You might be aware that sea cucumbers are soft-bodied creatures, a rich resource with many essential nutrients for the body such as selenium, choline, collagen, protein, fat, calcium, sugar... Sea cucumber is also a key ingredient in making salads, Vietnamese salads...
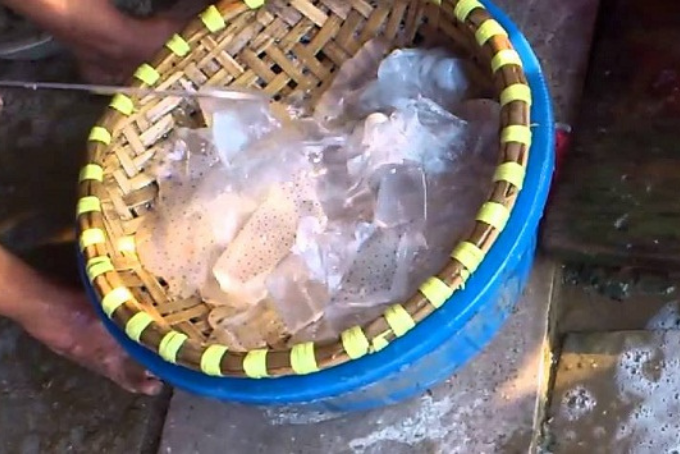

Is eating sea cucumber good for you - Benefits of sea cucumber
Sea cucumbers are not only processed into many delicious and attractive dishes but also considered effective medicinal support for treating diseases. However, we should also be cautious when consuming sea cucumbers as there may be some unexpected health risks.
1. Is Sea Cucumber Consumption Beneficial - The Effects of Sea Cucumber
Is Sea Cucumber Consumption Beneficial?
Sea cucumber is an aquatic animal capable of movement underwater by contracting and pushing water through its mouth while being able to move forwards or backwards. On average, 100g of sea cucumber contains 12.3g of protein, 0.1g of fat, 182mg of calcium, 3.9g of sugar, 132mg of iodine, 9.5mg of iron, and various other vitamins and trace elements.
The Benefits of Sea Cucumber Consumption
- Enhances overall health by providing a rich source of essential nutrients: Protein, antioxidants, and a small amount of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, choline... Additionally, jellyfish contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, essential for daily dietary intake. These unsaturated fatty acids can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Jellyfish also boasts a high level of polyphenols, natural compounds with powerful antioxidant properties. These nutrients are beneficial for brain function, protecting the body against chronic diseases such as cancer and type 2 diabetes.
- Supplies selenium to the body, a nutrient crucial for antioxidant defense, protecting cells from oxidative stress and preventing diseases like Alzheimer's. Selenium plays a vital role in metabolism and thyroid function.
- Increases choline intake in daily diet: Choline, an essential nutrient often lacking in many diets, is abundant in 58g of dried jellyfish, providing 10% of the daily nutritional value. This nutrient supports DNA synthesis, nervous system function, and lipid production for cell membranes. It enhances cognitive processing, memory retention, and helps alleviate anxiety.
- Provides abundant collagen for the body: Collagen, a crucial protein for the structure of liver, skin, and bones. The collagen content in jellyfish offers numerous benefits such as improving skin elasticity, reducing joint pain, antioxidant properties, and significant blood pressure reduction. Additionally, jellyfish collagen protects cells from harmful sun rays, enhances wound healing, and aids in treating joint inflammation.
- Jellyfish also aids in treating conditions like blood stasis causing fever, acne, cough, constipation, and muscle fatigue...
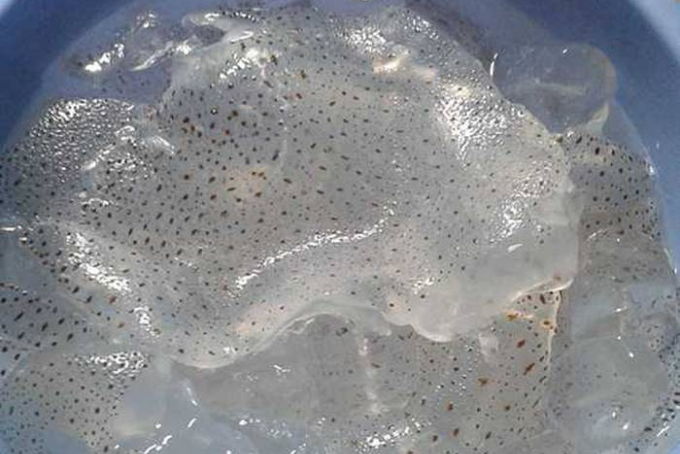

Benefits of Eating Jellyfish
Risks Associated with Consuming Jellyfish
While jellyfish offer numerous beneficial nutrients for human health, they also pose certain risks that should be avoided during processing and consumption.
- Allergic reactions: Jellyfish are generally safe for most people, but some may experience adverse reactions even after thorough preparation and cooking.
- Bacteria and pathogens: Improper cleaning and processing of jellyfish can lead to the presence of harmful bacteria or pathogens, posing health risks to consumers.
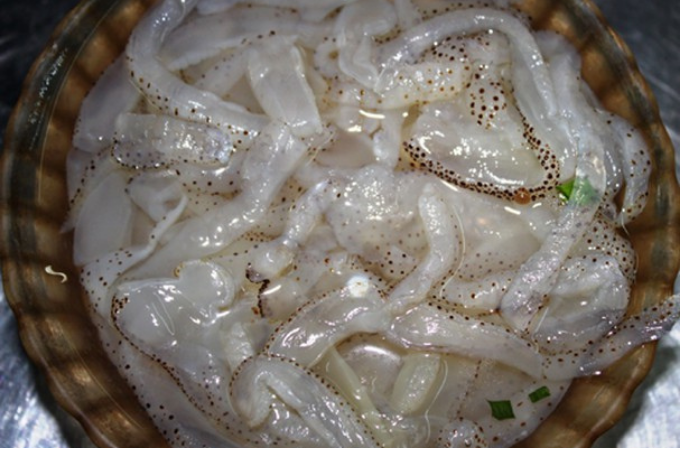

Risks Associated with Consuming Jellyfish
- High aluminum content: During the processing of jellyfish, alum is often used to clean and reduce its sliminess. Alum, chemically known as potassium aluminum sulfate, is used as a food preservative. Although certified safe, residual aluminum in jellyfish remains a concern. Excessive dietary aluminum may lead to Alzheimer's disease and appendicitis. Therefore, caution is advised during jellyfish preparation.
2. Safe Ways to Consume Jellyfish
- Jellyfish can spoil quickly at room temperature, so it's essential to clean and store them properly upon purchase. Typically, jellyfish are preserved using a mixture of alum and salt to disinfect and adjust the pH of the flesh while maintaining its texture. When cleaned and processed correctly, jellyfish are less likely to harbor harmful bacteria or pathogens. Therefore, it's recommended to consume jellyfish only when they have been thoroughly cleaned and processed.
- When selecting fresh jellyfish, choose ones with thick, pinkish-white flesh, resembling salt crystals, firm texture, no signs of leakage, and no stickiness. Avoid brownish jellyfish as they indicate spoilage and may pose health risks.
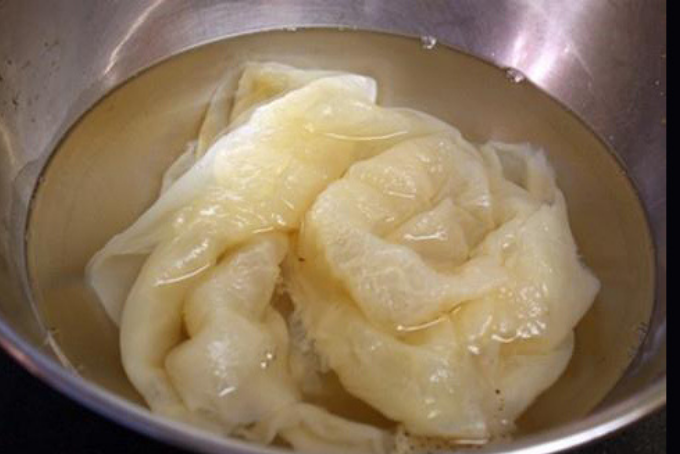

Safe Ways to Consume Jellyfish
- For dried or frozen jellyfish, ensure clear origin, expiration date, and transparent manufacturer information.
- Fresh jellyfish processing: Upon bringing fresh jellyfish from the sea, clean them thoroughly, remove toxins from the bell, then cut them into small pieces. Rinse the jellyfish with salt and a bit of alum, soak for 15 - 20 minutes. Repeat this process 3 - 4 times to ensure thorough cleaning. Additionally, coastal residents often use guava leaves or crushed seashells to rinse jellyfish, making them safer than using alum.
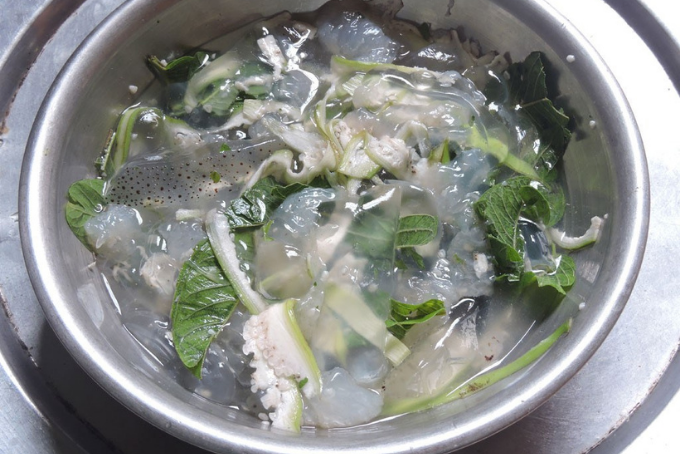

Soaking Jellyfish to Remove Mucus and Disease-Causing Bacteria
- Once the jellyfish turns pale yellow after soaking, remove it and soak in cold water for 15 minutes to prevent excessive saltiness. Then drain and rinse the jellyfish again, cut into bite-sized pieces, and blanch with boiling water.
3. Some Considerations When Eating Jellyfish
- Due to its cooling nature, jellyfish should be consumed cautiously by individuals with cold constitutions or digestive issues.
- It's not advisable for children to consume jellyfish, even if prepared meticulously, to avoid the risk of poisoning or other health issues due to their weaker immune systems.
- Never use fresh jellyfish without proper safe processing to eliminate toxins.
- If stung by a jellyfish while swimming in the sea, apply fresh jellyfish meat to the affected area to alleviate redness and itching. Then clean the area with sea spinach, chew and swallow the juice, and apply the remaining residue directly to the itchy spot.
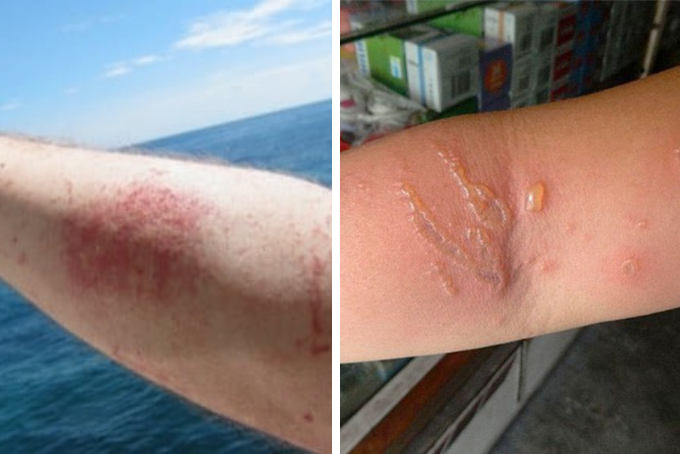
Risks of Touching Jellyfish
- Avoid contact and handling of jellyfish tentacles carefully as they contain numerous toxins, nematocysts, which are the jellyfish's self-defense mechanism.
- It's advisable to clean and rinse jellyfish multiple times with diluted saltwater and alum until it turns pale yellow before proceeding with the cooking process.
Through this article, we have gained insights into the questions: Is eating jellyfish good? What are the benefits of jellyfish? How to properly process jellyfish? The safest and most delicious way to consume jellyfish.
