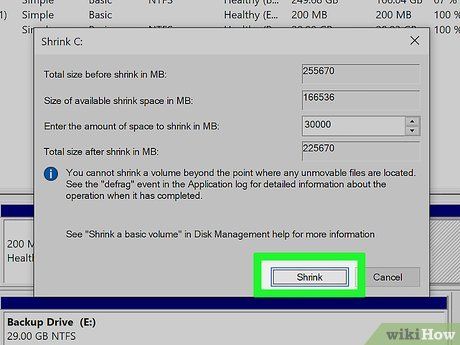
Initiate Shrink. This action generates a new partition of unallocated space on your hard drive.
Ready Your PC
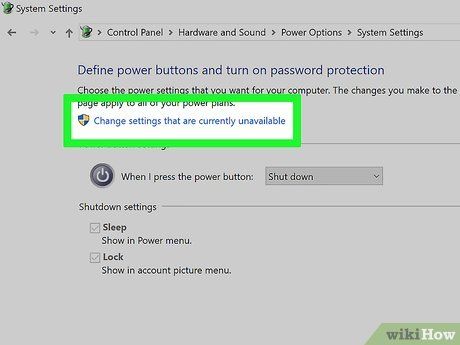
Disable Fast Boot. Follow these steps to deactivate Fast Boot on Windows.
- Access the Windows Start menu.
- Search for Control Panel and select its icon.
- Type Power Options in the upper-right search bar.
- Choose 'Choose what the power button does'.
- Opt for 'Change settings that are currently unavailable'.
- Ensure the checkbox next to 'Turn on fast startup (Recommended)' is unchecked.
- Click Save changes.

Access Your PC's BIOS. You must adjust the BIOS settings to accommodate a second operating system. The method varies depending on your computer's make and model. On startup, try pressing function keys (F1, F2, F9, F12), Esc, or Delete. Alternatively, reboot into the BIOS from within Windows:
- Open the Windows Start menu.
- Click the Power icon.
- Hold down 'Shift' and click Restart.
- Select Troubleshoot.
- Choose Advanced Options: UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Click Restart.
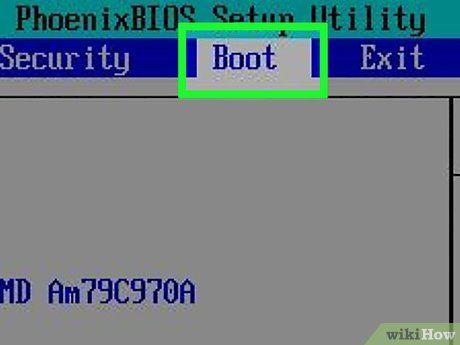
Deactivate Secure Boot. BIOS menus differ among computer models. Use your keyboard's arrow keys to navigate. Secure Boot is typically found in the Security, Boot, or Authentication menu. Locate it and set to 'Disabled'.
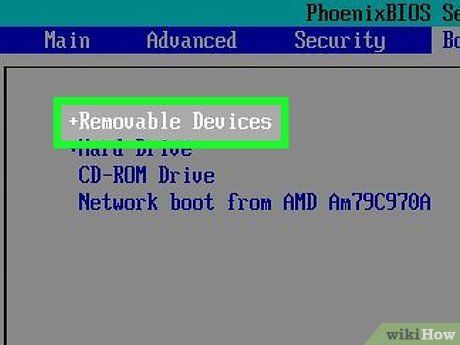
Prioritize Booting from USB. Access the Boot menu where you can typically set boot order. Ensure USB drive is first. If using a CD or DVD, set CD/DVD-ROM as primary boot source.
- For CD/DVD installation, ensure CD/DVD-ROM is the primary boot source.
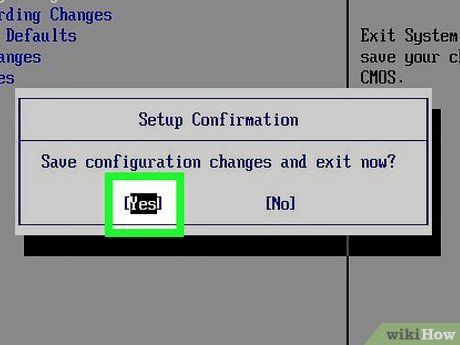
Save BIOS Changes. After modifying BIOS settings, locate the option to save changes. Select it to save and exit BIOS, prompting your computer to reboot.
Execute OS Installation. Proceed with installing the operating system now that BIOS settings are adjusted accordingly.
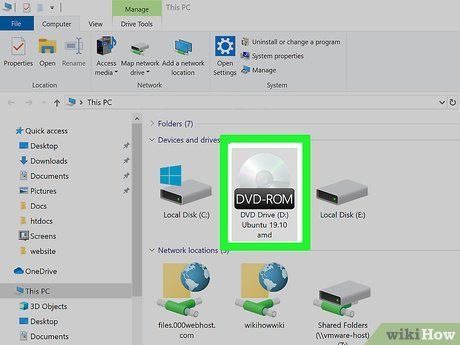
Introduce the Installation Disk. If you've crafted a USB installation disk via Rufus, plug it into an available USB port. Alternatively, insert a CD or DVD installation disk into your CD/DVD-ROM drive.
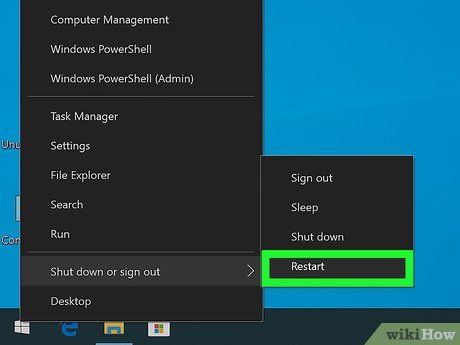
Reboot Your System. If your computer is already powered on, initiate a restart. Otherwise, press the power button to boot from the installation disk.
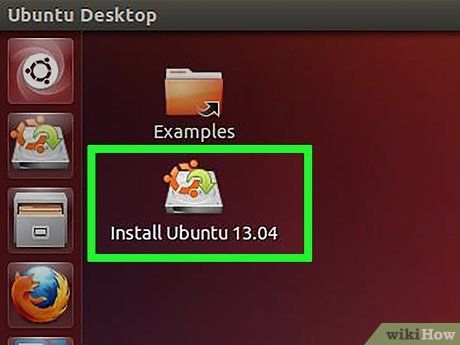
Await Setup Program Loading. Upon successful booting from the installation disk, the operating system's setup program should become visible.
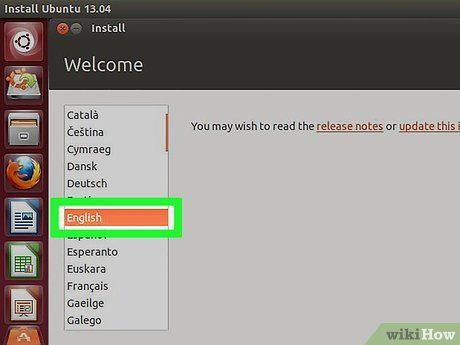
Choose Language and Keyboard Settings. Each operating system's setup program varies slightly. Generally, commence by selecting your preferred language and keyboard layout.
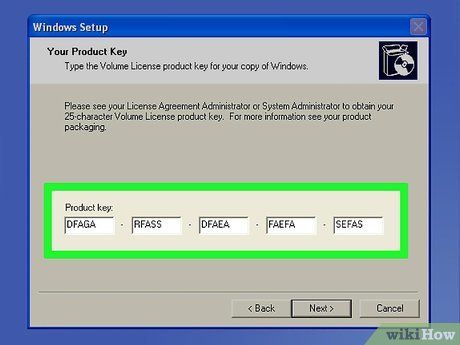
Input CD Key or Serial Number (if Required). While some OS like Ubuntu are free, others like Windows necessitate a purchased CD key or serial number. If prompted, provide the requisite serial number or CD key in the designated field.
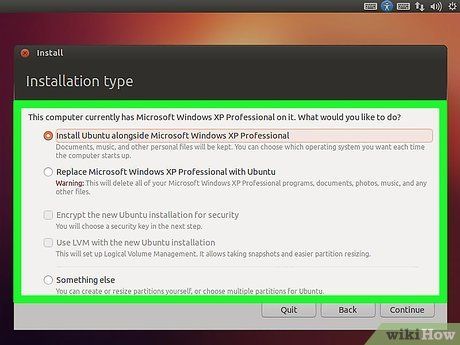
Opt for the 'Custom' or 'Other' Installation. When prompted to choose the installation type, select 'Custom', 'Other', 'Something Else', or a similar option. Opting for a standard installation might overwrite your current operating system.
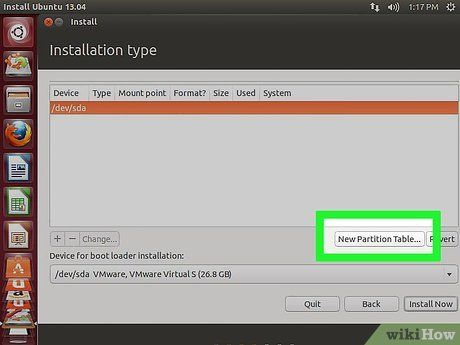
Format the Desired Drive. During the new OS installation, you'll be prompted to select and format the drive. Choose the previously partitioned unallocated space.
- If installing Linux, format the drive as Ext4.
- For Ubuntu installation, also format a portion of the unallocated space as a swap area. This area's size should match your computer's RAM capacity.
Complete Installation by Following Instructions. You'll likely need to create a username, password, and set time/date settings for your new OS. Simply follow the on-screen instructions to finish the installation process.
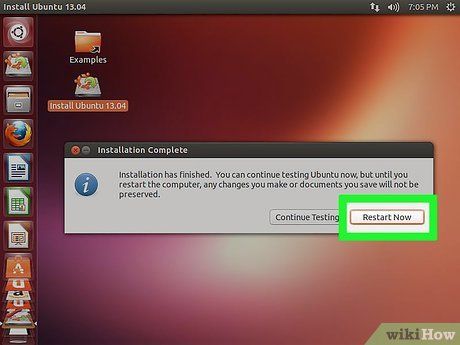
Reboot to Switch OS. After installing multiple operating systems, a menu will appear during boot-up, allowing you to select your desired OS. Restart your computer to switch between them.
Handy Tips
-
Installing a new OS on a fresh computer is straightforward as there's minimal backup/reinstallation. However, some preinstalled OSs lack necessary drivers. Ensure you have them before proceeding.
-
Certain OS pairs can coexist on a single partition, while others require separate partitions. Refer to their documentation or allocate separate partitions accordingly.
-
When installing multiple Windows versions, it's advisable to start with the older version.
Precautions
- Ensure you genuinely need both OSs before proceeding with installation.
- Backing up your files is highly recommended before installing a second OS.
Essentials
- Prepare a USB Flash Drive or installation disk for the second OS.
- Ensure your computer has sufficient hard drive space for the second OS installation.
