A scientific calculator simplifies common calculations with its versatile functions. Although each calculator varies slightly, they all encompass essential features required for middle and high school mathematics. Once you grasp its functionalities, it becomes a valuable tool for achieving success in math.
Step-by-Step Guide
Primary Operational Functions
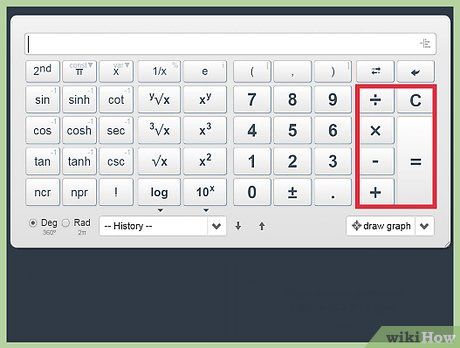 Utilize basic operation symbols for performing fundamental calculations.
Utilize basic operation symbols for performing fundamental calculations.
Modify the sequence of operations using the parentheses keys. This action supersedes the calculator’s default order of operations.
- Press the opening parentheses before entering the first number, and the closing parentheses after entering the last number. The calculator will prioritize this calculation before processing subsequent functions.
- If necessary, nest parentheses, ensuring you can manage them effectively.
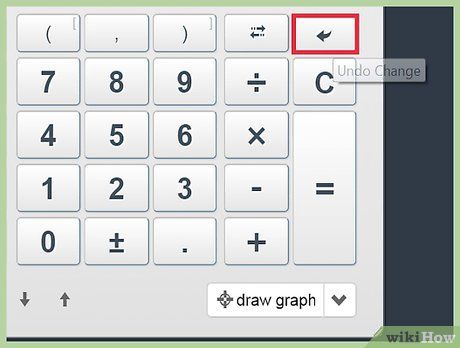 Rectify errors in your calculations.
Rectify errors in your calculations. Clear your calculations.
Clear your calculations.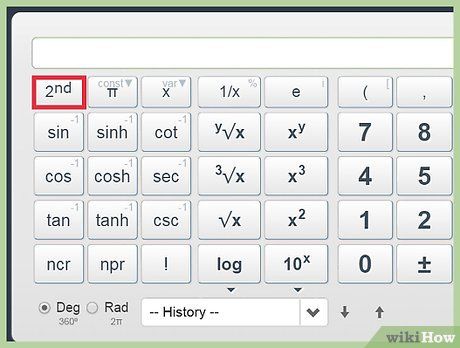 Discover the full range of functions available on the calculator.
Discover the full range of functions available on the calculator.Essential Algebraic Functions
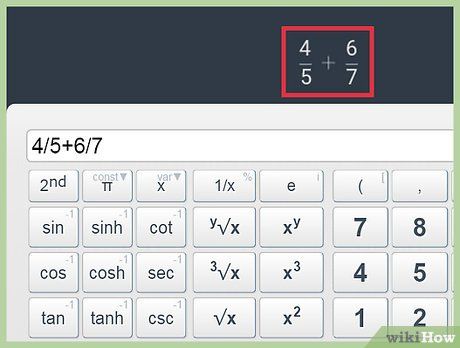 Form a fraction.
Form a fraction.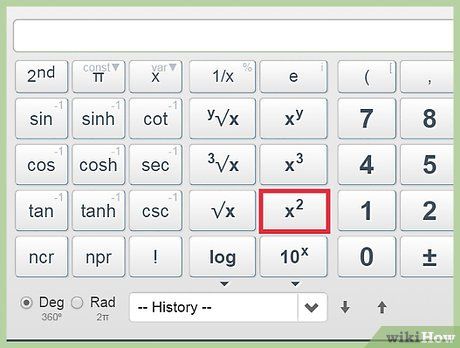 Find the square of a number.
Find the square of a number.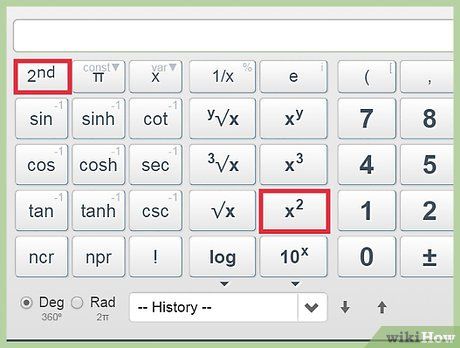 Calculate the square root.
Calculate the square root.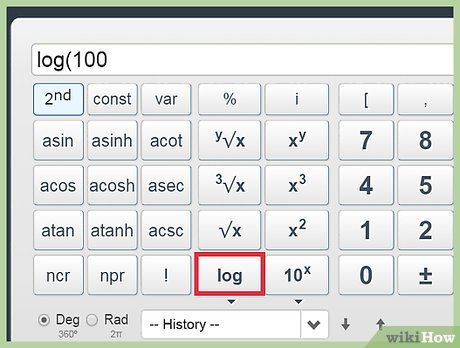 Determine logarithms.The logarithm of 100 to the base 10 is:
Determine logarithms.The logarithm of 100 to the base 10 is: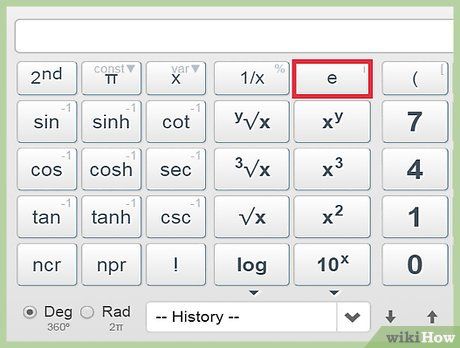 Employ the exponential function.The expression for e raised to the power of x:The second natural logarithm:The natural logarithm of 1, the second natural logarithm, and the natural logarithm of 1:
Employ the exponential function.The expression for e raised to the power of x:The second natural logarithm:The natural logarithm of 1, the second natural logarithm, and the natural logarithm of 1: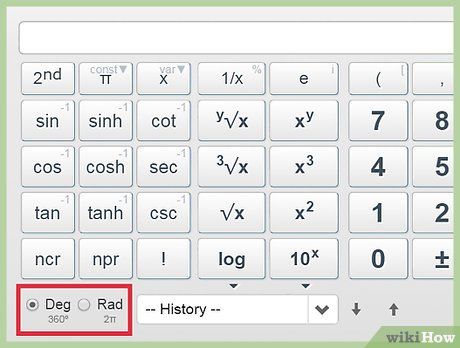 Determine trigonometric functions.The system of angular measurement: degrees, radians, and grads.The sine function at 60 degrees:
Determine trigonometric functions.The system of angular measurement: degrees, radians, and grads.The sine function at 60 degrees: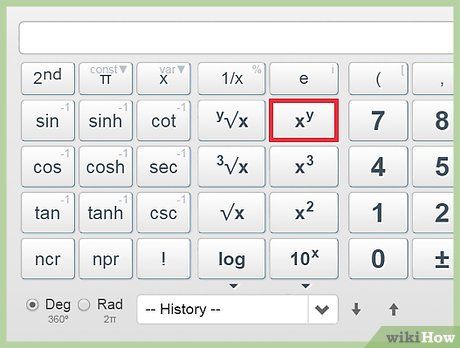 Compute the reciprocal of a given value.The expression for the reciprocal of x:The expression for the reciprocal of x:The equation 3 times the reciprocal of x:
Compute the reciprocal of a given value.The expression for the reciprocal of x:The expression for the reciprocal of x:The equation 3 times the reciprocal of x:Helpful hints:
Tips for calculator usage:
