Surgical masks, more commonly known as medical masks, are primarily utilized by healthcare professionals to safeguard themselves and others from the transmission of airborne infectious diseases, bodily fluids, and particulate matter. During outbreaks of contagious illnesses, public health agencies may also advise the general public to wear surgical masks for added protection. These masks are typically designed to fully cover both the nose and mouth.
Steps to Follow
Comprehending Medical Masks
Note: Although a medical mask can block most particles, small-sized particles may still penetrate it due to the mask not being sealed against your skin. Consequently, particles can also enter through any openings in the mask.

- While an N95 respirator can block 95% of particles as small as 0.3 microns, there remains a 5% chance that harmful particles may penetrate the respirator.
- N95 respirators are not suitable for children or individuals with facial hair.
- Some N95 masks include an exhalation valve designed to reduce condensation within the mask and facilitate easier breathing. However, these masks should not be used in sterile environments as the valve allows unfiltered air to exit the mask.
- Each type of N95 mask typically comes with detailed instructions from the manufacturer on how to properly wear and remove it. Following these instructions is crucial to ensure proper protection for both the wearer and others. Additionally, OSHA mandates that users receive training on how to properly fit and use N95 respirators.
Donning a Mask

- Apply soap to your wet hands and rub them together for at least 20 seconds before rinsing.
- Use a clean paper towel to dry your hands, and dispose of it in a trash bin afterward.
Tip: After washing your hands, use the paper towel to open or close doors before discarding it.
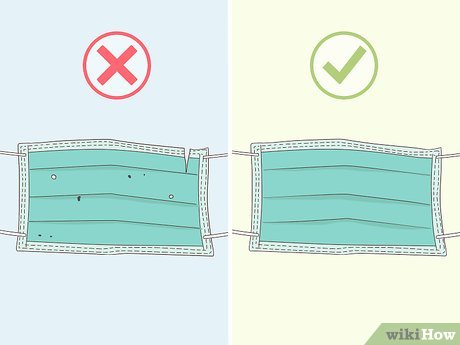

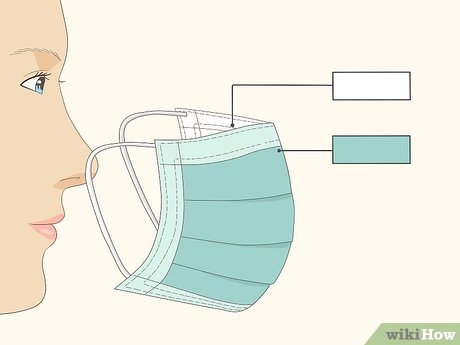
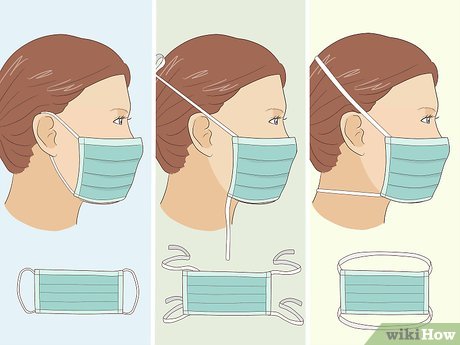
- Ear Loops: Some masks feature elastic ear loops on both sides. Hold the mask by the loops, place one loop around each ear.
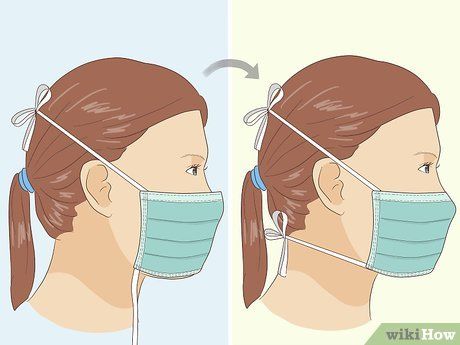
- Ties or Straps: Some masks come with fabric ties that are fastened at the back of your head. Hold the mask by the upper ties, secure them at the back of your head, and tie them together.
- Bands: Some masks have elastic bands that go around the back of your head instead of the ears. Position the mask in front of your face, pull the top band over your head, and place it at the crown. Then pull the bottom band over your head and position it at the base of your skull.
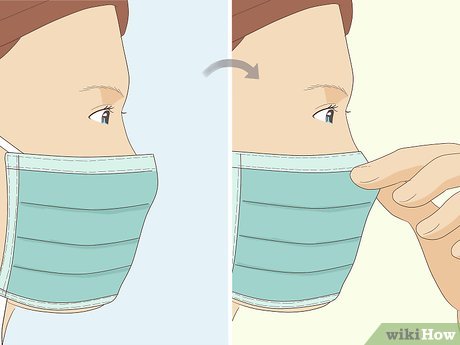
- If you've already tied the bottom straps, you may need to retighten them for a better fit.



Global Public Health Agency
Expert Advisory: Masks are effective only when used along with frequent hand-cleaning using alcohol-based hand rub or soap and water.
Removing a Mask

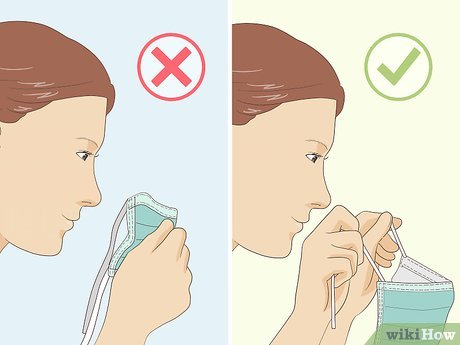
- Ear Loops — Hold the ear loops and remove them from each ear using your hands.
- Ties/Straps — Untie the bottom straps first, followed by the top straps, while holding the top ties.
- Bands — Lift the bottom elastic band over your head, then repeat with the top elastic band. Remove the mask while holding the top elastic band.

- In medical environments, there is usually a dedicated bin for disposing of biohazardous items such as used masks and gloves.
- In non-medical settings where the mask could be contaminated, place the mask inside a plastic bag, tie it securely, and then discard it in the trash bin.

Recommendations
- It is advisable to use soap and water whenever handwashing is necessary. However, if soap and water are unavailable, you can use a hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol. Make sure to rub your hands together for more than 10 seconds until they are dry.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides detailed information on medical masks and N95 respirators at http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npptl/topics/respirators/disp_part/respsource3healthcare.html. This resource includes photos of different mask types, comparisons, and a list of FDA-approved mask manufacturers.
Precautions
- Medical masks and N95 respirators are currently in short supply and should be reserved for medical professionals.
- Medical masks are single-use items intended for individual use. After being worn, they should be discarded and not reused.
- Various types of masks designed for non-medical purposes are available in hardware stores. These masks protect against dust particles during woodworking, metalworking, or other construction activities. They are not regulated by the FDA and are not suitable for medical use.
- Currently, the World Health Organization (WHO) does not recommend wearing face masks unless you are sick or caring for someone with COVID-19.
