This article introduces you to the LOGNORM.INV function - one of the commonly used statistical functions in Excel.

Description: The function returns the inverse value of the standard log-normal distribution of x. Where LN(x) is typically distributed with mean parameter and standard deviation. Use the function to analyze data transformed by log-normal distribution. The function is supported from Excel version 2010.
Syntax: LOGNORM.INV(probability, mean, standard_dev)
Where:
- probability: Probability associated with the standard log-normal distribution, is a required parameter.
- mean: The average value of LN(x), is a required parameter.
- standard_dev: The standard deviation of LN(x), is a required parameter.
Note:
- Any argument other than (cumulative) not being a number -> function returns the error value #VALUE!
- If probability ≤ 0 or probability ≥ 1 -> function returns the error value #NUM!
- If standard_dev ≤ 0 -> function returns the error value #NUM!
Example:
Find the inverse value of the standard log-normal cumulative distribution function as described in the data table below:
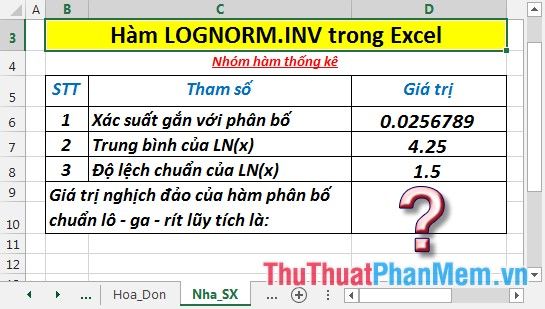
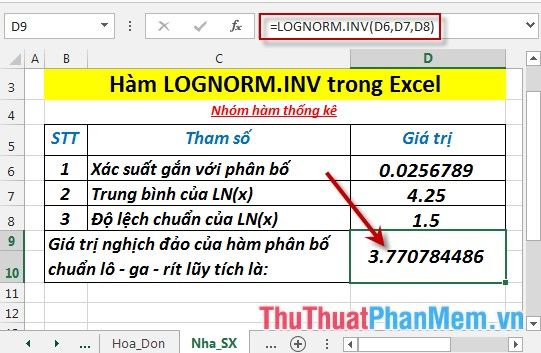
- In the cell where you want to calculate, enter the formula : =LOGNORM.INV(D6,D7,D8)

- Press Enter -> the inverse value of the standard log-normal cumulative distribution function is:
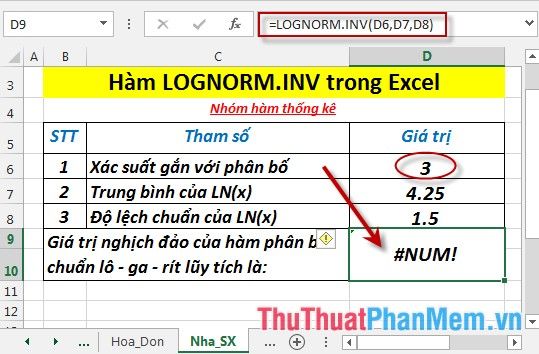
- If the probability associated with the standard cumulative distribution is less than 0 or greater than 1 -> the function returns the error value #NUM!
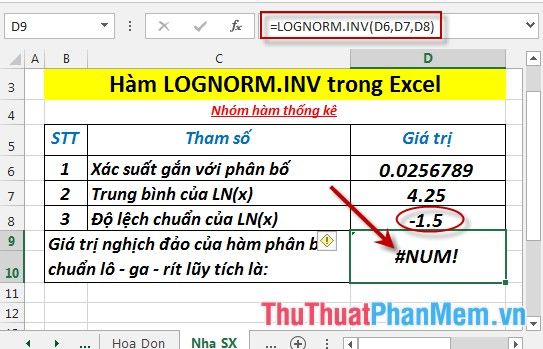
- If the standard deviation is less than 0 -> the function returns the error value #NUM!
Above are instructions and some specific examples of using the LOGNORM.INV function in Excel.
Wishing you success!
