A microscope serves as a powerful tool that enhances visual magnification, enabling the observation of minute structures with precision. Although available in various sizes, microscopes designed for domestic and educational purposes typically consist of common components: a base, an eyepiece, a lens, and a stage. Acquiring proficiency in the fundamental techniques of microscope usage not only ensures the preservation of equipment but also furnishes you with a valuable research instrument.
Stepwise Procedure
Microscope Setup
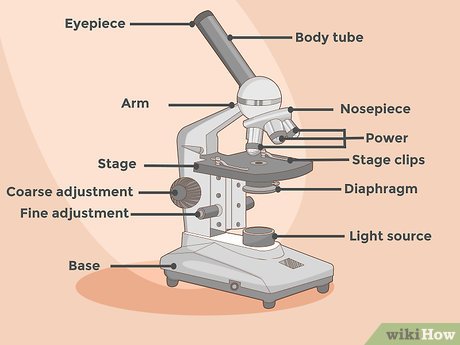
Understanding the Anatomy of the Microscope. Familiarizing yourself with the essential components of the microscope is crucial for proper operation. The eyepiece serves as the viewing port for observing specimens. While basic microscopes feature a single eyepiece, advanced models may incorporate a binocular eyepiece. Key components include:
- The stage, where slides are positioned for examination.
- The arm, linking the base to the eyepiece.
- The objective lens, responsible for magnification. Various objectives offer different levels of magnification.
- Coarse and fine focus knobs allow for focusing on specimens. The coarse focus knob, typically large and located on the side, moves the objective lens closer to or farther from the slide, facilitating rough focusing. The fine focus knob, smaller in size, enables precise focusing on the specimen.
- The base-mounted light source illuminates the specimen for viewing.
- The diaphragm, situated beneath the stage, regulates the amount of light reaching the specimen.
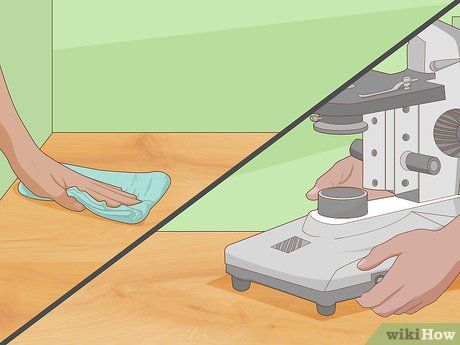
Position the microscope on a spotless, level surface. Ensure your workspace is free from any debris that could potentially cause damage to your microscope. Thoroughly clean the area with a suitable surface cleaner and a lint-free cloth, if necessary. Also, ensure that the table is conveniently located near an electrical outlet.
- When transporting the microscope, always support it from below the base and on the arm. Avoid lifting it solely by the arm.
- Once positioned on the table, proceed to plug in the microscope.

Keep your microscope manual accessible. Familiarize yourself with its contents, especially if you require specific instructions tailored to your model. Additionally, the manual contains valuable guidance on maintenance and cleaning procedures, if deemed necessary.
- Store the manual alongside your microscope for quick reference.
- In case of a misplaced manual, consider searching for a downloadable version on the manufacturer's website. If unavailable, contacting the company directly for a replacement copy may be necessary.
Preparing Microscope Slides

Prior to commencement, ensure your hands are clean. The natural oils present on your skin can easily transfer onto both slides and specimens, potentially causing damage to both. Wearing gloves, if available, is advisable.
- Maintain cleanliness of your hands and work area to minimize the risk of contamination.

Keep a lint-free cloth readily available for cleaning and handling slides. Utilize a lint-free cloth, specifically designed to avoid leaving behind fibers after cleaning. Given that slides often carry an electrostatic charge to aid in mounting, they are prone to attracting dust and contaminants. Using a lint-free cloth helps mitigate this issue.
- Avoid using paper towels, as they tend to leave lint residue.
- If wearing gloves, handling slides is permissible, but preferentially grip them by their edges.
Start with prepared slides. These slides already contain properly mounted specimens, which you can purchase from scientific suppliers or may come included with your microscope. Once you feel confident in using the microscope, you can attempt preparing your own slides.
- To create your own slide, select a specimen you wish to examine more closely, such as pond water or pollen.
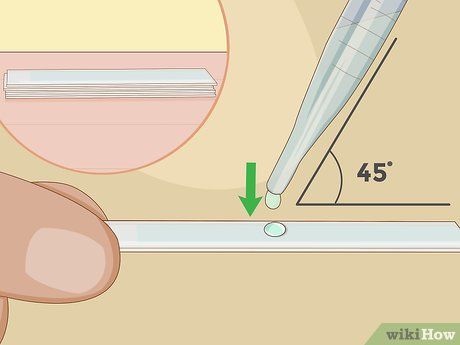
- Add a small drop of water or a few pollen spores directly onto the slide.
- Position a cover slip at a 45-degree angle to the slide and gently lower it onto the specimen. The water should help hold the cover slip in position.
- To preserve samples for longer periods, apply a small amount of clear nail polish around the edges of the slide to secure the cover slip.

Position the slide onto the microscope stage. Handle the slide by its edges to prevent leaving fingerprints or oils on the clean surface. Such contaminants can affect the quality of observation. Alternatively, use a lint-free cloth to handle the slide.
- If the slide is dirty, gently clean it with the lint-free cloth.
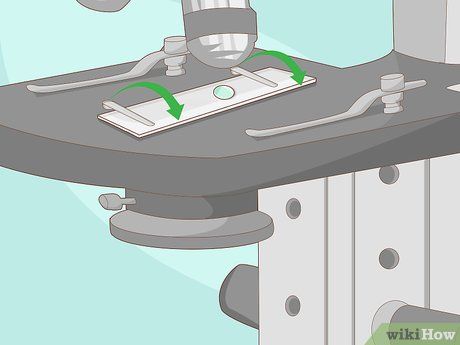
Secure the slide using the stage clips. The stage is equipped with two clips, either metal or plastic, designed to hold the slide in place securely, allowing you to free your hands for focusing the microscope. Inserting the slide under the clips should be a straightforward process.
- Avoid applying excessive force when inserting slides under the clips. They should lift slightly to accommodate the slide. If encountering difficulty, attempt to insert one clip at a time. Lift the clip, insert the slide, and then proceed to the second clip.
- Handle slides delicately as they can break if mishandled during this step.

Switch on the microscope. Typically, the power switch is located on the side of the microscope. A small circle of light should illuminate the center of your slide upon activation.
- If no light is visible, adjust the diaphragm until fully open. The diaphragm can be adjusted using a lever or rotating disc to regulate the amount of light passing through. Without sufficient light, observation will be hindered. Rotate the lever or disc until light becomes visible again.
- If light remains absent, check the power outlet or seek assistance to replace the microscope bulb.
Focusing the Microscope
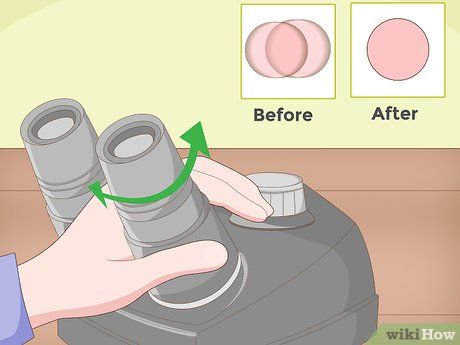
If you have binocular eyepieces, adjust them accordingly. Ensure both eyepieces are aligned to achieve the correct interpupillary distance, resulting in a single circle of light when viewing through both.
- If you observe two separate images, continue adjusting until a single circle of light is visible.
- Remove glasses, if worn, and utilize the microscope's settings for personalized focusing.
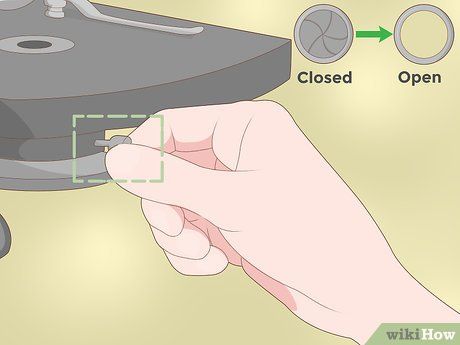
Open the diaphragm fully. Adjust the diaphragm to its widest opening to maximize light exposure on the slide, aiding in specimen observation. Utilize the available lever or spinning disc to achieve this setting.
- Ensure the diaphragm is fully open by moving the lever or spinning the disc accordingly.
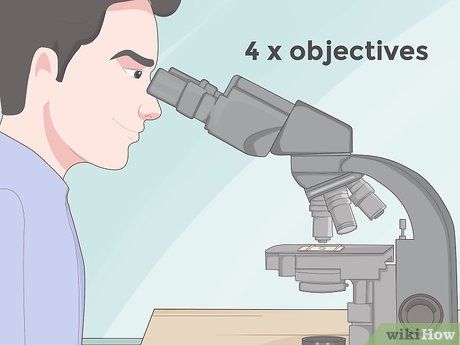
Commence focusing with the lowest power objective. Begin with the 4x objective lens, gradually increasing magnification until achieving focus. The 4x objective lens typically offers the lowest magnification and widest view, facilitating ease of focusing without missing details.
- Initiating with higher power objectives may lead to potential oversight of the specimen or its entirety.
- Common high power objectives include the 10x and 40x lenses.
- Note that the eyepiece's 10x magnification is multiplied by the objective's magnification, resulting in total magnifications of 40x, 100x, and 400x for 4x, 10x, and 40x objectives, respectively.

Center the slide on the stage, if required. As slides often exceed the size of the mounted specimen, ensure proper positioning by aligning it with the center of the light source. If the specimen is not visible, adjust the slide's position gradually while observing through the eyepiece.
- Remember that stage movement is mirrored, necessitating opposite adjustments to align the specimen properly within the lens.

Focus the slide utilizing adjustment knobs and diaphragm settings. Begin with the coarse adjustment knob, progressing to the fine adjustment knob, and adjusting light levels accordingly. While observing through the eyepiece, gradually turn the coarse focus knob until the image begins to come into focus.
- Utilize the fine adjustment knob for further focusing precision.
- Exercise caution during focusing to prevent stage contact with objective lenses.
- Adjust the diaphragm below the stage to optimize image clarity.
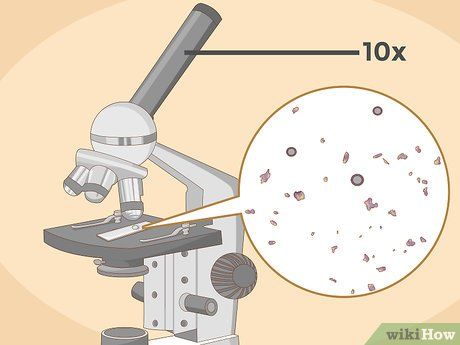
Enhance magnification using a higher objective lens. Transition to a higher objective only if you're unable to achieve satisfactory focus with the lower power objective. Higher magnification provides finer specimen details, although not all high objectives are suitable for every slide due to their close focusing capabilities.
- Exercise caution when switching objectives to avoid slide breakage.
- Employ the fine adjustment knob when utilizing higher objectives like the 10x option, as the coarse knob can potentially damage slides by bringing objectives too close to the stage.
- Experiment with various slides and objective combinations to improve microscope proficiency.

Protect the microscope with a dust cover when not in use. Dust and airborne particles pose risks to lenses, potentially causing damage. Maintaining clear lenses and a dust-free stage prevents such damage. Clean lenses only with approved solutions and lint-free cloths.
Tips
Warnings
- Avoid touching the microscope lens with bare fingers, as oil and fingerprints can impair its function. Clean using a lint-free cloth and appropriate spray if necessary.
Essential Supplies
- Flat, clean surface
- Access to electrical outlet
- Microscope slides
- Dust cover
- Lint-free cloths
- Adult supervision (*if under 7 years old)
