Explore the fundamentals of crafting and cutting with a laser cutter.
A laser cutter, a machine utilizing laser technology for material cutting and engraving, simplifies the process of replicating designs across various materials or creating multiple copies of an object. Simply select an image, optimize it for laser cutting, choose the material, and initiate the laser cutter. It offers a swift and efficient means of design replication.
Creating an Image File

Locate a suitable laser cutter. A mid-range laser cutter typically costs around US$1000, which may be a significant investment for beginners. Consider reaching out to local universities or technical institutes to inquire about access to their laser cutter facilities for experimentation. This allows you to explore different models before committing to a purchase.
- If purchasing your own laser cutter, explore the option of acquiring a pre-owned model to reduce costs.

Choose the material for cutting or engraving. Laser cutters are capable of working with wood, plastic, cardboard, foam, fabric, and thin metal sheets. Avoid materials containing chlorine due to toxic fumes, such as PVC, vinyl, and printed circuit boards. Note that glass can be engraved but not cut, and thick metal is unsuitable for cutting.
Select an image for cutting or engraving. This could be a photograph, computer-generated drawing, or text. Begin with simple images and progress to more complex ones as you gain familiarity with the machine.
- For photographs, ensure high contrast and minimal shadows.
Import the image into compatible software for your laser cutter. Refer to the laser cutter's specifications or user manual for compatible software information. Save the image file on your computer, then open the software and use the 'import' function to upload the image.
- Popular software choices include Adobe Illustrator and CoreIDRAW, available for download online.
EXPERT TIP

Ylva Bosemark

Utilize online tutorials for software learning. Ylva Bosemark, a jewelry designer, advises: 'Starting with Rhino made learning CorelDRAW and Adobe Illustrator much easier. These two softwares are commonly used with laser cutters, featuring precise and specific commands. Additionally, CorelDRAW provides useful tutorials on their website. Online tutorials are invaluable.'
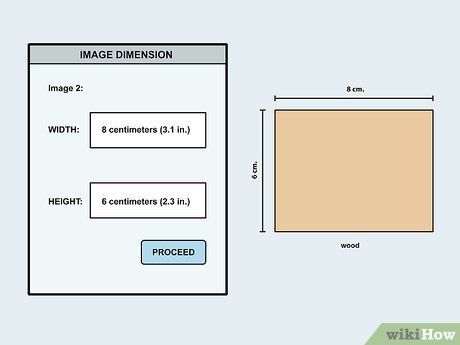
Adjust image dimensions to match material size. Ensure the image size aligns with your material dimensions to prevent missing sections. Access image settings and modify dimensions accordingly, specifying the correct unit of measurement.
Prepare image for laser cutting. In image settings, choose 'photo-optimized' for photo cutting, or select a resolution of at least 333dpi for digital drawings or text. Experiment with different effects as you familiarize yourself with the laser cutter.
Machine Adjustment
Position the material at the center of the laser cutting mat. This ensures optimal results. If your material is too large, trim it to fit flat inside the machine. Press any key to allow the laser to test its dimensions across the mat. If the laser exceeds the material area, reposition it accordingly.
- Remember to resize your image if you trim the material.
- If the material is bent, place a heavy metal rod on its edges to keep it flat.
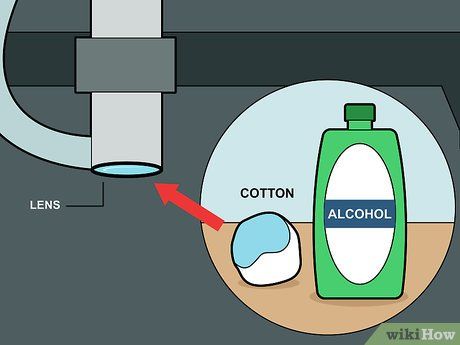
Clean the lens using rubbing alcohol. Dampen a piece of cotton wool with rubbing alcohol and gently clean the laser cutter lens. This can be done while the lens is still installed in the machine.
- Find rubbing alcohol at drugstores or grocery stores.
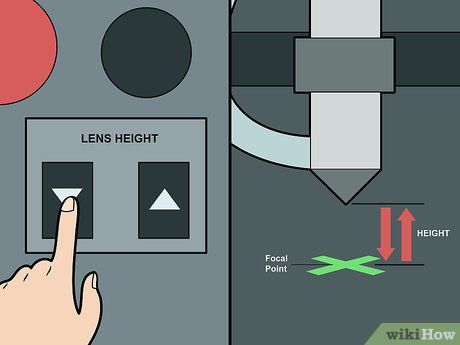
Adjust the lens height. Most modern laser cutters feature an automatic lens height sensor or button. Once the material is positioned correctly, press the 'adjust lens height' button on the machine if it doesn't adjust automatically. Proper lens height adjustment focuses the laser accurately.
- If your machine lacks a lens height button, refer to the user manual for manual adjustment instructions, as methods vary between models.

Activate the fume extractor. Turn on the fume extractor using the switch located on the large tube behind the laser cutter. This device removes fumes and dust from the material during laser cutting.
- Avoid materials containing chloride, even with a fume extractor.
Configuring Print Settings
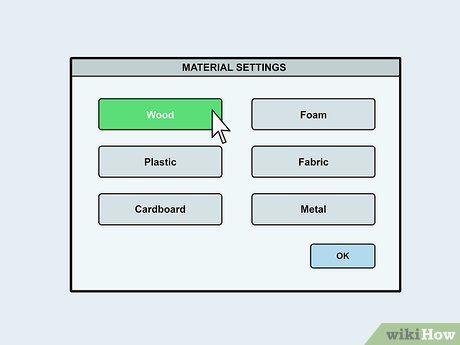
Choose the material you're working with. In the material settings, specify the type of material you're using. This selection determines the laser settings. For instance, cutting wood requires stronger pressure compared to cutting foam.
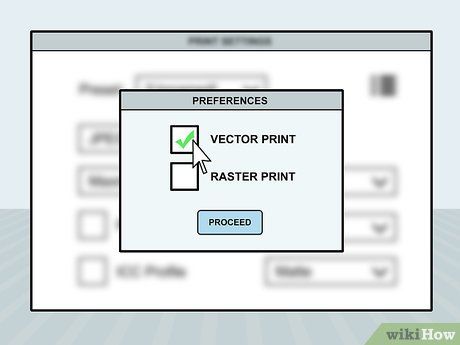
Select the type of cuts needed. Access the print menu and choose preferences. From there, select the cutting method: raster or vector. Opt for 'vector print' for cutting and 'raster print' for engraving.

Initiate the printing process. Hit the print button and observe your image taking form. Avoid moving the material during cutting to maintain alignment.
- If you intend to print multiple copies, replace the cut object with a new piece of material and press print again.
Pro Tips
Essential Items- Laser Cutter
- Materials (fabric, card, wood, foam, thin metal)
- Compatible Software
- Cotton Wool
- Rubbing Alcohol















