Exploring the vast expanse of the night sky reveals a multitude of stars, offering a delightful pursuit for many. Initiating the process of identifying constellations and stars is straightforward. Many prominent stars, such as Polaris or Alpha Centauri, are integral parts of constellations. Acquiring knowledge about these constellations aids in locating these stars. Additionally, utilizing various resources such as charts, websites, and applications facilitates the identification of stars and constellations. With these aids, aspiring stargazers can swiftly embark on their journey into amateur astronomy.
Steps
Locating Major Stars within Constellations
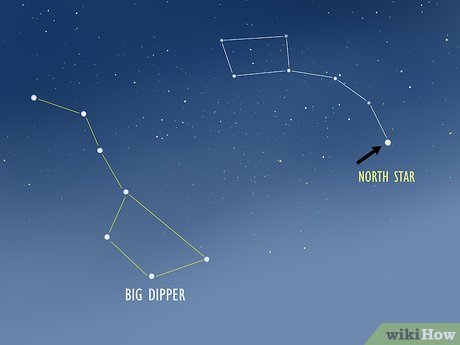
Discovering the North Star through the Big Dipper. The North Star, also known as Polaris, serves as a guiding beacon, marking the North Pole and facilitating celestial navigation. Begin by identifying the Big Dipper, a prominent component of the Ursa Major constellation resembling a ladle. This can be found towards the northern direction. Trace the handle of the ladle until it bends, then shift your gaze to the opposite side of the bend. This will lead you to the Little Dipper. Continue following the handle until reaching its end, where the North Star resides.
- The visibility of the North Star is limited to observers in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, navigational aid is provided by the Southern Cross constellation, guiding towards the South Pole.
- The Big Dipper remains visible above 41 degrees north latitude, encompassing the northern portion of the United States. Below this latitude, it descends below the horizon, reappearing only during dawn.
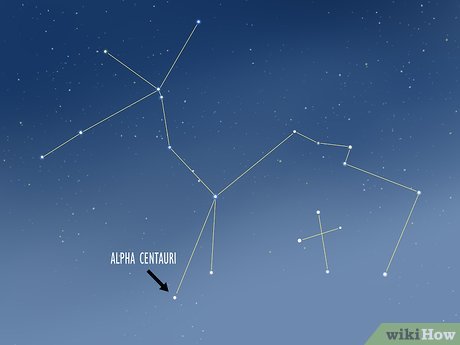
Pinpoint Alpha Centauri using the Centaurus constellation. Alpha Centauri, Earth's nearest star, presents an exciting challenge for observation. In the Southern Hemisphere, commence by locating the Southern Cross constellation, characterized by four bright stars forming a distinct cross marking the South Pole. This celestial feature resides in the southern sky. Draw an imaginary line connecting the two stars closest to each other. Extend this line outward from the brighter of the two stars until encountering another prominent star adjacent to the Southern Cross. This star is Alpha Centauri.
- Alpha Centauri occupies a position far south in the night sky, rendering it invisible from most parts of the Northern Hemisphere. However, residents near the equator may catch a glimpse of it in early May.
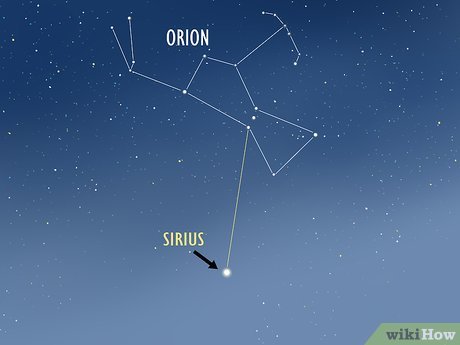
Utilize the Orion constellation to locate Sirius. The Orion constellation appears slightly southward in the Northern Hemisphere and prominently to the north in the Southern Hemisphere. Identifying Orion is facilitated by identifying the trio of medium-brightness stars forming a straight line, representing the constellation's belt. Locate the bow section of the constellation by identifying the four stars forming a curved line. Then, trace a straight line downward from the side of Orion's belt opposite the bow to find Sirius.
- Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, often requires no assistance from constellations for identification.
- Orion's conspicuous brightness makes it easily identifiable regardless of light pollution levels in urban areas. It reaches its zenith during winter but can also be observed closer to the horizon during summer.
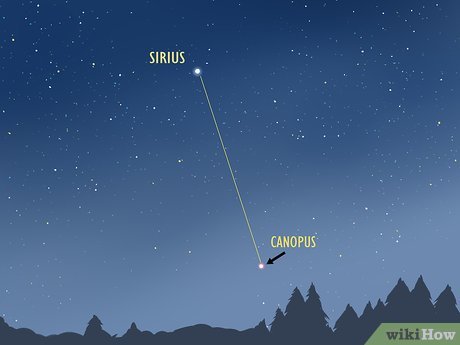
Direct your gaze downward from Sirius to locate Canopus. Canopus, the second brightest star in the night sky, becomes readily apparent once Sirius is located. Envision an imaginary line extending vertically downward from Sirius. Canopus can be found slightly to the right of this line, just above the horizon.
- Canopus exhibits a slight reddish hue when positioned close to the horizon.
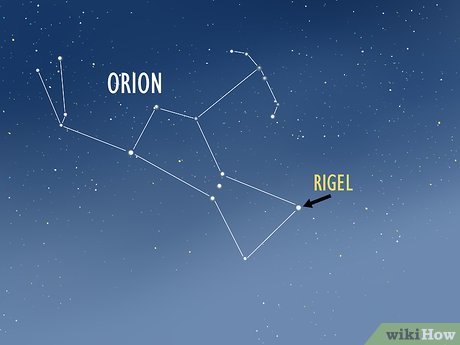
Identify Rigel on the lower right side of Orion. Rigel, another of the brightest stars in the night sky and the brightest in the Orion constellation, is easily located within Orion. Once Orion is identified, shift your focus downward and to the right of Orion's belt. This area corresponds to Orion's right foot, where Rigel is situated within the constellation.
- Rigel's slightly bluish-purple tint enhances its visibility within Orion.
- Rigel is particularly interesting to identify due to its frequent appearance in science fiction media, such as Star Trek, where it often serves as a namesake for places or characters.
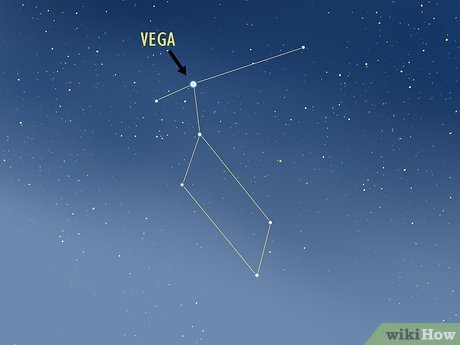
Locate Vega using the Lyra constellation. Vega, a luminous blue star, forms the foundation of the Lyra constellation. Lyra typically appears directly overhead in the night sky for observers in the Northern Hemisphere, with its peak visibility occurring in the northern direction during the summer months. The constellation is delineated by four stars forming a box that leads to a straight line representing the base, with Vega positioned at the midpoint of this line.
- Vega's brilliance often allows for its identification independent of the surrounding constellation. Observers can look for its distinct blue hue when searching for it in the northern sky.
Harnessing Charts and Applications

Employ a star chart for pinpointing other stars and constellations. A star chart, customized to your hemisphere and the current season, serves as a visual guide to the night sky. Some charts are adjustable, allowing you to align them with different times of the year. Obtain a chart corresponding to the present season and orient it according to your viewing direction and time of day. Rotate the outer rim of the chart to synchronize it with the current time. Hold the chart up to the sky when properly aligned to identify other stars and constellations.
- Ensure you select the appropriate star chart for your hemisphere—Northern or Southern.
- Star charts are available for purchase online at affordable prices. Alternatively, some websites offer free printable versions.

Explore star atlases to enhance your knowledge of the night sky. Delving deeper into celestial knowledge facilitates the identification of stars. Familiarize yourself with directional cues, optimal viewing times, and methods for distinguishing between stars and planets. This wealth of information gleaned from books and atlases enhances your stargazing proficiency.
- Consider utilizing resources from reputable sources such as the National Parks Service, NASA, National Geographic, and Norton. These entities provide reliable information and atlases.
- Most of these resources can be accessed at your local library, eliminating the need for significant expenditure.
Access stargazing apps for interactive insights into the night sky. Stargazing apps offer convenience, particularly if you lack a physical star chart or prefer digital solutions. Browse the app store for astronomy or stargazing applications suitable for nocturnal use. Opt for an app featuring a robust star locator functionality to aid in identifying various celestial bodies.
- Stargazing apps vary in complexity, ranging from basic star charts to comprehensive sky-mapping programs. Select an app aligning with your preferences. Experiment with multiple free apps to determine your preference.
- Well-known free apps include StarChart and the NASA app. Alternatively, more advanced options like SkySafari, Starmap, and Pocket Universe offer enhanced features for a nominal fee.
Explore star mapping websites to strategize your stargazing endeavors. Search online for star mapping platforms and input your location data. These websites generate visual representations of the night sky above your location, aiding in the identification and location of various celestial bodies.
- Popular star mapping websites include In-The-Sky.org, earthsky.org, and stargazing.net. Additionally, both NASA and National Geographic websites offer comprehensive stargazing resources and articles.
- Some websites enable the printing of customized star maps, ensuring you have a tangible reference during your stargazing outings.
Pointers
-
Consider utilizing a compact telescope for stargazing. It enables you to observe fainter stars that may be challenging to discern with the naked eye.
-
If you reside in an urban area, light pollution could obscure many celestial bodies. Venture to the countryside for a brief excursion, allowing you to marvel at the stars amidst complete darkness.










