Many hobbyist astronomers and seasoned skywatchers alike regard Saturn as the most enchanting celestial object visible to the naked eye. Transitioning from its illustrated depiction to witnessing its actual presence is a truly mesmerizing experience. Locating Saturn amidst a night sky teeming with stars can be challenging, but understanding Saturn's orbit can significantly aid in finding optimal viewing conditions and predicting its whereabouts, ultimately making the task of locating Saturn much easier. Refer to Step 1 for detailed instructions.
Instructions
Understanding Saturn's Orbit
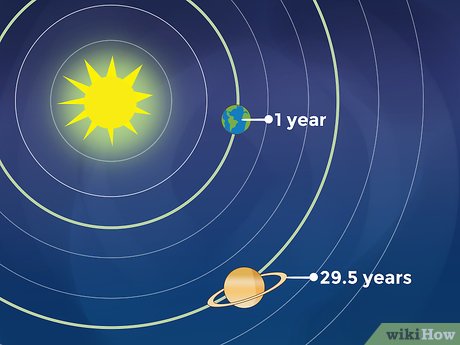
Comprehend Saturn's Relationship with Earth's Rotation. While Earth completes one orbit around the sun annually, Saturn takes approximately twenty-nine and a half years to complete the same journey. Saturn remains visible for at least a portion of each year as Earth passes between Saturn and the Sun. Depending on the time of year and the alignment of our planets, locating Saturn in the night sky may be more or less challenging.
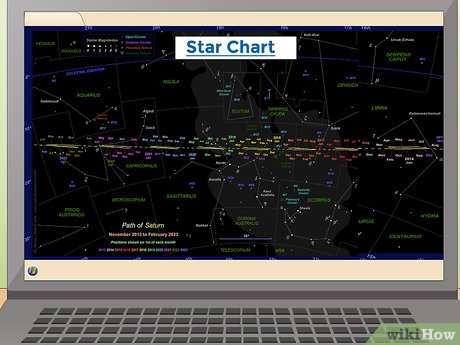
Tracing Saturn's Predicted Path. Simply pointing your telescope randomly into the night sky won't lead you to Saturn. You need precise knowledge of its location and appearance. Refer to a star chart depicting Saturn's trajectory and select a time when it aligns with a recognizable constellation.
- Starting in 2014, Saturn will be near the Libra constellation, transitioning to Scorpius later in the year. By May 2015, Saturn will retrograde, moving westward toward Libra again, offering an excellent viewing opportunity.
- Over the next decade, Saturn will gradually shift eastward in the Northern hemisphere's sky, moving toward Capricornus.
- During a period in 2017, Saturn will be obscured from Earthly view, too close to the Sun for observation.
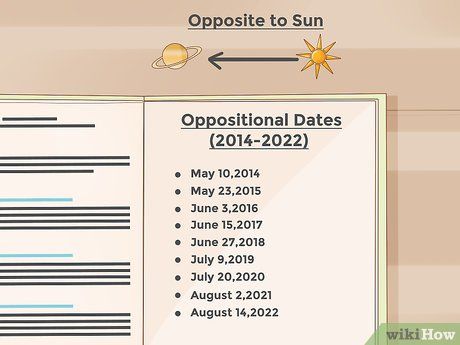
Selecting the Optimal Oppositional Date. Saturn's opposition marks its closest approach to Earth, making it appear brightest in the sky. This occurs approximately every 378 days. During opposition, Saturn will be due south in the Northern hemisphere and due north in the Southern hemisphere, most visible around midnight local time. Opposition dates from 2014 to 2022 include:
- May 10, 2014
- May 23, 2015
- June 3, 2016
- June 15, 2017
- June 27, 2018
- July 9, 2019
- July 20, 2020
- August 2, 2021
- August 14, 2022
Locating Saturn
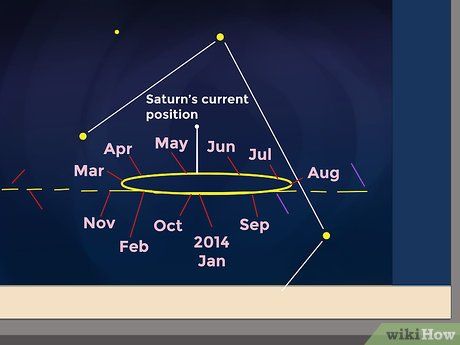
Identifying the Nearest Constellation to Saturn's Current Position for Reference. Familiarize yourself with the constellation closest to Saturn's current location. Then, use a Saturn position chart to pinpoint its exact position relative to that constellation.
- In 2014, Saturn will be near Libra, while in January 2016, it will be directly north of Antares in the Scorpius constellation. You can track Saturn's path here: http://www.nakedeyeplanets.com/saturn.htm
- If viewing on an oppositional date, aim your telescope due south.

Spotting Saturn's Distinctive Golden Glow. Saturn typically exhibits a steady golden color and lacks the twinkling characteristic of stars. Its planet-like brightness may not be as prominent as some stars, but its distinctive hue sets it apart. Use the nearby constellation as a reference point to distinguish Saturn's unique coloration.
Opt for a Telescope. While Saturn is visible to the naked eye, using a telescope allows for a more fulfilling experience, especially when observing its distinctive rings. With a telescope, Saturn's unique shape becomes more apparent compared to other celestial bodies.
- A powerful telescope with a yellow filter can enhance the visibility of Saturn's specific light spectrum, making the viewing experience more enjoyable.

Observe the Shadowed Edges. Saturn appears darkened due to shadows cast by its rings, imparting a quasi-3D appearance and elongated shape when viewed through a telescope.
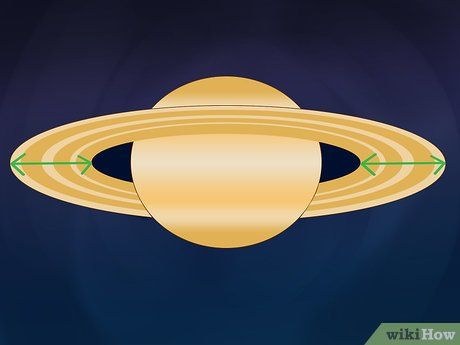
Examine the Ring System. Through a capable telescope, Saturn's rings appear flat but lend a rounded, marble-like quality to the planet. Additionally, the distinct A (outer) and B (inner) ring belts can be discerned, adding to the allure of Saturn's celestial features.
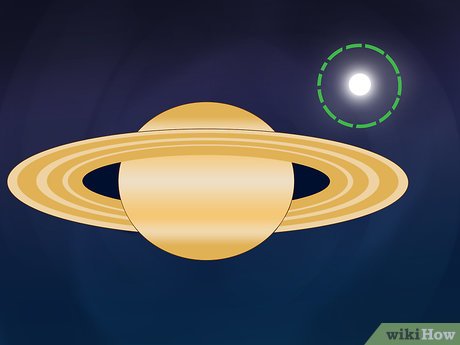
Explore the Moon Collection. Beyond its iconic rings, Saturn boasts numerous moons, which may be visible in proximity to the planet under favorable viewing conditions with a sufficiently powerful telescope. There are even applications available to assist in identifying these moons.
Observing Properly
Acquaint Yourself with Basic Stargazing. Starting with familiar constellations and star charts can provide a foundation for your stargazing journey.
Escape Urban Lights. Urban environments obscure much of the night sky due to light pollution. Seek out darker locations or join local astronomy groups for better viewing opportunities.

Choose Optimal Stargazing Nights. Select nights with favorable weather conditions and clear skies to avoid disappointment caused by unexpected cloud cover.
Begin with Binoculars. Binoculars offer a user-friendly entry point into amateur astronomy. As you progress, consider investing in a quality telescope, either individually or through shared ownership with fellow enthusiasts.
- A basic telescope suffices for observing Saturn initially. For advanced options, telescopes like NexStar ($800) offer automated sky navigation, while professional-grade models like the 11-inch Schmidt Cassegrain ($1,200) provide enhanced features. Choose equipment according to your budget and dedication.

Explore Local Observatories. Visiting observatories allows for learning from experienced astronomers and gaining insights into celestial observations, particularly useful for objects like Saturn.
- Plan visits during optimal viewing periods advertised by observatories. Griffith Observatory in Los Angeles, Yerkes Observatory in Wisconsin, and McDonald Observatory in Texas are notable options across the country.
Helpful Hints














