Foot pain is a common issue among growing children, stemming from various causes. If your child complains of foot discomfort, it could be due to growth-related heel pain, foot conditions like flat feet, or ill-fitting footwear. Additionally, children aged seven to eight often experience ankle and foot discomfort due to their high activity levels. Identifying the underlying cause is essential before addressing your child's foot pain, requiring evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Recommended Actions
Determining the Source of the Foot Issue

Engage with your child about their foot pain. Encourage your child to pinpoint the specific areas of discomfort in their feet, such as sharp pain or throbbing sensations. Additionally, inquire if they experience pain in other lower limb areas like knees, ankles, or calf muscles. This information aids in identifying the origin of the pain and potential causes.
- Pain localized in the heel area might indicate Sever's disease, a condition related to foot growth plate disturbances, commonly observed in active children, particularly during early puberty.
- Widespread foot pain accompanied by discomfort in ankles and calf muscles could suggest flat feet.

Evaluate if your child has injured their foot. Accidents like falls, twists, or impacts can result in foot sprains, strains, bruises, or fractures, leading to pain. Seek medical attention if your child experiences foot pain following an injury or sudden onset of pain.
- Limping may not always indicate foot injury; it could be due to pain elsewhere in the hips, legs, or feet.
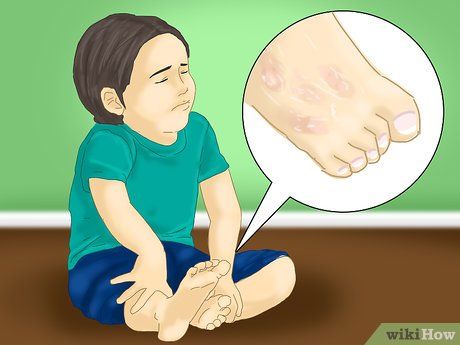
Notice if your child complains of foot skin itchiness or burning. Itching between toes or dry, scaly skin with a burning sensation could indicate athlete's foot, caused by a fungal infection. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent worsening; consult a doctor for appropriate medications.
- Athlete's foot requires medical attention to prevent complications. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter powders, ointments, or creams.

Inspect your child's outdoor footwear. Ill-fitting or unsuitable shoes can cause foot discomfort. Check for sharp areas inside shoes that might rub against your child's feet, leading to blisters or abrasions.
- Poorly fitting shoes often cause surface discomfort like blisters, but persistent muscle and joint pain indicate underlying foot issues.

Examine your child's feet for bunions or ingrown toenails. Bunions appear as bumps on the side of the foot and can be hereditary or due to birth defects. Consult a podiatrist for treatment. Watch for signs of ingrown toenails or plantar warts, seeking medical attention for proper care.
- Check for signs of ingrown toenails, such as redness or tenderness around the nail. Medical intervention is recommended for ingrown toenails.
- Plantar warts, common in children, may cause discomfort when walking and should be treated by a medical professional.

Observe your child's walking pattern for signs of toe walking or limping. Toe walking or limping could indicate pediatric heel pain, also known as Sever's disease, caused by growth plate issues in the foot. Consult a doctor for evaluation and treatment options to prevent long-term foot problems.
- Pediatric heel pain results from growth plate irregularities, leading to strain on the heel bone and tendons. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent chronic foot issues.
- If pediatric heel pain is suspected, consult a family doctor for referral to a specialist for assessment and management.
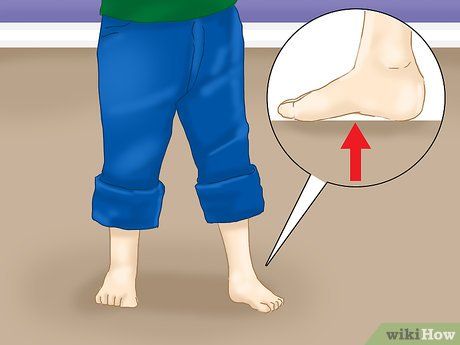
Observe if your child's arches flatten when standing flat on the ground. Flattened arches may indicate flat feet, a condition requiring professional attention if severe or symptomatic. Flat feet may manifest with tenderness, cramping, or pain in the foot, leg, or knee, along with difficulties finding comfortable shoes or participating in physical activities like running or jogging.

Seek immediate medical attention if your child cannot bear weight on his feet or experiences foot pain alongside fever and limping. If your child struggles to bear any weight on his feet or experiences intense foot pain or burning, seek urgent care. These symptoms may indicate a serious foot issue requiring prompt treatment.
Utilizing Home Remedies

Invest in shoe insoles for your child. Consider purchasing cushioned insoles for your child's shoes if they contribute to foot pain. These insoles can alleviate soreness or stiffness by providing additional support, ensuring your child wears appropriate footwear, especially during sports or outdoor activities.
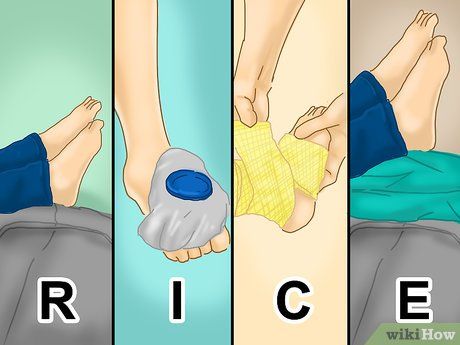
Implement R.I.C.E. If your child experiences throbbing foot pain after physical activity, try R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) for temporary relief. Guide your child to rest, apply ice packs, use compression bandages, elevate their feet, and consider over-the-counter pain medication if necessary.
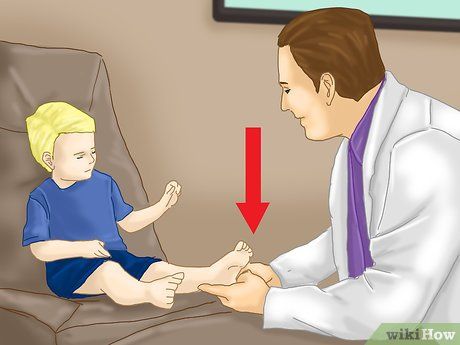
If your child's foot pain persists despite home remedies, seek professional medical attention. Arrange a visit with your family doctor if your attempts at home treatments prove ineffective. Often, pediatricians or orthopedists can address foot pain. In more complex cases, a referral to a podiatrist or foot and ankle surgeon may be necessary.
- A podiatrist specializes in diagnosing and treating foot conditions in children, including issues with growth plates, bones, and soft tissues.

Request medicated cream for athlete's foot from your doctor. Upon diagnosing athlete's foot, your doctor may prescribe an antifungal cream or powder. Treatment typically lasts about four weeks, with an additional week of application after symptoms subside to ensure complete eradication of the fungus.
- Switching to moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes can prevent future fungal growth, enhancing treatment effectiveness.
Visiting a Podiatrist with Your Child
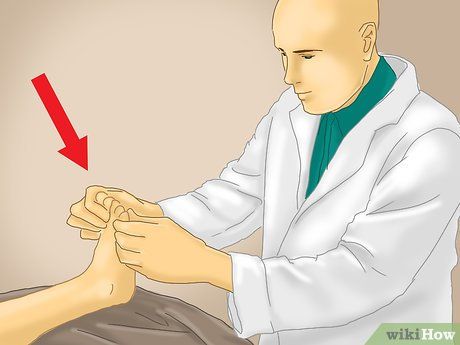
Facilitate a thorough examination of your child's feet by the podiatrist. The examination may include various movements and positions to assess foot function and structure. Additionally, the podiatrist may inquire about family medical history and may conduct X-rays for further evaluation.
- X-rays provide detailed insights into your child's foot bone structure.

Discuss potential treatment approaches with the podiatrist. Following assessment, the podiatrist will propose suitable treatments based on the diagnosis. Non-surgical options may include rest, medication, stretching exercises, arch supports, orthotics, or physical therapy to address foot issues such as flat feet or pediatric heel pain.
- These interventions aim to alleviate pain, promote healing, and improve foot function.
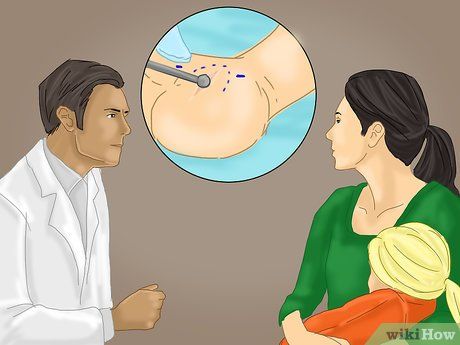
If your child's flat feet are severe, surgery may be considered. In such instances where non-surgical methods prove ineffective, your podiatrist may recommend foot surgery. The procedure typically involves lengthening the Achilles tendon and heel bone, aiming to correct the condition.
- Surgical intervention is usually suggested for children aged eight or older. The procedure involves techniques like calcaneal lengthening osteotomy to address flat footedness.
