Have you ever pondered over the purpose of that tiny dial marked 'gain' on your digital microphone? Despite its role in regulating sound volume, setting it just right can pose a challenge. Since the gain dial lacks numbering, achieving optimal audio levels can be perplexing. Factors like proximity to the microphone and vocal intensity influence the gain. Thankfully, proficient recording software enables you to monitor sound levels and fine-tune settings for an impeccable audio experience.
Key Points to Remember
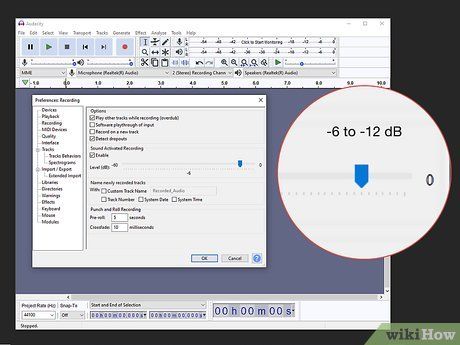
- For digital microphones, aim for a decibel level between -6 and -12 dB. Adjust the gain using the microphone dial—turning it clockwise increases the gain.
- If using an analog microphone, employ a preamp. Locate the 'gain' or 'trim' dial and set it between -8 and -12 dB.
- Regardless of microphone type, assess settings through trial recordings and fine-tune gain levels as necessary.
Step-by-Step Approach
Optimizing Digital Microphone Settings

Connect the microphone's USB cable to your device and launch the recording software. Position yourself near the recording area, ensuring ample space around the microphone. Plug the USB cable into your computer and open the recording software to monitor the mic's input.
- Arrange your setup as you would during actual usage to facilitate accurate gain adjustment.
- Although digital microphones are straightforward to adjust, pre-testing ensures optimal gain levels.
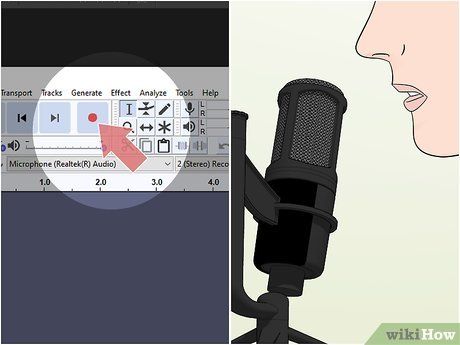
Initiate recording and speak into the microphone. Stand in the designated spot and vocalize at the intended volume level. This method yields a more precise assessment of mic performance. For instrument-based recording, play the instrument during the test.
- A brief soundcheck suffices for gain adjustment—no need for extensive recordings.
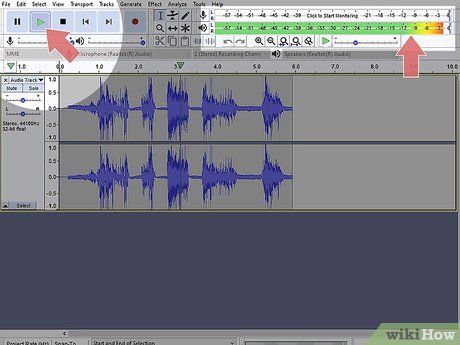
Utilize the recording software to playback the test audio. Monitor the volume using the dB meter and evaluate audio quality. Avoid audio clipping, which distorts sound and is challenging to rectify. Some software features an active meter to monitor dB levels during microphone usage.
- Audio clipping occurs when dB levels exceed 0 dB, resulting in distorted recordings.
- Check the microphone tab in the recording program for an active meter.

Adjust the microphone gain by turning the dial clockwise. Locate the gain dial, usually labeled and marked with a white stripe. Increase gain for higher volume and decrease it for softer output. Experiment with gain settings, typically adjusted manually due to the absence of labeled increments.
- Visualize the gain dial like a clock, with the 12 o'clock position indicating minimal gain.
- Gain dials lack numerical labels, necessitating manual adjustment and frequent testing.
Adjusting Digital Microphone Levels
Conduct multiple test recordings to fine-tune the microphone gain. After each adjustment, initiate a new recording and monitor the volume level while evaluating audio quality. Continue this process until achieving an optimal setting for producing high-quality recordings.
- Iteratively testing and adjusting the audio settings is essential for achieving desired recording quality.
Optimizing Analog Microphone Performance

Connect the microphone to a mixer or preamp to manage gain settings. Analog microphones lack built-in gain controls, necessitating connection to external devices such as mixers or preamps. These devices offer individual gain controls for each microphone, facilitating precise adjustments.
- Preamps amplify microphone signals, enhancing recording quality for subsequent editing.
- Venues equipped with sound systems, including mixers, provide suitable connections for microphone and recorder setups.

Adjust the gain by rotating the control dial to -8 to -12 dB. The gain dial, labeled as 'gain' or 'trim,' typically features clear markings for precise adjustment. Rotate the dial clockwise to achieve negative gain ratings, ensuring optimal sound levels.
- If the device lacks labeled gain controls, approximate the 2 o'clock position for the dial, followed by iterative adjustments based on recording evaluations.
Activate the sound recorder to monitor microphone audio. Ensure connectivity between your recorder and mixer or preamp. If using a computer, launch the recording software and locate the decibel meter displaying mic volume. Utilize this meter to determine optimal gain settings.

Perform a test recording by speaking into the microphone. Assume the recording position in front of the mic, replicating conditions for the actual recording. Adjust your vocal volume to match the intended performance level. For instrument recording, tune the instrument beforehand. Verify proper setup and adjustment of auxiliary devices such as amplifiers.
- Many mixers and recording software feature illuminated meters during mic usage. Monitor these meters to gauge audio decibel levels for adjustment purposes.
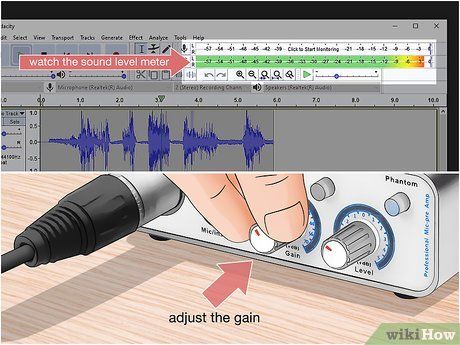
Adjust the gain level based on test recording feedback. Evaluate sound quality during playback, observing the sound level meter in recording software if applicable. Identify any instances of loud or distorted sound and reduce gain accordingly. Conduct additional test recordings to confirm optimal gain settings.
- For multi-mic setups, ensure uniform gain levels across all microphones, especially in scenarios like concert instrument recording.
- If audio sounds subdued, incrementally raise gain levels for increased volume, exercising caution to prevent distortion from excessive loudness.
Insights
-
Distinguish between gain and volume adjustments, utilizing separate controls on microphones, mixers, or preamps. Gain influences mic input volume, while volume regulates output volume.
-
Various microphone types exhibit different sound capture and amplification capabilities. For instance, condenser mics excel at capturing subtle sounds but may distort louder inputs such as booming bass or powerful singing voices.
-
Post-recording, editing software enables fine-tuning; however, excessive manipulation risks audio distortion. Incorrect gain settings may lead to irreparable soft or loud audio during post-processing.
Cautions
- Ensure frequent testing of sound levels before performances as the gain setting significantly impacts recording quality. Incorrect gain levels may result in soft or distorted audio, posing challenges during post-recording correction.
Essentials
Adjusting Digital Microphones
- Microphone
- Microphone cable
- Recorder or computer equipped with recording software
- Optional: Microphone stand or clip
Utilizing Analog Microphones
- Microphone
- Microphone cable
- Recorder or computer with recording software
- Mixer or preamp
- Optional: Microphone stand or clip
