Discovering a beetle's identity among the vast 350,000 species can be a challenge. However, whether indoors or out, knowing the type of beetle you've encountered is invaluable. Learn how to closely examine its features and use its appearance for identification.
Simple Steps
Spotting Key Features of Beetles
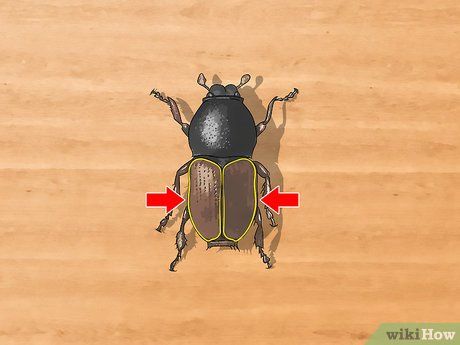
Identifying Hard Wing Coverings

Examine the insect's mouth for sharp mandibles. Beetles possess strong mandibles for consuming various materials such as other insects, plants, fungi, and decaying matter. Inspect the underside of the insect's head for these characteristic mouthparts.

Count the insect's legs to confirm if it's a beetle. Beetles typically have six legs distributed across their body segments. During their larval stage, all legs are located on the front segment, while in other stages, legs span both front and back segments. Verify the leg count and positioning to determine beetle status.
Spotting Large Beetles

Recognize a click beetle by its slender body and distinctive clicking sound. Click beetles, scientifically known as Elateridae, can produce a clicking noise by snapping their body sections together. Typically black or dark brown, they feature grooves along their backs.
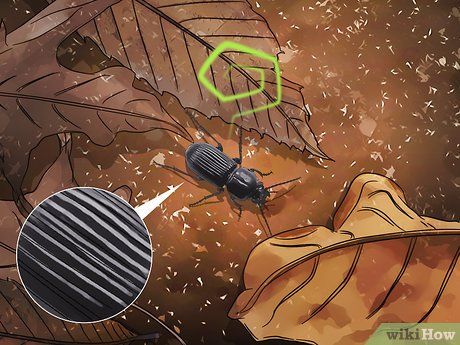
Identify ground beetles by their swift movement and pungent odor. These black beetles with dorsal grooves emit a strong smell and move rapidly. Often found under debris, they may occasionally enter homes. Despite their speed and odor, they pose no threat to humans or pets as they prey on other insects.

Spot longhorn beetles near dead trees, recognized by their long antennae. Resembling longhorn cattle, these beetles boast antennae varying in shape and color. Found predominantly around dead trees, they exhibit a range of hues including black, brown, green, yellow, and red.

Identify mealworms by their distinctive scoop-shaped head. Despite their name, mealworms are actually beetles characterized by a rounded head with a scoop neck. Typically outdoor dwellers, they may infest stored grains if not properly contained.
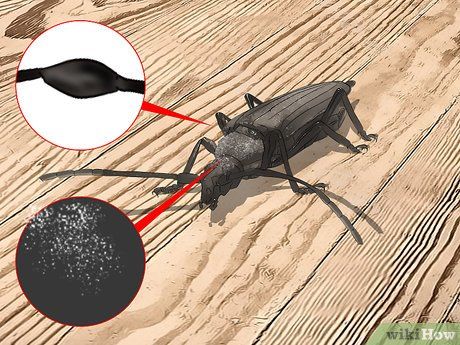
Recognize oldhouse borers by white wing spots and enlarged leg segments. Notable for gray hairs on their back and three dark eyes near the mouth, oldhouse borers often appear in homes 4 to 7 years post-construction.
Spotting Small Beetles

Identify carpet beetles by their black bodies and elongated abdomens. Particularly, black carpet beetles are oval-shaped and dark-colored, ranging from 0.12 to 0.19 inches. Varied color carpet beetles resemble them but feature yellow and green markings.

Spot elm beetles by their distinctive green and black stripes. These 0.25-inch-long beetles primarily feed on elm tree leaves and lay eggs on leaf undersides. Effective management with pesticides may be necessary to control potential tree damage.

Recognize ladybugs by their brightly colored, rounded bodies and characteristic black spots. Also known as lady beetles or ladybirds, they exhibit a variety of color patterns including yellow, orange, red, and black. With over 450 species in North America, they're a diverse group.

Guard your ham against larder beetles, known for infesting cured ham. Recognizable by a silver streak on their black oval bodies, larder beetles can spoil food if left uncovered. Keep ham refrigerated when not in use to prevent infestation.

Watch for cylindrical bark beetles, especially around firewood stacks. Measuring only 0.12 inches, these beetles commonly infest firewood and live trees, contributing to forest fire hazards. Their presence results in dry, dead wood which fuels forest fires.

Identify drugstore beetles by wing cover lines and a slightly bent head. Ranging from brown to reddish-brown and measuring 0.1 to 0.14 inches, they infest packaged food. Beware of a humped appearance, which distinguishes cigarette beetles from drugstore beetles.

Spot rust beetles by their flattened, rust-colored bodies and clubbed antennae. Also known as confused flour beetles, they infest corn flour and packaged products. Ensure food safety by storing flours in air-tight containers.
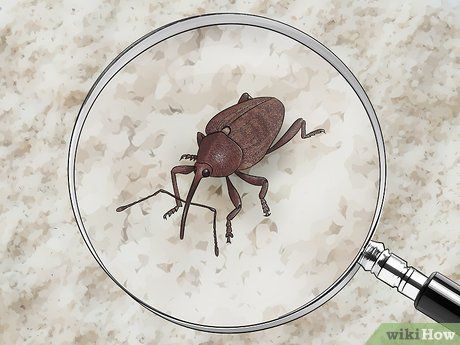
Check rice and grains for weevils, characterized by long beaks and slender bodies. These tiny brown pests, measuring 0.12 inches, commonly infest stored grains. Prevent infestations by storing grains in air-tight glass, metal, or hard plastic containers.

Identify saw-toothed beetles by protrusions on their thorax. These 0.12-inch-long beetles favor sunflower seeds and nuts but can infest large quantities of grains. Regular sanitation of storage bins minimizes the risk of infestation.
Helpful Tips
- Given the diversity of beetles, use distinguishing features to narrow down the category before consulting entomology websites for identification. Browse through images until you find a match!
