Pericarditis refers to the inflammation or swelling of the pericardium, the double-layered membrane enveloping the heart. This crucial structure provides support and aids in proper heart function. Typically, pericarditis manifests as sharp chest pain resulting from the friction between these layers. While often sudden, pericarditis tends to resolve spontaneously, especially in mild cases.
Essential Information
- Rest is paramount for pericarditis recovery; avoid strenuous activities until symptoms subside completely.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers may offer relief, alongside maintaining an upright or slightly forward-leaning posture.
- If symptoms persist, medical intervention may include colchicine (Colcrys) or prednisone prescriptions.
- In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address pericarditis complications.
Practical Steps
Managing Pericarditis at Home
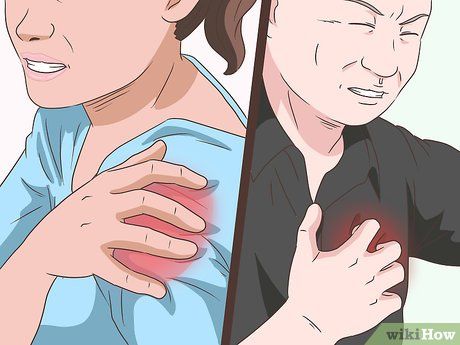
Identify pericarditis symptoms promptly. Pericarditis typically manifests as sudden, fleeting episodes of intense chest pain, often resembling a heart attack. Recognizing these symptoms enables timely intervention. Additional signs may include discomfort while lying down, chest pressure, fever, weakness, breathing difficulties, palpitations, coughing, and fatigue.

Prioritize adequate rest. Rest is crucial for managing mild pericarditis episodes. During an attack, refrain from strenuous activities and opt for rest until symptoms alleviate. It's advisable to resume normal activities only when pericarditis symptoms cease completely, particularly if accompanied by fever.
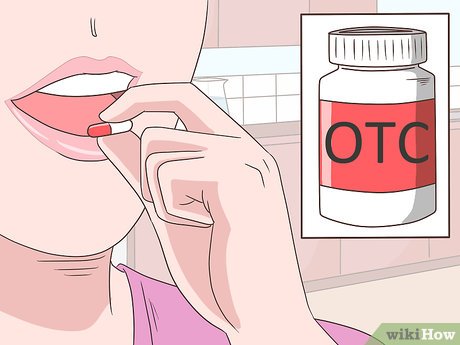
Utilize over-the-counter pain relievers. For recurrent pericarditis, consider OTC pain relievers recommended by your physician to alleviate pain and inflammation. Common choices include aspirin and ibuprofen. Adhere to prescribed dosages for effective symptom relief.
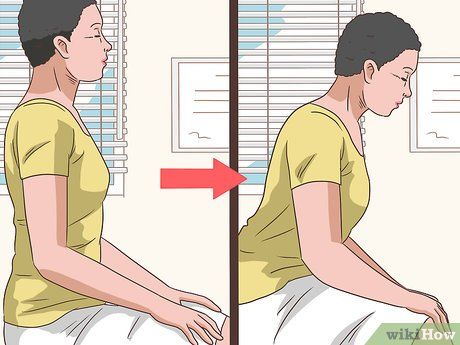
Adjust your posture for comfort. Experiment with different positions to alleviate pericarditis discomfort. Sitting upright or leaning forward may provide relief, while lying down or deep breathing could exacerbate symptoms. Pay attention to what position offers the most comfort during an episode.

Reduce the likelihood of pericarditis. While pericarditis may not always be preventable, you can lower the risk of recurrence and complications by:
- Seeking timely treatment
- Adhering to your treatment regimen
- Continuing regular medical check-ups
Consulting a Healthcare Professional for Pericarditis
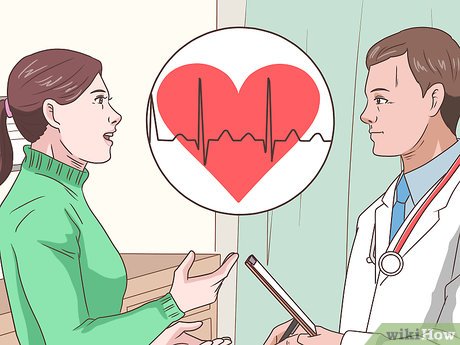
Visit your doctor promptly. Diagnosis of pericarditis requires medical evaluation. If home remedies fail to alleviate prolonged symptoms or you suspect pericarditis, schedule an appointment with your doctor. Provide detailed information about your symptoms, including their location, intensity, and any alleviating or exacerbating factors.
- Inform your doctor of any recent illnesses, heart-related incidents, or existing medical conditions.
- Cooperate with your doctor's inquiries to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Consider colchicine therapy. Colchicine (Colcrys) may be prescribed for acute or recurrent pericarditis to reduce inflammation and symptom duration. However, ensure compatibility with your medical history and other medications, as colchicine may not be suitable for individuals with certain health conditions or medication regimens.

Explore prednisone treatment. In severe cases or when other therapies fail, prednisone, a corticosteroid, may be prescribed to alleviate pericarditis symptoms. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully, especially if prednisone is recommended for recurrent or unresponsive symptoms.

Consider surgical intervention for pericarditis complications. Pericarditis can lead to severe complications, such as cardiac tamponade and constrictive pericarditis. Surgery may be necessary to address these conditions. Your doctor may recommend one of the following procedures:
- Pericardiocentesis: a minimally invasive procedure to drain excess fluid from the pericardium, relieving pressure on the heart.
- Pericardiectomy: surgical removal of the pericardium and any scar tissue.
- Pericardial window: creation of an opening in the pericardium to drain fluid and prevent future accumulation.
Useful Tips
Important Warnings
- If you experience unexplained chest pain, seek immediate medical attention to rule out a heart attack. It's crucial to determine the cause of chest pain promptly.
