Add your computer to an Active Directory domain with this concise guide. Do you need to link a computer or server to your organization's Active Directory domain? To join a domain on Windows 10, Windows 11, and earlier versions, you'll require the Pro, Education, or Enterprise edition of the operating system. On a Mac, you can join a domain using the Directory Utility tool. This guide will walk you through the process in a few simple steps.
Things You Should Be Aware Of
- In Windows, join a domain via System Properties (sysdm.cpl) > Change > Domain. You'll need administrator access on the computer and an account with appropriate permissions on the domain. On a Mac, navigate to Directory Utility > Services, and choose Active Directory to input the domain information.
Steps to Follow
Configuring with Windows
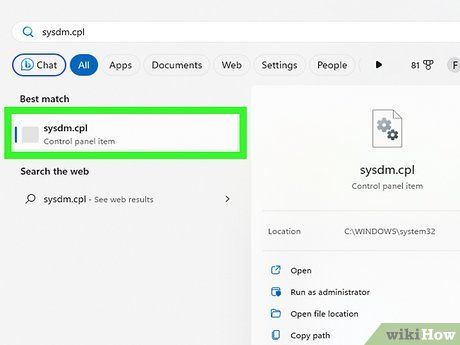
Access the System Properties panel. This can be done on any Windows version, including Windows 11 and Windows 10, directly from the Windows search bar. Here's how:
- Click the search bar or magnifying glass at the bottom of the screen or press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type sysdm.cpl and hit Enter.
- The System Properties panel will open automatically to the Computer Name tab.
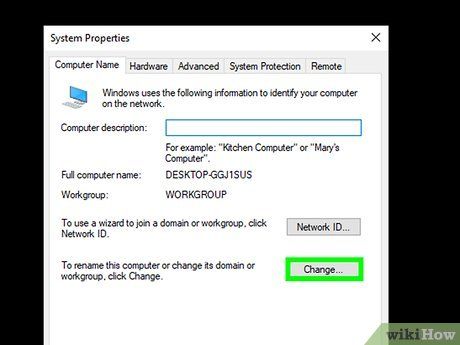
Click on the Change… button. Located in the lower-right corner.
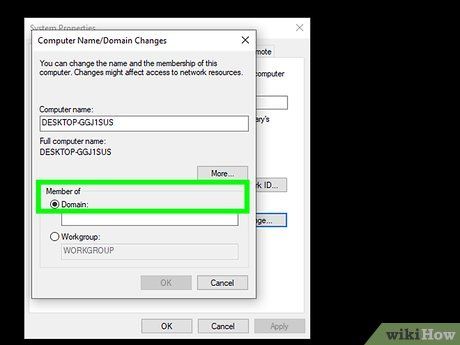
Choose the Domain option. This option is found below the 'Member of' section at the bottom of the pop-up window.
- If the option is grayed out, your Windows version might not support joining a domain. You'll need Pro, Enterprise, Education, or Ultimate (for Windows 7 and earlier) to do so.
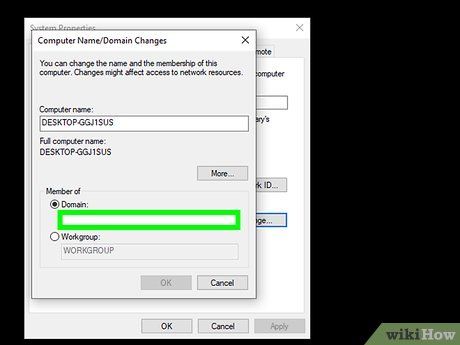
Input the domain's address. Enter the hostname of the domain you wish to join in the 'Domain' field.
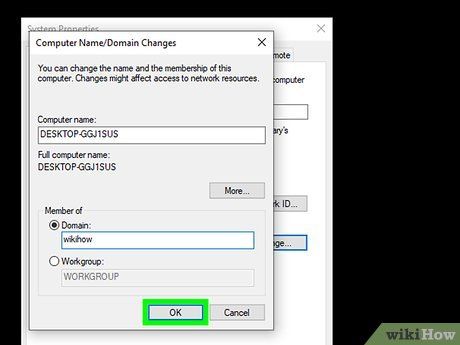
Click the 'OK' button.
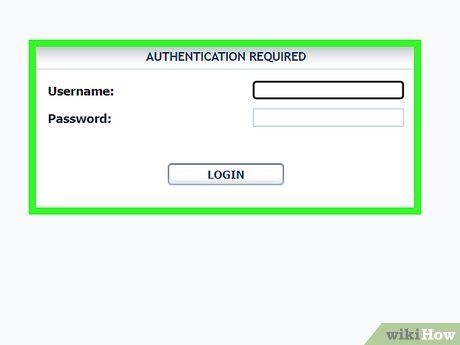
Login to the domain.
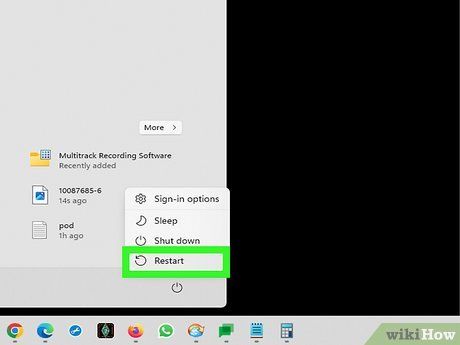
Restart your computer.
Using a Mac
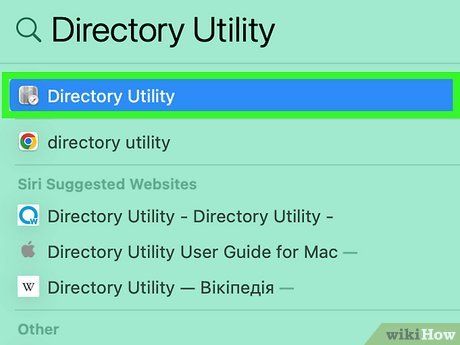
Open Directory Utility on your Mac. To join a Mac to an AD domain, access Directory Services. Type 'directory utility' into Spotlight search, then click 'Directory Utility' in the search results.
Click 'Services'. It's located at the top of the window.
Click the lock icon and sign in. To join a domain, you'll need to unlock Directory Utility with your administrator-level account (or use Touch ID).
Select 'Active Directory' and click the pencil icon. This allows you to edit your Active Directory domain settings.
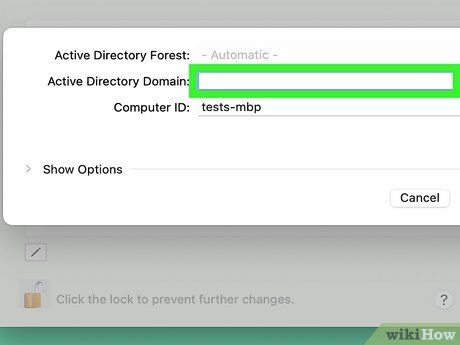
Enter the domain hostname. If you're unsure, contact your network administrator.
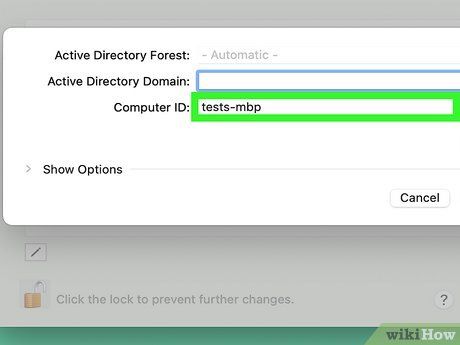
Enter a computer ID if necessary. By default, your Mac will use its regular hostname. If needed, enter a different hostname into the 'Computer ID' field. There are two scenarios where you might want to do this: if your organization has specific host naming conventions or if your Mac's hostname contains a hyphen, preventing it from binding to a domain. In such cases, provide a new computer ID without a hyphen.
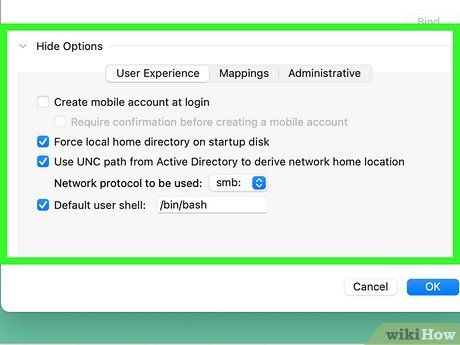
Set additional options. Click the triangle next to 'Show Options' to reveal more options:
- On the User Experience panel, configure mobile user accounts, home folders, and more.
- On the Mappings panel, map group IDs and user IDs to Active Directory attributes.
- On the Administrative panel, designate this domain as your preferred controller, control admin privileges for AD admins on your Mac, and manage which domain users can connect to your Mac.
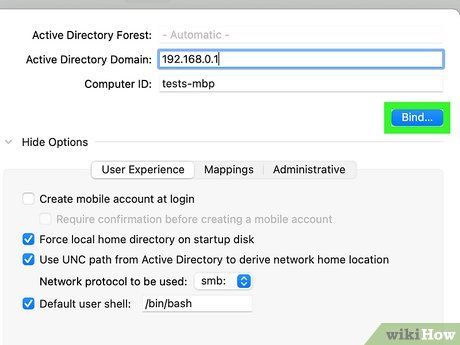
Click 'Bind'. You'll then be prompted to provide additional information.

Enter the requested details and click 'OK'. You'll need to input:
- Username and password of an Active Directory account with permission to join a computer to a domain.
- The computer's OU (organizational unit).
- Choose whether to add Active Directory to the Mac's authentication and contacts search policies.
Once you click 'OK', this will confirm the domain information and add your Mac to the domain.
