Yield to Maturity (YTM) measures the total return, encompassing both interest and capital gain, achieved from holding a bond until its maturity date. Expressed as a percentage, YTM informs investors about the potential ROI if they purchase the bond and retain it until the issuer repays them. While precise YTM calculation can be challenging, approximation can be made using bond yield tables or online YTM calculators.
Steps to Follow
Expert Guidance for Calculations
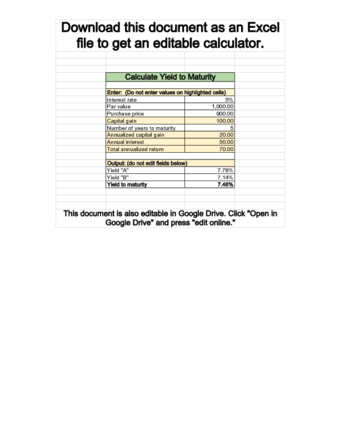 Advanced Yield to Maturity Calculator
Advanced Yield to Maturity CalculatorEstimating the Yield to Maturity
 Collect the necessary information.
Collect the necessary information.- C = the annual coupon payment, representing the bondholder's yearly interest.
- F = the bond's face value, indicating its full worth.
- P = the price paid by the investor for the bond.
- n = the number of years until maturity.
 Compute the estimated yield to maturity.
Compute the estimated yield to maturity.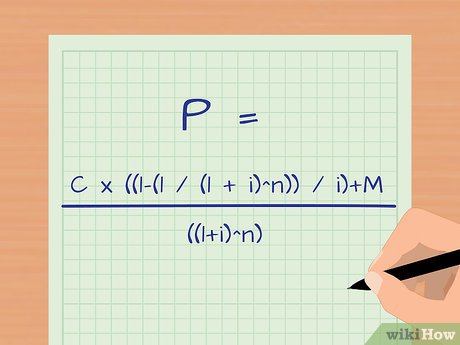 Verify the accuracy of your calculation.
Verify the accuracy of your calculation.Using Trial and Error to Determine Yield to Maturity
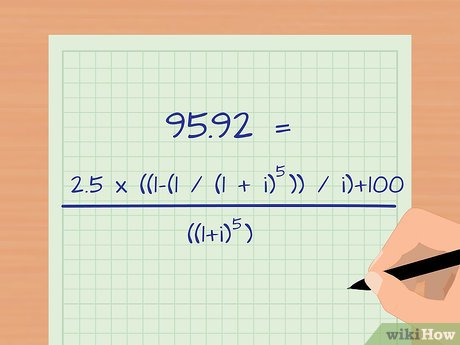 Collect the necessary data and input it into the equation.
Collect the necessary data and input it into the equation.
Estimate the interest rate by considering the bond price and yield relationship. You needn't guess randomly. Since this bond is priced at a discount, the yield to maturity will exceed the coupon rate. Begin with an interest rate higher than 5 percent and plug it into the formula. For instance, starting with 6 percent annually translates to 3 percent semi-annually. After iterations, you'll narrow the precise yield range between 6 and 7 percent annually, or 3 and 3.5 percent semi-annually.
- Remember, you're plugging in an estimated semi-annual rate, effectively halving the annual rate.
- Starting with 6.9 percent (3.45 percent semi-annually), you get $95.70, slightly off.
- Decreasing to 6.8 percent (3.4 percent semi-annually), the result matches the purchase price of $95.92, pinpointing the yield at 6.8 percent.

Test a narrower range of interest rates for precision. Plug values between 6 and 7 percent into the formula, incrementally decreasing by a tenth of a percent. This method yields a precise calculation of the yield to maturity.
- Starting with 6.9 percent (3.45 percent semi-annually), you get $95.70, close but not exact.
- Decreasing to 6.8 percent (3.4 percent semi-annually), the result matches the purchase price of $95.92, indicating a precise yield of 6.8 percent.
Understanding Yield to Maturity

Assess bond investment viability using it. Before purchasing, investors often determine a required yield, assessing whether a bond will meet their expectations. Calculating yield to maturity provides concrete data to compare different bonds.

Familiarize yourself with yield to maturity variations. Issuers may opt to redeem or repurchase bonds before maturity, altering the yield. Yield to call (YTC) calculates the rate between the present and the call date, while yield to put (YTP) computes the rate until the issuer puts the bond.
- Yield to call (YTC) assesses the rate between the present and the call date of a bond.
- Yield to put (YTP) evaluates the rate until the issuer puts the bond.

Recognize the constraints of yield to maturity. YTM fails to consider taxes or transaction costs, effectively reducing bond yield. Moreover, these calculations serve as estimates only, susceptible to market fluctuations.
