Although encountering a fox can be daunting for some, they seldom pose an immediate threat to humans and typically avoid aggression, unless afflicted with rabies. It's essential to remember that foxes are wild creatures, necessitating caution in any interactions. While attempting to domesticate a wild fox is generally discouraged, forming a bond with a fox frequenting your vicinity may pose minimal risk. Alternatively, consider the possibility of legally adopting a domesticated fox if permissible in your region.
Procedures
Forging a Connection with a Wild Fox
- Eliminate or deactivate any motion-triggered sprinklers, as these can also deter them.

- Avoid daily feeding to prevent reliance on human-provided food; aim for weekly feedings instead.
- Ensure wild foxes do not enter your home by leaving doors open during feeding times, which could lead to unwelcome visits from other foxes.
- While foxes may consume dog food, initially focus on the recommended foods to maintain their natural diet.
- Keep pets away from designated feeding areas.
- Avoid feeding certain foods, including grains, chocolate, grapes, avocados, caffeine, and others, to prevent harm.

- Avoid hand-feeding wild foxes, as they are likely to flee if approached or touched.
- Exercise caution, especially around foxes with offspring, as they may act defensively to protect their young.
Acquiring and Training a Domestic Fox
- Upon approval, consult the adoption agency for guidance on fox care essentials to adequately prepare for its arrival.

- Regular veterinary visits will acclimate your fox to the caregiver and minimize fear during examinations.

- Consider burying the enclosure 3 feet deep to prevent digging underneath.
- Provide essential amenities within the space, including food and water, a sleeping area, hide box, toys, and a litter box.
- As foxes are adept climbers, ensure the enclosure has a secure top.

- Recognize that not all foxes enjoy physical contact; adapt your approach based on individual personality traits.
- Avoid exposing your fox to small prey animals, such as rabbits and birds, to prevent hunting instincts from developing.
- Allocate sufficient playtime to accommodate a fox's high energy levels.
- Establish a regular walking routine to promote calm behavior indoors and prevent boredom-induced destructive behavior.

- Ensure that only safe toys are accessible and reinforce appropriate play behavior through positive reinforcement techniques, such as praising and rewarding with treats.

- Consider using an enclosed litter box to minimize mess caused by digging tendencies. If necessary, transition to puppy pads if digging behavior persists.
- Avoid punitive measures in training; instead, redirect your fox to the appropriate toileting area and offer positive reinforcement for desired behavior.
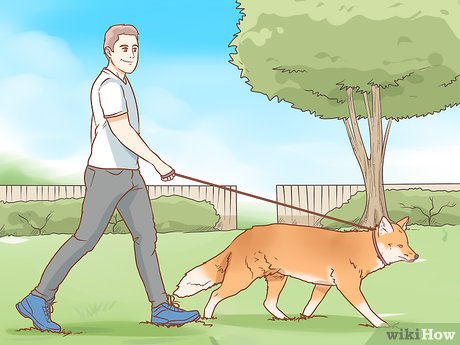
- Teach your fox to walk on a leash gradually, starting with collar introduction before leash attachment. Ensure a snug collar fit to prevent escape.
- Engage your fox in fetch games, rewarding successful retrieves to strengthen the bond between you and your pet.

- To deter inappropriate behavior like playing with forbidden items or toileting indoors, use a spray bottle with water accompanied by a firm 'no' command, avoiding harsh shouting.
Guidelines
Precautions
- Exercise caution when feeding wild foxes to prevent dependence and potential aggressive behaviors towards humans and neighbors.
- Avoid feeding foxes grains, as these can adversely affect their health.
- Prepare for the strong odor of fox urine by using washable furniture covers and initiating prompt potty training.
- Ensure sufficient time and resources for the constant supervision, training, and socialization required by pet foxes.
- Maintain a calm demeanor during fox training to avoid negative reactions that may hinder progress.
- Recognize the strong bond foxes form with mates or siblings and consider potential emotional impacts when separating them.
- Familiarize yourself with local laws regarding fox ownership, as regulations vary by region.
- Conduct thorough research on different fox species to understand their unique personalities and care needs.
